Abstract
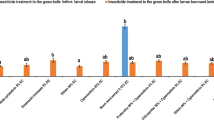
Pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) is an important pest of cotton worldwide; causing significant economic loss to cotton growers. Its control under field condition is difficult, as it remains inside the boll and feeds internally. Therefore, under this study we have evaluated different insecticides viz., Quinalphos 25% EC, Profenofos 50% EC, Thiodicarb 75% WP, Chlorantraniliprole 18.5% SC, Spinosad 45% SC, Neem oil (0.3% W/W), Cypermethrin 25% EC, Triazophos 40% EC, Deltamethrin 2.8% EC and the combination of Profenofos 40% + Cypermethrin 4% EC and Deltamethrin 1% + Triazophos 35% EC for the management of P. gossypiella in cotton under rainfed conditions. The results revealed that combination of Profenofos 40% + Cypermethrin 4% EC showed most effective and offered lowest number of exit holes (0.3 to 0.5), mines on epicarp (2.0 to 7.0), larvae/plant (0.3 to 1.0) and per cent locule damage (1.3 to 7.3%) in green bolls as compared to individual formulations. Among individual formulations, Cypermethrin 25% EC effectively controlled pink bollworm larval damage (0.3 to 1.1 exit holes, 3.3 to 4.0 mines on epicarp, 0.9 to 1.7 larvae and 1.3 to 13.0% locule damage in green bolls after 10 days of spray) as compared to other treatments. Further, maximum seed cotton yield was recorded (11.6 to 12.04 q/ha) in Profenofos 40% + Cypermethrin 4% EC treated fields. The integration of these insecticide molecules proved to be effective in the management of pink bollworm under field conditions.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data and materials are mentioned in the manuscript.
References
Akhtar ZR, Arif MJ, Mansoor-ul-Hassan SB, Irshad U, Majid M, Yin YG (2016) Genetic resistance in pink bollworm against transgenic cotton: an evidence from Pakistan. Pak Entomol 38:153–157
Anonymous (2018) Annual report of Cotton Corporation of India, pp 10–32
Bajya DR, Baheti HS, Raza SK (2015) Field efficacy of newer insecticide formulation Ampligo 150 ZC against bollworm complex in cotton. J Cotton Res Devel 29:94–98
Bhamare VK, Wadnerkar DW (2018a) Efficacy of insecticidal combinations on cotton square and boll shedding due to bollworm complex. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 1:1188–1192
Bhamare VK, Wadnerkar DW (2018b) Potency of insecticidal combination against bollworm complex of cotton. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 1:1164–1168
CABI (2017) Invasive species compendium: Pectinophora gossypiella (pink bollworm). Available:https://www.cabi.org/isc/datasheet/39417#70AF7142-7A8-B4F36A0BA4F14FA270EED
Chakravarthy VS, Reddy TP, Reddy VD, Rao KV (2014) Current status of genetic engineering in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L): an assessment. Crit Rev Biotechnol 34:144–160
Dandale HG, Thakare AY, Rao NGV (1998) Management of cotton bollworms with non pyrethriodal insecticides in Central India. Pestol 22:46
Dandale HG, Rao NGV, Tikar SN, Nimbalkar SA (2001) Efficacy of spinosad against cotton bollworms in comparison with some synthetic pyrethriods. Pestol 25:24–28
Dharajothi B, Gopalakrishnan N, Natarajan K, Manjula TR (2009) Evaluation of certain insecticides against pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella Saunders. J Ind Soc Cot Improv 34:91–95
Dhurua S, Gujar GT (2011) Field-evolved resistance to Bt toxin Cry1Ac in the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), from India. Pest Manag Sci 67:898–903
Ghure SK, Kharbade SB, Patil SD (2008) Bioefficacy of new pesticides against bollworm complex of cotton (Gossypium spp.). Int J Plant Prot 1:106–109
Gopalakrishnan N, Manickam S, Prakash AH (2007) Problems and prospects of cotton in different zones of India. AICRP on Cotton, Coimbatore, pp 11–21
Henderson CF, Tilton EW (1955) Tests with acaricides against the brow wheat mite. J Econ Entomol 48:157–161
Kharbade SB, Wayal CB (2009) Evaluation of some insecticide molecules against pink boll worm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) on cotton. J Cot Res Dev 23:149–151
Kranthi KR, Jadhav DR, Wanjari RR, Shaker Ali SS, Russell D (2001) Carbamate and organophosphate resistance in cotton pests in India, 1995 to 1999. Bull Entomol Res 91:37–46
Kranthi KR, Jadhav DR, Kranthi S, Wanjari RR, Ali S, Russell D (2002) Insecticide resistance in five major insect pests of cotton in India. Crop Prot 21:449–460
Kranthi KR (2007) Insecticide resistance management in cotton to enhance productivity. Training manual of model training course on long staple cotton (ELS) December 15-22, 2007 held at ICAR-Central Institute for Cotton Research, Nagpur, India
Kranthi KR (2015) Pink bollworm strikes Bt Cotton. Cotton statistics and News 35(1):6. https://www.cicr.org.in/pdf/Kranthi_art/Pinkbollworm.pdf
Maha Lakshmi MS, Prasad NVVSD (2021) Efficacy of new insecticides against pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella Saunders (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) on rainfed cotton. Chem Sci Rev Lett 10:90–93
Mohan KS, Ravi KC, Suresh PJ, Sumerford D, Head GP (2012) Field resistance to the Bacillus thuringiensis protein Cry 1 Ac expressed in Bollgard® hybrid cotton in pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (saunders), populations in India. Pest Manag Sci 72(4):738–746
Naik VCB, Kumbhare S, Kranthi S, Satija U, Kranthi KR (2018) Field evolved-resistance of pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) to transgenic Bt-cotton expressing Cry1Ac and Cry2Ab in India. Pest Manag Sci. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.5038
Ojha A, Sree KS, Sachdeo B, Rashmi MA, Ravi KC, Suresh PJ, Mohan KS, Bhatnagar RK (2014) Analysis of resistance to Cry 1 Ac in field-collected pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae), populations. GM Crops and Food 5:280–286
Patil SB (2003) Studies on management of cotton pink bollworm Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechidae). Dissertation, University of Agricultural Sciences, Dharwad, Karnataka, India
Prasad NVVSD, Mahalakshmi MS, Rao NHP (2007) Efficacy of insecticides against pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) on cotton. Ind J Environ Ecoplan 14:459–462
Sabry AH, Hassan KA, Rahman AA (2014) Relative toxicity of some modern insecticides against the pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossyipiella (Saunders) and their residues effects on some natural enemies. Int J Sci Environ Tech 3:481–491
Sanghi AH, Ahmed T, Aslam M, Laila K, Asma A (2018) Efficacy of different insecticides against pink bollworm Pectinophora gassypiella (Saund.) (Lepidopera: Gelechidae) on cotton crop in ecological zone of Rahim yar khan. Int J Compre Biol Sci 5:15–22
Saunders WW (1843) Description of a species of moth destructive to cotton crops in India. Trans Entomol Soc Lond 3:284
Singh JP, Lather BPS, Mor BR (1988) Exit behavior of pink bollworm (Pectinophora gossypiella) larvae. Ind J Agril Sci 58:236–237
SPSS (2015) IBM SPSS statistics for windows (Version 23.0). IBM Corp, Armonk Chicago, IL
Tabashnik BE, Van Rensburg JB, Carrière Y (2009) Field-evolved insect resistance to Bt crops: definition, theory, and data. J Econ Entomol 102(6):2011–2023
Varia MV, Bharadiya AM, Kaneria PB, Vaddoria MA (2020) Bio-efficacy of selected insecticides against pink bollworm in Bt cotton. Cross Current Int J Agri Vet Sci 2(8):40–46
Younis AM, Hamouda HHS, Ibrahim AS, Zeitoum MAZ (2007) Field evaluation of certain pesticides against the cotton bollworms with special reference to their negative impact on beneficial Arthropoda. Proceedings 8th African Crop Science Society, Elminia, Egypt, October 27–31, pp 993–1002
Acknowledgements
The authors gratefully acknowledge the Head, Division of Crop Protection and the Director of ICAR-CICR, Nagpur for institutional support in the execution of the present work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Naik, V.C.B., Narode, M.K., Kumbhare, S. et al. Efficacy of novel insecticides and their combinations against pink bollworm, Pectinophora gossypiella (Saunders) (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) in cotton. Int J Trop Insect Sci 43, 397–407 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00939-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00939-8