Abstract
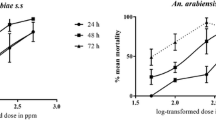
Biocontrol compared to chemical insecticides is an alternative to reduce the population size of an organism in an environmentally friendly way. Mixtures between plant extracts and microorganisms are an alternative to reduce mosquitoes´ resistance to the most commonly used insecticides. In this study, the effect of Metarhizium anisopliae was tested separately and in combination with Azadirachta indica seed extract against Anopheles albimanus larvae under laboratory conditions. Five fungal concentrations between 1 × 103 and 1 × 107 conidia/ml were tested for individual bioassays, and five concentrations between 0.1 and 1000 ppm neem extracts were used. The interaction between fungus and extract was tested at 1 × 103 conidia/ml, 1 × 104 conidia/ml and 1 × 105 conidia/ml with 1 ppm of A. indica extract in binary mixtures. Lethal concentrations 50 were 3.99 × 105 conidia/ml and 16 ppm for M. anisopliae and A. indica extract, respectively. The presence of 1 ppm of A. indica extract did not affect the germination of M. anisopliae conidia nor the fungus growth. Mixtures of 1 ppm A. indica extract and M. anisopliae conidia increased An. albimanus larvae mortality compared with each of these biocides alone and a synergistic effect was found. Results indicate that M. anisopliae and A. indica extract binary mixture is an excellent alternative for the biological control of An. albimanus larvae.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahumada ML et al (2016) Spatial distributions of Anopheles species in relation to malaria incidence at 70 localities in the highly endemic Northwest and South Pacific coast regions of Colombia. Malar J 15:407. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12936-016-1421-4
Balouiri M, Sadiki M, Ibnsouda SK (2016) Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review. J Pharm Anal 6:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2015.11.005
Becker N, Zgomba M, Petric D, Dahl C, Boase C, Lane J, Kaiser A (2003) Mosquitoes and Their Control. Springer, US, Heidelberg
Beier J (2008) Malaria Control in the Highlands of Burundi: An Important Success Story. Am J Trop Med Hyg 79:1–2
Benserradj O, Mihoubi I (2014) Larvicidal activity of entomopathogenic fungi Metarhizium anisopliae against mosquito larvae in Algeria. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 3:54–62
Bilal H, Hassan SA, Khan IA (2012) Isolation and efficacy of entomopathogenic fungus (Metarhizium anisopliae) for the control of Aedes albopictus Skuse larvae: suspected dengue vector in Pakistan. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2:298–300. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(12)60026-4
Blanford S, Jenkins N, Read A, Thomas M (2012) Evaluating the lethal and pre-lethal effects of a range of fungi against adult Anopheles stephensi mosquitoes. Malar J 11:365. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-11-365
Bown D, Nelson M (1993) Anopheline Vectors of Human Plasmodia. In: Kreier J (ed) Parasitic Protozoa (Second Edition). Academic Press, San Diego, pp 267–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-426015-3.50010-8
Bukhari T, Middelman A, Koenraadt C, Takken W, Knols B (2010) Factors affecting fungus-induced larval mortality in Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles stephensi. Malar J 9:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-9-22
Caminade C et al (2014) Impact of climate change on global malaria distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:3286–3291. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302089111
Castiglioni E, Vendramin JD, Alves SB (2003) Compatibilidad de Beauveria bassiana y Metarhizium anisopliae con Nimkol-L para el combate de Heterotermes tenuis. Man Integr Pla Agro 69:38–44
Chandramohan B et al (2016) Neem by-products in the fight against mosquito-borne diseases: Biotoxicity of neem cake fractions towards the rural malaria vector Anopheles culicifacies (Diptera: Culicidae). Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 6:472–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.11.013
De-Garcia C, Restrepo S, Franco-Molano A, Toquica M, N. V, (2012) Biologia de hongos, 1st edn. Universidad de los Andes, Colombia
Droby S, Wisniewski M, Teixidó N, Spadaro D, Jijakli H (2016) The science, development, and commercialization of postharvest biocontrol products. Postharvest Biol Technol 122:22–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.04.006
Dua V, Pandey A, Raghavendra L, Gupta A, Sharma T, Dash A (2009) Larvicidal activity of neem oil (Azadirachta indica) formulation against mosquitoes. Malar J 8:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-8-124
Environmental protection agency US (2019) The Toxicity Relationship Analysis Program. https://archive.epa.gov/med/med_archive_03/web/html/trap.html. Accessed 23 Jun 2018
Farenhorst M, Farina D, Scholte E, Takken W, Hunt R, Coetzee M, Knols B (2008) African water storage pots for the delivery of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae to the malaria vectors Anopheles gambiae s.s. and Anopheles funestus. Am J Trop Med Hyg 78:910–916
Flórez J (2005) Farmacología humana. Elsevier-Masson, Madrid
Fonseca I, Quiñones ML (2005) Resistencia a insecticidas en mosquitos (Diptera: Culicidae): mecanismos, deteccion y vigilancia en salud publica. Rev Colomb Entomol 31:107–115
Fuller DO, Ahumada ML, Quiñones ML, Herrera S, Beier JC (2012) Near-present and future distribution of Anopheles albimanus in Mesoamerica and the Caribbean Basin modeled with climate and topographic data. Int J Health Geogr 11:13–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-072X-11-13
Gonzales R, Carrejo N (2018) Introducción al estudio taxónomico de Anopheles de Colombia: claves y notas para su identificación. Santiago De Cali, Universidad Del Valle. https://doi.org/10.25100/peu.309
Gomes A, Paula R, Ribeiro A, Moraes O, Santos W, Silva P, Samuels I (2015) Neem oil increases the efficiency of the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae for the control of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) larvae. Parasit Vectors 8:669. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-015-1280-9
Kamareddine L (2012) The Biological Control of the Malaria Vector. Toxins 4:748–767. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxins4090748
Kelly-Hope L, McKenzie F (2009) The multiplicity of malaria transmission: a review of entomological inoculation rate measurements and methods across sub-Saharan Africa. Malar J 8:19. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-8-19
Kovendan K, Shanthakumar SP, Praseeja C, Kumar PM, Murugan K, Vincent S (2014) Mosquitocidal properties of Morinda citrifolia L. (Noni) (Family: Rubiaceae) leaf extract and Metarhizium anisopliae against malaria vector, Anopheles stephensi Liston. (Diptera: Culicidae). Asian Pac J Trop Dis 4:S173–S180. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2222-1808(14)60435-7
Lemes A, Davolos C, Legori P, Fernandes O, Ferré J, Lemos M, Desiderio J (2014) Synergism and Antagonism between Bacillus thuringiensis Vip3A and Cry1 Proteins in Heliothis virescens, Diatraea saccharalis, and Spodoptera frugiperda. PLoS ONE 9:e107196. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107196
Liu N (2015) Insecticide Resistance in Mosquitoes: Impact, Mechanisms, and Research Directions. Annu Rev Entomol 60:537–559. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-ento-010814-020828
Mareggiani G (2001) Manejo de insectos plaga mediante sustancias semioquímicas de origen vegetal. Man Int Pla 60:22–30
Michaelakis A, Strongilos A, Bouzas E, Koliopoulos G, Couladouros E (2009) Larvicidal activity of naturally occurring naphthoquinones and derivatives against the West Nile virus vector Culex pipiens. Parasitology Res 104:657–662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-008-1242-7
Murugan K et al (2016) In vivo and in vitro effectiveness of Azadirachta indica-synthesized silver nanocrystals against Plasmodium berghei and Plasmodium falciparum, and their potential against malaria mosquitoes. Res Vet Sci 106:14–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rvsc.2016.03.001
Okumu F, Knols B, Fillinger U (2007) Larvicidal effects of a neem (Azadirachta indica) oil formulation on the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Malar J 6:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-6-63
Parra G, Suarez L (2012) Mosquitos (Díptera: Culicidae) vectores potenciales de arbovirus en la región de Urabá, noroccidente de Colombia. I C M T 32:252–262
Pascual M, Ahumada J, Chaves L, Rodó X, Bouma M (2006) Malaria resurgence in the East African highlands: Temperature trends revisited. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:5829–5834. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0508929103
Pinault LL, Hunter FF (2011) New highland distribution records of multiple Anopheles species in the Ecuadorian Andes. Malar J 10:236. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-10-236
Prakash S (2014) Metabolites of Metarhizium anisopliae against Malaria Vectors and Non Target Organisms. E O H 4:2. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0983.1000147
Rhodes C et al (2022) Anopheles albimanus (Diptera: Culicidae) Ensemble Distribution Modeling: Applications for Malaria Elimination. InSects 13:221. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13030221
Sani I, Yusuf U, Suleiman M (2017) Larvicidal potentials of Metarhizium anisopliae and Paecilomyces sp on Culex quinquefasciatus (Say) (Diptera: Culicidae). J Zoolog Bioscie Res 4:1. https://doi.org/10.24896/jzbr.2017411
Scholte E et al (2005) An entomopathogenic fungus for control of adult African malaria mosquitoes. Science 308:1641–1642. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1108639
Scholte E, Njiru B, Smallegange R, Takken W, Knols B (2003) Infection of malaria (Anopheles gambiae s.s.) and filariasis (Culex quinquefasciatus) vectors with the entomopathogenic fungus Metarhizium anisopliae. Malar J 2:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2875-2-29
Seydou T, Ndione R, Toure M, Seye F, Ndiaye M (2017) Larvicidal and Synergic Effects of two Biopesticides (Azadirachta indica and Metarhizium anisopliae) against Larvae of Culex quinquefasciatus (Diptera, Culicidae) (Say, 1823). Int J Sci 3:109–115. https://doi.org/10.18483/ijSci.1258
Shaalan E, Canyon D, Younes M, Abdel H, Mansour A (2005) A review of botanical phytochemicals with mosquitocidal potential. Environ Int 31:1149–1166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2005.03.003
Sharma P, Batabyal L, Mohan L, Maurya P, Srivastava CN (2007) Larvicidal Efficiency of Certain Seed Extracts Against Anopheles stephensi, with Reference to Azadirachta indica. J Asia Pac Entomol 10:251–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1226-8615(08)60359-3
Sun Y-P, Johnson E (1960) Analysis of Joint Action of Insecticides Against House Flies. J Econ Entomol 53:887–892. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/53.5.887
Tanser F, Sharp B, Sueur D (2003) Potential effect of climate change on malaria transmission in Africa. Lancet 362:1792–1798. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(03)14898-2
WHO (2021) World malaria report 2021
Acknowledgements
We thank School of Basic and Applied Sciences at Universidad de La Salle for providing essential laboratory and mosquito colony facilities and Ph.D. Jesús Eduardo Escovar for training on mosquitoes group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving animals were in accordance with national, and institutional guidelines.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Beltrán, M., Lozano, L.C. Synergistic larvicidal activity of Metarhizium anisopliae and Azadirachta indica extract against the malaria vector Anopheles albimanus. Int J Trop Insect Sci 43, 129–136 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00924-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00924-1