Abstract
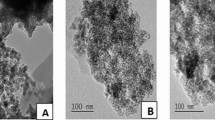
Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae) is one of the main pests in diverse protected and outdoor crops in the world and also in Iran. This pest has been historically controlled by chemical pesticides; however, chemical control failures and shortened residual control of abamectin were recently reported that led to the development of resistance in T. urticae. The current study aimed to develop abamectin-containing nanoliposomes/nanoniosomes by the thin-film hydration method and compare their physicochemical properties. Then, lethal and sub-lethal effects of these formulations and the commercial formulation of abamectin were examined against T. urticae under laboratory conditions (28 ± 1 °C, 60 ± 5% relative humidity, and a photoperiod of 16 h:8 h L:D). Both formulations presented high entrapment efficiency and continuous release behavior with a nanoscale size. Among tested formulations, the nanoniosomal form exhibited the most toxicity against T. urticae (LC50: 50 μg/ml). Our findings also showed that sub-lethal concentrations (LC20) of the tested formulations of abamectin exerted negative effects on T. urticae because these products enhanced the cumulative mortality of mites and reduced their performance. The population of T. urticae was treated with sub-lethal concentrations of the commercial formulation (i.e., the nanoniosomal form) and caused 8.35, 2.59, and 4.90 folds increment in one generation, respectively. However, such a formulation caused 23.06 folds increment in the population of controls. We demonstrated that in addition to commercial formulation, these stable and effective newly-designed nanopesticides could be applied for the management of such a destructive mite.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method for computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267
Abd-El-Azim H, Ramadan A, Nafee N, Khalafallah N (2018) Entrapment efficiency of pyridoxine hydrochloride in unilamellar liposomes: experimental versus model-generated data. J Liposome Res 28:112–116
Abdel-Halim K, Kalmosh F (2019) Acaricidal activity of nano-abamectin against the two-spotted spider mite; Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae). J Life Sci 2019:81–86
Ashley JL, Herbert DA, Lewis EE, Brewster CC, Huckaba R (2006) Toxicity of three acaricides to Tetranychus urticae (Tetranychidae: Acari) and Oriusinsidiosus (Anthocoridae: Hemiptera). J Econ Entomol 99:54–59
Azod F, Shahidi-Noghabi S, Mahdian K, Smagghe G (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of spirotetramat and abamectin on predatory beetles (Menochilus sexmaculatus) via prey (Agonoscena pistaciae) exposure, important for integrated pest management in pistachio orchards. Belg J Zool 146:113–122
Badawy ME, Taktak NE, Awad OM, Elfiki SA, El-Ela NEA (2015) Larvicidal activity of temephos released from new chitosan/alginate/gelatincapsules against Culex pipiens. Int J Mosq Res 2:45–55
Borzoui E, Naseri B, Abedi Z, Karimi-Pormehr MS (2016) Lethal and sublethal effects of essential oils from Artemisia khorassanica and Vitex pseudo-negundo against Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). Environ Entomol 45:1220–1226
Brown S, Kerns DL, Gore J, Lorenz G, Stewart S (2017) Susceptibility of two - spotted spider mites (Tetranychus urticae) to abamectin in Midsouth cotton. Crop Prot 98:179–183
Chi H (2018) TWOSEX-MSChart: a computer program for the age-stage, two-sex life table analysis. http://140.120.197.173/ecology/Download/TWOSEXMSChart.rar (accessed 19 Sep 2017)
Chun S, Feng J (2021) Preparation of abamectin nanoparticles by flash nanoprecipitation for extended photostability and sustained pesticide release. ACS Appl Nano Mater 4:1228–1234
De A, Bose R, Kumar A, Mozumdar S (2014) Management of insect pests using nanotechnology: as modern approaches. In De A, Bose R, Kumar A, Mozumdar S, eds. Targeted delivery of pesticides using biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles. India: Springer, New Delhi, pp. 29–33
de Andrade DF, Zuglianello C, Pohlmann AR, Guterres SS, Beck RCR (2015) Assessing the in vitro drug release from lipid-core nanocapsules: a new strategy combining dialysis sac and a continuous-flow system. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 16:1409–1417
de Oliveira JL, Campos EVR, Bakshi M, Abhilash PC, Fraceto LF (2014) Application of nanotechnology for the encapsulation of botanical insecticides for sustainable agriculture: prospects and promises. Biotech Adv 32:1550–1561
Efron B, Tibshirani RJ (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. Chapman and Hall, New York, p 456
El Wakeil N, Alkahtani S, Gaafar N (2017) Is nanotechnology a promising field for insect pest control in IPM programs?. New Pesticides and Soil Sensors. Academic Press, 273–309
Ferreira CBS, Andrade FHN, Rodrigues ARS, Siqueira HAA, Gondim MGC (2015) Resistance in field populations of Tetranychus urticae to acaricides and characterization of the inheritance of abamectin resistance. Crop Prot 67:77–83
Ghaffari M, Kalantar SM, Hemati M, Dehghani Firoozabadi A, Asri A, Shams A (2021) Co-delivery of miRNA-15a and miRNA-16-1 using cationic PEGylated niosomes downregulates Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. Biotechnol Lett 43:981–994
Giongo AMM, Vendramim JD, Forim MR (2016) Evaluation of neem-based nanoformulations as alternative to control fall armyworm. Ciênc Agrotec 40:26–36
Gunay MS, Ozer AY, Erdogan S, Bodard S, Baysal I, Gulhan Z (2017) Development of nanosized, pramipexole-encapsulated liposomes and niosomes for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 17:5155–5167
Gorman KJ, Hewitt FM, Denholm I, Devine GJ (2001) New developments in insecticide resistance in the glasshouse whitefly (Trialeurodes vaporariorum) and the two-spotted spider mite (Tetranychus urticae) in the UK. Pest Manag Sci 58:123–130
Haghiralsadat F, Amoabediny G, Sheikhha M, Zandieh Doulabi B, Naderinezhad S, Helder M, Forouzanfar T (2017) New liposomal doxorubicin nanoformulation for osteosarcoma: Drug release kinetic study based on thermo and pH sensitivity. Chem Biol Drug Des 90:368–379
Hemati M, Haghiralsadat F, Jafary F, Moosavizadeh S, Moradi A (2019a) Targeting cell cycle protein in gastric cancer with CDC20siRNA and anticancer drugs (doxorubicin and quercetin) co-loaded cationic PEGylated nanoniosomes. Int J Nanomed 14:6575–6585
Hemati M, Haghiralsadat F, Yazdian F, Jafari F, Moradi A, Malekpour-Dehkordi Z (2019b) Development and characterization of a novel cationic PEGylated niosome-encapsulated forms of doxorubicin, quercetin and siRNA for the treatment of cancer by using combination therapy. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:1295–1311
Horowitz AR, Mendelson Z, Ishaaya I (1997) Effect of abamectin mixed with mineral oil on the sweetpotato whitefly (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae). J Econ Entomol 90:349–353
Huang JF, Tian M, Lv CJ, Li HY, Zhong GH (2011) Preliminary studies on induction of apoptosis by abamectin in Spodoptera frugiperda (Sf9) cell line. Pestic Biochem Physiol 100:256–263
Huang YB, Chi H (2012) Assessing the application of the Jackknife and Bootstrap techniques to the estimation of the variability of the net reproductive rate and gross reproductive rate: a case study in Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae). Agric for Entomol 61:37–45
Hwang IC, Kim TH, Bang SH, Kim KS, Kwon HR, Seo MJ, Youn YN, Park HJ, Yasunaga-Aoki C, Yu YM (2011) Insecticidal effect of controlled release formulations of Etofenprox based on nano-bio technique. J Fac Agric Kyushu Univ 56:33–40
Insecticide Resistance Action Committee (IRAC) Mode of Action Classification (2020) Prevention and management of insecticide resistance in vectors of public health importance. Second edition, p. 71. https://www.iraconline.org
Kah M, Weniger AK, Hofmann T (2016) Impacts of (nano) formulations on the fate of an insecticide in soil and consequences for environmental exposure assessment. Environ Sci Technol 50:10960–10967
Khot LR, Sankaran S, Maja JM, Ehsani R, Schuster EW (2012) Applicationsof nanomaterials inagricultural production and crop protection: a review. Crop Prot 35:64–70
Mahmood I, Imadi SR, Shazadi K, Gul A, Hakeem KR (2016) Effects of pesticides on environment. In: Hakeem K, Akhtar M, Abdullah S (eds) Plant, Soil and Microbes. Springer, Cham, pp 253–269
Majd-Marani S, Naseri B, Nouri-Ganbalani G, Borzoui E (2017) The effect of maize hybrid on biology and life table parameters of the Trogoderma granarium (Coleoptera: Dermestidae). J Econ Entomol 1(110):1916–1922
Memarizadeh N, Ghadamyari M, Zamani P, Sajedi RH (2013) Studied resistance mechanism to Abamectin in Iranian population of the two-spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae. Acarologia 53:235–246
Martínez LC, Plata-Rueda A, Rodríguez-Dimaté FA, Campos JM, dos Santos Júnior VC, Da Silva RG, Fernandes FL, Silva WM, Wilcken CF, Zanuncio JC, Serrão JE (2019) Comparative toxicity of six insecticides on the Rhinoceros beetle (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Flav Entomol 97:1056–1062
Martínez LC, Plata-Rueda A, Zanuncio JC, Serrão JE (2014) Exposure to insecticides reduces populations of Rhynchophoruspalmarum in oil palm plantations with bud rot disease. Insects 10:111
Memarizadeh N, Ghadamyari M, Talebi K, Torabi E, Adeli M, Jalalipour R (2019) Resistance mechanisms to abamectin in iranian populations of the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae). Acarologia 53:235–246
Mohammadzadeh M, Bandani A, Sabahi Q (2014) Comparison of susceptibility of two populations of Tetranychus urticae Koch to two acaricides, abamectin and propargite. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2013.869890
Monjarás-Barreraa JI, Chacón-Hernándezb JC, Cerna-Cháveza E, Ochoa-Fuentesa YM, Aguirre-Uribea LA, Landeros-Flores J (2018) Sublethal effect of Abamectin in the functional response of the predator Phytoseiulus persimilis (Athias-Henriot) on Tetranychus urticae (Koch) (Acari: Phytoseiidae, Tetranychidae). Braz J Biol Sci. https://doi.org/10.1590/1519-6984.180184
Müller C (2018) Impacts of sublethal insecticide exposure on insects-facts and knowledge gaps. Basic Appl Ecol 30:1–10
Nouri-Ganbalani G, Borzoui E, Abdolmaleki A, Abedi Z, Kamita SG (2016) Individual and combined effects of Bacillus thuringiensis and Azadirachtin on Plodiainterpunctella Hubner (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Insect Sci 16(95):1–8
Nuruzzaman M, Rahman MM, Liu Y, Naidu R (2016) Nanoencapsulation, nano-guard for pesticides: a new window for safe application. J Agric Food Chem 64:1447–1483
Park YL, Lee JH (2005) Impact of two spotted spider mite (Acari:Tetranychidae) on growth and productivity of glasshouse cucumber. J Econ Entmol 98:457–463
Piraneo TG, Bull J, Morales MA, Lavine LC, Walsh DB, Zhu F (2015) Molecular mechanisms of Tetranychus urticae chemical adaptation in hop fields. Scientific Reports 5:17090
Ragaei M, Sabry KH (2014) Nanotechnology for insect pest control. Int J Sci Environ Technol 3:528–545
Riga M, Tsakireli D, Llias A, Morou E, Myridakis A, Stephanou EG, Nauen R, Dermauw W, Van Leeuwen T, Paine M, Vontas J (2014) Abamectin is metabolized by CYP392A16, a cytochrome P450 associated with high levels of acaricide resistance in Tetranychus urticae. Insect Biochem Mol Boil 46:43–53
Robertson JL, Russell RM, Priesler HK, Savin NE (2007) Bioassays with Arthropods, 2nd edn. CRC, Boca Raton
Saber M, Ahmadi Z, Mahdavinia G (2018) Sublethal effects of spirodiclofen, abamectin and pyridaben on life-history traits and life-table parameters of two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp Appl Acarol 75:55–67
Saini P, Gopal M, Kumar R, Srivastava C (2014) Development of pyridalyl nanocapsule suspension for efficient management of tomato fruit and shoot borer (Helicoverpa armigera). J Environ Sci Health B 49:344–351
SAS (2011) SAS® software version 9.3, user’s manual. SAS Institute, Cary, NC
Scott N, Chen H, Rutzke CJ (2003) Nanoscale science and engineering for agriculture and food systems: a report submitted to cooperative state research, education and extension service, the united states department of agriculture: national planning workshop, 18–19 Nov 2002, Washington, DC. USDA, 62
Uddin N, Alam Z, Miah RU, Mian IH, Mustarin KE (2015) Toxicity of pesticides to Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari:Tetranychidae) and their side effects on Neoseiulus californicus (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Int J Acarol 41:688–693
Van Leeuwen T, Vontas J, Tsagkarakou A, Dermauw W, Tirry L (2010) Acaricide resistance mechanisms in the two -spotted spider mite Tetranychus urticae and other important Acari: A review. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 40:563–572
Walker GW, Kookana RS, Smith NE, Kah M, Doolette C, Reeves P, Lovell W, Anderson DJ, Turney TW, Navarro DA (2018) Ecological risk assessment of nano-enabled pesticides: A perspective on problem formulation. J Agri Food Chem 66:6480–6486
Wang Y, Cui H, Sun C, Zhao X, Cui B (2014) Construction and evaluation of controlled-release delivery system of Abamectin using porous silica nanoparticles as carriers. Nanoscale Res Lett 9:1–6
Werdin González JOW, Stefanazzi N, Murray AP, Ferrero AA, Fernández Band BS (2015) Novel nano-insecticides based on essential oils to control the German cockroach. J Pest Sci 88:393–404
Werdin González JO, Gutiérrez MM, Ferrero AA, Fernández Band BS (2014) Essential oils nanoformulations for stored-product pest control—characterization and biological properties. Chemosphere 100:130–138
Worrall E, Hamid A, Mody K, Mitter N, Pappu H (2018) Nanotechnology for plant disease management agronomy 8:285
Wu M, Adesanya AW, Morales MA, Walsh DB, Lavine LC, Lavine MD, Zhu F (2018) Multiple acaricide resistance and underlying mechanisms in Tetranychusurticae on hops. J Pest Sci 92:543–555
Acknowledgements
We kindly appreciate the Vali-e-Asr University of Rafsanjan (Rafsanjan: Iran) for supporting the present project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teymouri, N., Alizadeh, A., Haghiralsadat, F. et al. Evaluation of sublethal effects of abamectin nanoformulation on Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae): nanoliposomal versus nanoniosomal abamectin. Int J Trop Insect Sci 42, 2805–2817 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00763-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-022-00763-0