Abstract
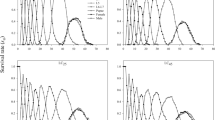
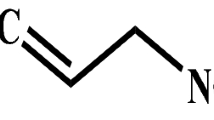
Present study assessed the effect of Emamectin benzoate (EMB) on the survival, growth and nutrition efficiency of Helicoverpa armigera. Dietary EMB exhibited a significant systemic toxicity in H. armigera larvae resulting in LD50 and LD90 value of 0.092 µg/mL and 0.156 µg/mL, respectively. Feeding with 0.05–0.2 µg/mL EMB caused 10–100% larval mortality in a dose-dependent manner. Feeding the IV instars of H. armigera with 0.1–1.6 µg/mL EMB-incorporated diet deterred feeding significantly. Substantial deterrent effects of EMB with lower LD50 values indicate the noteworthy systemic toxicity of EMB on the H. armigera larvae. Both choice and no-choice bioassay with dietary EMB showed a distinct preference of larvae towards control diet. Feeding the larvae with sublethal doses of 0.05 − 0.01 µg/mL EMB impaired ingestion and digestion, and induced considerable post-ingestive toxicity in larvae. Relative Consumption Rate (RCR) and the Relative Growth Rate (RGR) were recorded in the range of 1.653–3.985 and 0.385–0.978, respectively. The nutrition indices of larvae revealed reduction in Efficiency of Conversion of Ingested Food (ECI) by 10–24% and Efficiency of Conversion of Digested Food (ECD) by 2.0–52% and in Approximate Digestibility (AD) by 09–63%. The noticeable decrease in the food utilization, digestion and assimilation may have resulted in the observed reduced larval growth. The decreased metabolic efficiency in H. armigera larvae implicated that dietary EMB probably weakened the biochemical machinery of larval gut and reduced physiological fitness. The results suggest that use of EMB can be an effective tool in Integrated Pest Management program of H. armigera.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbott WS (1925) A method of computing the effectiveness of an insecticide. J Econ Entomol 18:265–267. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/18.2.265a
Abo-Elghar GE (1993) Influence of abamectin and juvenile hormone analogues on food utilization ingestion and larval growth of cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Bull Entomol Soc Egypt Econ Ser 20:173–183
Ahmad M, Arif MI, Ahmad Z (2003) Susceptibility of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to new chemistries in Pakistan. Crop Prot 22:539–544. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0261-2194(02)00219-3
Ahmad M, Rasool B, Ahmad M, Russell DA (2019) Resistance and synergism of novel insecticides in field populations of cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) in Pakistan. J Econ Entomol 112:859–871. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/toy409
Amer AE, El-Sayed AA (2014) Effect of different host plants and artificial diet on Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) development and growth index. J Entomol 11:299–305. https://doi.org/10.3923/je.2014.299.305
Argentine JA, Jansson RK, Halliday WR, Rugg D, Jany CS (2002) Potency, spectrum and residual activity of four new insecticides under glasshouse conditions. Fla Entomol 85:552–563. https://doi.org/10.1653/0015-4040(2002)085[0552:PSARAO]2.0.CO;2
Barnby MA, Klocke JA (1987) Effects of azadirachtin on the nutrition and development of the tobacco budworm, Heliothis virescens (Fabr.) (Noctuidae). J Insect Physiol 33:69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(87)90076-X
Beach MR, Todd JW (1985) Toxicity of avermectin to larva and adult soybean looper (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and influence on larva feeding and adult fertility and fecundity. J Econ Entomol 78:1125–1128. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/78.5.1125
Bengochea P, Sánchez-Ramos I, Saelices R, Amor F, Del Estal P et al (2014) Is emamectin benzoate effective against the different stages of Spodoptera exigua (Hübner) (Lepidoptera, Noctuidae)? Irish J Agric Food Res 53:37–49
Birah A, Mahapatro G, Gupta G (2008) Toxicity evaluation of emamectin benzoate against tobacco caterpillar (Spodoptera litura) by three different assay techniques. Indian J Entomol 70:200–205
Bird LJ (2015) Baseline susceptibility of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) to indoxacarb, emamectin benzoate, and chlorantraniliprole in Australia. J Econ Entomol 108:294–300. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/tou042
Bream AS, Ghoneim KS, Mohamed HA (1999) Food metabolic changes in larvae of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) induced by tebufenozide. Bull Entomol Soc Egypt Econ Ser 26:11–24
Carneiro E, Silva LB, Maggioni K, dos Santos VB, Rodrigues TF et al (2014) Evaluation of insecticides targeting control of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Am J Plant Sci 5:2823–2828. https://doi.org/10.4236/ajps.2014.518298
Dagar VS, Kumar S (2018) Emamectin benzoate: Potential larvicide and antifeedant agent against cotton boll worm Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Appl Natural Sci 10:564–571. https://doi.org/10.31018/jans.v10i2.1738
Dhaliwal GS, Jindal V, Mohindru B (2015) Crop losses due to insect pests: global and Indian scenario. Indian J Entomol 77:165–168. https://doi.org/10.5958/0974-8172.2015.00033.4
Dunbar DM, Lawson DS, White SM, Ngo N, Dugger P, Richter D (1998) Emamectin benzoate: control of the heliothine complex and impact on beneficial arthropods, 2. Proc Beltwide Cotton Conf., San Diego, pp 1116–1118
El-Dewy ME (2017) Influence of some novel insecticides on physiological and biological aspects of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisduval). Alex Sci Exch J 38:250–258. https://doi.org/10.21608/asejaiqjsae.2017.3353
El-Malla MA, Radwan EM (2008) Residual toxicity of abamectin and spinosad insecticides on the cotton leafworm, Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Bull Entomol Soc Egypt Econ Ser 34:119–129
El-Naggar JB, Jehan BA (2013) Sublethal effect of certain insecticides on biological and physiological aspects of Spodoptera littoralis (Boisd.). Nat Sci 11:19–25
El-Shazly NM (1993) Quantitative evaluation of food intake and assimilation by Spilostethus pandurus (Scopoli), (Hemiptera: Lygacidae). Bull Entomol Soc Egypt 71:109–101
El-Sheikh, El-Sayed A (2015) Comparative toxicity and sublethal effects of emamectin benzoate, lufenuron and spinosad on Spodoptera littoralis Boisd. (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Crop Prot 67:228–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2014.10.022
Farrar RR, Barbour JD, Kennedy GG (1989) Quantifying food consumption and growth in insects. Ann Entomol Soc Am 82:593–598
Firake DM, Pandey R (2009) Relative toxicity of Proclaim 5% SG (Emamectin benzoate) and Dipel 8L (Bacillus thuringiensis var. kurstaki) against Spodoptera litura (Fab.) by leaf roll method. Curr Biotica 3:445–449
Hill L, Goldsworthy GJ (1968) Growth, feeding activity, and the utilization of reserves in larvae of Locusta. J Insect Physiol 14:1085–1098. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(68)90047-4
Ishaaya I, Kontsedalov S, Horowitz AR (2002) Emamectin, a novel insecticide for controlling field crop pests. Pest Manag Sci 58:1091–1095. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.535
Ishtiaq M, Saleem MA, Razaq M (2012) Monitoring of resistance in Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) from four districts of the Southern Punjab, Pakistan to four conventional and six new chemistry insecticides. Crop Prot 33:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2011.11.014
Jansson RK, Brown R, Cartwright B, Cox D, Dunbar DM et al (1997) Emamectin benzoate: a novel avermectin derivative for control of lepidopterous pests in cotton. In: Beltwide Cotton Conferences (USA) 2:1078–1082
Li X, Schuler MA, Berenbaum MR (2007) Molecular mechanisms of metabolic resistance to synthetic and natural xenobiotics. Annu Rev Entomol 52:231–253. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.151104
Mironidis GK, Savopoulou-Soultani M (2014) Development, survivorship, and reproduction of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) under constant and alternating temperatures. Environ Entomol 37:16–28. https://doi.org/10.1603/0046-225X(2008)37[16:DSAROH]2.0.CO;2
Mishra M, Gupta KK, Kumar S (2014) Impact of stem extracts of yellow oleander, Thevetia neriifolia (Apocynaceae) on the feeding potential of IV Instars of gram pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera Hübner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Int J Adv Life Sci 7:408–416. https://doi.org/10.4137/IJIS.S29127
Mishra M, Gupta KK, Kumar S (2015) Impact of the stem extract of Thevetia neriifolia (Apocynaceae) on food consumption and growth of early fourth instars of Helicoverpa armigera. Malaya J Biosci 2:26–35
Naseri B, Fathipour Y, Moharramipour S, Hosseininaveh V (2009) Comparative life history and fecundity of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different soybean varieties. Entomol Sci 12:147–154. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-8298.2009.00310.x
Parsaeyan E, Saber M, Bagheri M (2013) Toxicity of emamectin benzoate and cypermethrin on biological parameters of cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner) in laboratory conditions. J Crop Prot 2:477–485
Paul U, de Little S, Kirkland L, Pirtle E, Maino J (2018) Managing insecticide resistance (Helicoverpa armigera, green peach aphid) and an update on Russian wheat aphid, GRDC Updates. Accessed 13 Jan 2020. https://grdc.com.au/resources-and-publications/grdc-update-papers/tab-content/grdc-update-papers/2018/03/managing-insecticide-resistance-helicoverpa-armigera-green-peach-aphid-and-an-update-on-russian-wheat-aphid
Pienkowski RL, Mehring PR (1983) Influence of avermectin B1 and carbofuran on feeding by alfalfa weevil larvae (Coleoptera-Curculionidae). J Econ Entomol 76:1167–1169
Rashwan MH (2013) Impact of certain novel insecticides on food utilization ingestion and larval growth of the cotton leafworm Spodoptera littoralis. (Boisd.) N Y Sci J 6:1–7
Rosell G, Quero C, Coll J, Guerrero A (2008) Biorational insecticides in pest management. J Pest Sci 33(2):103–121
Saber M, Parsaeyan E, Vojoudi S, Bagheri M, Mehrvar A, Kamita SG (2013) Acute toxicity and sublethal effects of methoxyfenozide and thiodicarb on survival, development and reproduction of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Crop Prot 43:14–17
Sarwar M (2015) Usage of biorational pesticides with novel modes of action, mechanism and application in crop protection. Int J Mater Chem Phys 1(2):156–162
Slansky FJR, Scriber JM (1985) Food consumption and utilization. In: Kerket A, Gilber, LI (ed) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology, Pergamon Oxford, pp 87–163
Sundaramurthy VT (1977) Effect of an inhibitor of chitin deposition on the growth and differentiation of tobacco caterpillar Spodoptera litura Fb. (Noctuidae: Lepidoptera). J Plant Dis Protect 84:597–601
Vojoudi S, Saber M, Hejazi MJ, Talaei-Hassanloui R (2011) Toxicity of chlorpyrifos, spinosad and abamectin on cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera and their sublethal effects on fecundity and longevity. Bull Insectol 64:189–193
Wang D, Gong P, Li M, Qiu X, Wang K (2009) Sublethal effects of spinosad on survival, growth and reproduction of Helicoverpa armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). Pest Manag Sci 65:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.1672
Wasihun YW (2016) Biological control of chickpea pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera Hubner (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) A global concern. World Sci News 45:92–110
Wheeler DA, Isman MB (2001) Antifeedant and toxic activity of Trichilia americana extract against the larvae of Spodoptera litura. Entomol Exp Appl 98:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1570-7458.2001.00751.x
Woodring JP, Clifford CW, Roe RM, Beckman BR (1978) Effects of CO2 and anoxia on feeding, growth, metabolism, water balance, and blood composition in larval female house crickets, Acheta domesticus. J Insect Physiol 24:499–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(78)90051-3
Acknowledgements
The authors are highly grateful to the University Grant Commission (UGC), New Delhi for providing financial assistance to carry out the present investigations. Authors are also thankful to National Bureau of Agricultural Insect Resources (NBAIR) Live Insect Repository for providing Helicoverpa armigera (Accession No: NBII-MP-NOC-01) culture to carry out the investigations. Thanks are extended to the Principal, Acharya Narendra Dev College for providing infrastructure and research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dagar, V.S., Mishra, M. & Kumar, S. Effect of dietary stress of emamectin benzoate on the fitness cost of American bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hübner, 1808). Int J Trop Insect Sci 40, 1069–1077 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00168-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00168-x