Abstract
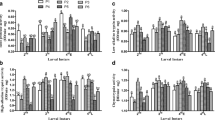
The diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.), has become the most destructive insect pest of Brassica crop plants, such as B. napus throughout the world including Iran. In this study, nutritional indices, digestive enzyme activity and cold hardiness of P. xylostella on seven canola cultivars including Delgan, H19, Modena, Okapi, Opera, RGS003, and SLM046 were studied under laboratory conditions (25 ± 1 °C, 65 ± 5% RH, 16:8 L:D). Fourth instar larvae fed on cultivar SLM046 had the highest efficiency of conversion of ingested and digested food (4.35 ± 0.24% and 4.99 ± 0.31%, respectively). Relative consumption rate (RCR) of P. xylostella 4th instar was higher when fed on Opera cultivar (5.62 ± 0.15 mg/mg/day) while it was lower on Okapi (3.33 ± 0.15 mg/mg/day). The larvae fed on cultivars SLM046 and Okapi had the highest (0.194 ± 0.007 mg/mg/day) and the lowest (0.088 ± 0.003 mg/mg/day) relative growth rate (RGR), respectively. We found a significantly higher amylolytic and proteolytic activity in the midgut of the larvae fed cultivar SLM046. Our findings showed that the activity of enzyme inhibitors and polyphenol oxidase, as antidigestive compounds, are major reasons for the low nutritional efficiency of P. xylostella larvae on some cultivars. The results of the present study indicate that cultivar Okapi is an unsuitable host for the feeding of P. xylostella. These results develop our knowledge of the negative effects of plant defenses on P. xylostella.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akandeh M, Kocheili F, Soufbaf M, Rasekh A, Mozafari K (2016) Effect of canola physical mutation on Plutella xylostella (L.) life table. J Agric Sci Technol 18:985–998
Barto K, Enright S, Eyles A, Wallis C, Chorbadjian R, Hansen R, Herms DA, Bonello P, Cipollini D (2008) Effects of fertilization and fungal and insect attack on systemic protein defenses of Austrian pine. J Chem Ecol 34:1392–1400
Behmer ST (2009) Insect herbivore nutrient regulation. Annu Rev Entomol 54:165–187
Blanco-Labra A, Chagolla-Lopez A, Martinez-Gallardo N, Valdes-Rodriguez S (1995) Further characterization of the 12 kDa protease/alpha amylase inhibitor present in maize seeds. J Food Biochem 19:27–41
Borzoui E, Naseri B, Nouri-Ganbalani G (2017) Effects of food quality on biology and physiological traits of Sitotroga cerealella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). J Econ Entomol 110(1):266–273
Borzoui E, Bandani AR, Goldansaz SH, Talaei-Hassanlouei R (2018) Dietary protein and carbohydrate levels affect performance and digestive physiology of Plodia interpunctella (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae). J Econ Entomol 111(2):942–949
Brown J, McCaffrey JP, Harmon BL, Davis JB, Brown AP, Erickson DA (1999) Effect of late season insect infestation on yield, yield components and oil quality of Brassica napus, B. rapa, B. juncea and Sinapis alba in the Pacific northwest region of the United States. J Agric Sci 132:281–288
Chapman, R. F., Simpson, S. J. and Douglas, A. E. (2013) The insects: structure and function. Available: http://books.google.co.uk/books?id= NXJEi8fo7CkC
Chougule NP, Doyle E, Fitches E, Gatehouse JA (2008) Biochemical characterization of midgut digestive proteases from Mamestra brassicae (cabbage moth; Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and effect of soybean Kunitz inhibitor (SKTI) in feeding assays. J Insect Physiol 54:563–572
Cipollini DF, Bergelson J (2001) Plant density and nutrient availability constrain constitutive and wound-induced expression of trypsin inhibitors in Brassica napus. J Chem Ecol 27:593–610
Constabel, C. P. and Barbehenn, R. (2008) Defensive roles of polyphenol oxidase in plants. In: Schaller, A. (ed). Induced plant resistance to herbivory. Springer science? Business media, Germany. Ch12
Dastranj M, Borzoui E, Bandani AR, Franco OL (2017) Inhibitory effects of an extract from non-host plants on physiological characteristics of two major cabbage pests. Bull Entomol Res 17:1–10
Després L, David JP, Galett C (2007) The evolutionary ecology of insect resistance to plant chemicals. Trends Ecol Evol 22:298–307
Ebrahimi N, Talebi AA, Fathipour Y (2009) Demographic parameters of the diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) on five rapeseed cultivars. J Entomol Soc Iran 28(2):49–59
Elpidina EN, Vinokurov KS, Gromenko VA, Rudenskaya YA, Dunaevsky YE, Zhuzhikov DP (2001) Compartmentalization of proteinases and amylases in Nauphoeta cinerea midgut. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 48:206–216
Fallahnejad-Mojarrad N, Goldasteh S, Rafiei-Karahroudi Z, Vafaei Shoushtari R (2016) The effect of seeds of bean, canola and soybean cultivars on α-amylase digestive activity of Helicoverpa armigera. J Entomol Res 3:211–222 (In Persian with English abstract)
FAO. (2011) FAOSTAT. Available at: http://faostat.fao.org/faostat/form/collection= Production
Fathipour Y, Kianpour R, Bagheri A, Karimzadeh J, Hesseininaveh V (2019) Bottom-up effects of Brassica genotypes on performance of diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Crop Prot 115:135–141
Franco OL, Rigden DJ, Melo FR, Bloch C, Silva CP, Grossi de Sa MF (2000) Activity of wheat alpha-amylase inhibitors towards bruchid alpha-amylases and structural explanation of observed specificities. Eur J Biochem 267:2166–2173
Furlong MJ, Wright DJ, Dosdall LM (2013) Diamondback moth ecology and management: problems, progress, and prospects. Annu Rev Entomol 58:517–541
Gatehouse AM, Norton E, Davison GM, Babbe SM, Newell CA, Gatehouse JA (1999) Digestive proteolytic activity in larvae of tomato moth, Lacanobia oleracea, effects of plant protease inhibitors in vitro and in vivo. J Insect Physiol 45(6):545–558
Giongo AMM, Vendramim JD, de Freitas SDL, da Silva MFDGF (2015) Growth and nutritional physiology of Spodoptera frugiperda (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) fed on Meliaceae fractions. Revista Colombiana de Entomologia 41(1):33–40
Hopkins RJ, van Dam NM, van Loon JJA (2009) Role of glucosinolates in insect plant relationships and multi-trophic interactions. Annu Rev Entomol 54:57–83
Hosseininejad S, Naseri B (2015) Nutritional and growth indices of Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) on different corn hybrids. Arthropod Plant Interact 9:633–640
Justus KA, Dosdall LM, Mitchell BK (2000) Oviposition by Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) and effect of phylloplane waxiness. J Econ Entomol 93:1152–1159
Kahuthia-Gathu R, Löhr B, Poehling HM (2008) Development and reproductive potential of diamondback moth Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) on cultivated and wild crucifer species in Kenya. Int J Trop Insect Sci 28:19–29
Karasov WH, Martínez del Rio C, Caviedes-Vidal E (2011) Ecological physiology of diet and digestive systems. Annu Rev Physiol 73:69–93
Kegley, S., Hill, B. and Orme, S. (2007) PAN Pesticide Database, Pesticide Action Network, North America, http://wwwpesticideinfoorg Cited 23 Nov 2007
Kianpour R, Fathipour Y, Karimzadeh J, Hosseininaveh V (2013) Influence of different host plant cultivars on nutritional indices of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Crop Protect 3(1):43–49
Lazarevic J, Peric-Mataruga V, Vlahovic M, Mrdakovic M (2004) Effects of rearing density on larval growth and activity of digestive enzymes in Lymantria dispar L. (Lepidoptera: Lymantriidae). Folia Biol 52:1–2
Levesque KR, Fortin M, Mauffette Y (2002) Temperature and food quality effects on growth, consumption and post ingestive utilization efficiencies of the forest tent caterpillar Malacosoma disstria. Bull Entomol Res 92(2):127–136
Liu Z, Gong P, Wu K, Wei W, Sun J, Li D (2007) Effects of larval host plants on over-wintering preparedness and survival of the cotton bollworm, Helicoverpa armigera (Hubner) (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Insect Physiol 53:1016–1026
Lou Y, Baldwin IT (2004) Nitrogen supply influences herbivore-induced direct and indirect defenses and transcriptional responses in Nicotiana attenuate. Plant Physiol 135:496–506
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Majd-Marani S, Naseri B, Nouri-Ganbalani G, Borzoui E (2018) Maize hybrids affected nutritional physiology of the khapra beetle, Trogoderma granarium Everts (Coleoptera: Dermestidae). J Stored Prod Res 77:20–25
Mansouri SM, Nouri-Ganbalani G, Fathi SAA, Naseri B, Razmjou J (2013) Nutritional indices and midgut enzymatic activity of Phthorimaea operculella (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) larvae fed different potato germplasms. J Econ Entomol 106(2):1018–1024
Mitchell C, Brennan RM, Graham J, Karley AJ (2016) Plant defense against herbivorous pests: exploiting resistance and tolerance traits for sustainable crop protection. Front Plant Sci 7:1132
Mohammadzadeh M, Izadi H (2018a) Cold acclimation of Trogoderma granarium Everts is tightly linked to regulation of enzyme activity, energy content, and ion concentration. Front Physiol 9:1427
Mohammadzadeh M, Izadi H (2018b) Different diets affecting biology, physiology and cold tolerance of Trogoderma granarium Everts (Coleoptera: Dermestidae). J Stored Prod Res 76:58–65
Mohammadzadeh M, Bandani AR, Borzoui E (2013) The effect of cereal seed extracts on amylase activity of the rose sawfly, Arge rosae Linnaeus (Hymenoptera: Argidae). Arch Phytopathol Plant Protect 46:2476–2485
Mohammadzadeh M, Borzoui E, Izadi H (2017) Physiological and biochemical differences in diapausing and nondiapausing larvae of Eurytoma plotnikovi (Hymenoptera: Eurytomidae). Environ Entomol 46(6):1424–1431
Müller C, Sieling N (2006) Effects of glucosinolate and myrosinase levels in Brassica juncea on a glucosinolate-sequestering herbivore- and vice versa. Chemoecology 16:191–201
Naseri B, Borzoui E, Majd-Marani S, Mansouri SM (2017) Influence of different food commodities on life history, feeding efficiency, and digestive enzymatic activity of Tribolium castaneum (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae). J Econ Entomol 110(5):2263–2268
Nathan SS, Chung PG, Murugan K (2005) Effect of biopesticides applied separately or together on nutritional indices of the rice leaf folder Cnaphalocrocis medinalis. Phytoparasitica 33(2):187–195
Nouri-Ganbalani G, Borzoui E, Shahnavazi M, Nouri A (2018) Induction of resistance against Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lep.: Plutellidae) by jasmonic acid and mealy cabbage aphid feeding in Brassica napus L. Frontiers in. Physiology 9:859
Pauchet Y, Muck A, Svatos A, Heckel DG, Preiss S (2008) Mapping the larval midgut lumen proteome of Helicoverpa armigera, a generalist herbivorous insect. J Proteome Res 7:1629–1639
Petzold-Maxwell J, Wong S, Arellano C, Gould F (2011) Host plant direct defence against eggs of its specialist herbivore, Heliothis subflexa. Ecol Entomol 36:700–708
Sancho E, Villarroel MJ, Andreu E, Ferrando MD (2009) Disturbances in energy metabolism of Daphnia magna after exposure to tebuconazole. Chemosphere 74:1171–1178
Shelton AM, Wyman JA, Cushing NL, Apfelbeck K, Dennehy TJ, Mahr SER, Eigenbrode SD (1993) Insecticide resistance of diamondback moth (Lepidoptera: Plutellae) in North America. J Econ Entomol 86:11–19
Soo Hoo CF, Fraenkel G (1966) The consumption, digestion, and utilization of food plants by a polyphagous insect, Prodenia eridania (Cramer). J Insect Physiol 12:711–730
Sorensen JS, Dearing MD (2006) Efflux transporters as a novel herbivore countermechanism to plant chemical defenses. J Chem Ecol 32:1181–1196
Stout MJ, Fidantsef AL, Duffey SS, Bostock RM (1999) Signal interactions in pathogen and insect attack: systemic plantmediated interactions between pathogens and herbivores of the tomato, Lycopersicon esculentum. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 54:115–130
Tan CW, Chiang SY, Ravuiwasa KT, Yadav J, Hwang SY (2012) Jasmonate-induced defenses in tomato against Helicoverpa armigera depend in part on nutrient availability, but artificial induction via methyl jasmonate does not. Arthropod Plant Interact 6(4):531–541
Van Handel E (1985) Rapid determination of glycogen and sugars in mosquitoes. J Am Mosq Control Assoc 1:299–301
Waldbauer GP (1968) The consumption and utilization of food by insects. Adv Insect Physiol 5:229–288
War AR, Paulraj MG, Ahmad T, Buhroo AA, Hussain B, Ignacimuthu S, Sharma HC (2012) Mechanisms of plant defense against insect herbivores. Plant Signal Behav 7(10):1306–1320
Wouters FC, Reichelt M, Glauser G, Bauer E, Erb M, Gershenzon J, Vassão DG (2014) Reglucosylation of the benzoxazinoid DIMBOA with inversion of stereochemical configuration is a detoxification strategy in lepidopteran herbivores. Angewandte Zuschriften Chem Ecol 126:11502–11506
Zheng XL, Wang P, Cheng WJ, Lu W, Xian ZH, Lei CL, Wang XP (2014) Effects of the larval host plant on the supercooling capacity and physiological characteristics of beet armyworm pupae, Spodoptera exigua (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J Plant Dis Protect 121(5):202–210
Zvereva EL (2002) Effects of host plant quality on overwintering success of the leaf beetle Chrysomela lapponica (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Eur J Entomol 99:189–195
Acknowledgments
The work received financial support from the University of Mohaghegh Ardabili (Ardabil, Iran) which is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nouri-Ganbalani, G., Naseri, B., Majd-Marani, S. et al. Canola cultivars affect nutrition and cold hardiness of Plutella xylostella (L.) (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). Int J Trop Insect Sci 40, 741–750 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00125-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-020-00125-8