Abstract
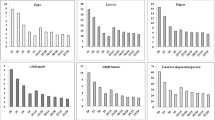
The eggplant shoot and fruit borer (ESFB), Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) is a notorious insect pest that causes havoc across all eggplant cultivation areas in Bangladesh. Remarkably, its relationship with environmental factors such as temperature is not clearly defined. We measured the effects of a range of temperatures (22, 24, 26, 28, and 30 °C) on the population growth parameters of ESFB under laboratory conditions (60 ± 5% relative humidity and 16 L:8 D photoperiod), developing an age-stage, two-sex life table. Results indicate that temperature significantly reduced development times and adult total lifespan and affected ESFB life table parameters (P < 0.05). Specifically, the egg hatching time reduced from 5 days at 22 °C to 3 days at 30 °C, while larval and pupal duration reduced from 12 to 8 days and 10 to 7 days respectively. Thus, the generation time (T) was longer (29 days) at 22 °C and shorter (22 days) at 30 °C; meanwhile, the highest fecundity (61 eggs per female) was recorded at 28 °C and the net reproduction rate (Ro) was higher at 24–30 °C, being (18–24) offspring/individual. Consequently, the ESFB population reared at 28 °C and 30 °C had higher finite rates (λ = 1.15 and 1.14 respectively) and intrinsic rates of natural increase (r = 0.14 and 0.13 respectively), testifying the most suitable temperatures for their growth and reproduction. Our findings contribute to understanding ESFB bionomics and occurrences, and thus, might enhance implemented management strategies, particularly in developing pesticide application schedules.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amarasekare P, Sifuentes R (2012) Elucidating the temperature response of survivorship in insects. Funct Ecol 26(4):959–968
Amarendra KP, Tripathi CPM (2008) Effect of temperature on the development, fecundity, progeny sex ratio and life-table of Campoletis chlorideae, an endolarval parasitoid of the pod borer, Helicoverpa armigera. BioControl 53:461–471
Andrew NR, Terblanche JS (2013) The response of insects to climate change. Climate of Change: Living in a Warmer World. David Bateman Ltd, Auckland, pp 38–50
Bale JS, Masters GJ, Hodkinson ID, Awmack C, Bezemer TM, Brown VK, Butterfield J, Buse A, Coulson JC, Farrar J, Good JE (2002) Herbivory in global climate change research: direct effects of rising temperature on insect herbivores. Glob Chang Biol 8(1):1–6
Birch LC (1948) The intrinsic rate of natural increase of an insect population. J Anim Ecol 17:15–26
CABI (2018) Crop protection compendium datasheet on Leucinodes orbonalis. http://www.cabi.org/cpc/?compid=1&dsid=30498&loadmodule=datasheet&page=868&site=161. Accessed 20 Oct 2018
Campbell A, Frazer BD, Gilbert N, Gutierrez AP, Mackauer M (1974) Temperature requirements of some aphids and their parasites. J Appl Ecol 11:431–438
Chi H (1988) Life table analysis incorporating both sexes and variable development rates among individuals. Environ Entomol 17:26–34
Chi H (2018) TWOSEX-MSChart: a computer program for the age-stage, two-sex life table analysis. http://140.120.197.173/Ecology/. Accessed 26 Apr 2018
Chi H, Liu H (1985) Two new methods for the study of insect population ecology. Bull Inst Zool Acad Sin 24(2):225–240
Chi H, Su HY (2006) Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Aphidius gifuensis (Ashmead) (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) and its host Myzus persicae (Sulzer) (Homoptera: Aphididae) with mathematical proof of the relationship between female fecundity and the net reproductive rate. Environ Entomol 35:10–21
Dhankar BS (1988) Progress in resistance studies in the eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) against shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guen.) infestation. Trop Pest Manag 34(3):343–345
Dixon AF, Honěk A, Keil P, Kotela MA, Šizling AL, Jarošík V (2009) Relationship between the minimum and maximum temperature thresholds for development in insects. Funct Ecol 23(2):257–264
Efron B, Tibshirani R (1993) An introduction to the bootstrap. CRC Press, UK
Golizadeh A, Kamali K, Fathipour Y, Abbasipour H (2009) Effect of temperature on life table parameters of Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae) on two brassicaceous host plants. J Asia-Pacific Entomol 12(4):207–212
Hansen J, Ruedy R, Sato M, Lo K (2010) Global surface temperature change. Rev Geophys 48(4)
Huang YB, Chi H (2011) The age-stage, two-sex life table with an offspring sex ratio dependent on female age. J Agric For 60:337–345
Huang YB, Chi H (2012) Age-stage, two-sex life tables of Bactrocera cucurbitae (Coquillett) (Diptera: Tephritidae) with a discussion on the problem of applying female age-specific life tables to insect populations. Insect Sci 19:263–273
Islam T, Das G, Uddin MM (2016) Field evaluation of promising biorational pesticides against brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee. J Biopest 9(2):113–118
Islam Z (1994) Key factor responsible for fluctuations in rice yellow stem borer populations in deepwater rice ecosystems. Int J Trop Insect Sci 15(4–5):461–468
Jat KL, Pareek BL, Swaroop S (2002) Seasonal incidence of shoot and fruit borer (Leucinodes orbonalis Guen.) on eggplant (Solanum melongena L.) in Rajasthan. Ann Biol 18:165–169
Katiyar OP, Mukharji SP (1974) Development of Leucinodes orbonalis Guenée at certain temperatures. Indian J Hort 31(3):291–294
Kaur PR, Yadav GS, Wargantiwar RK, Burange PS (2014) Population dynamics of brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) under agroclimatic conditions of Hisar, Haryana, India. Ecoscan 8(1&2):1–5
Lall BS, Ahmad SQ (1965) The biology and control of brinjal (eggplant) fruit and shoot borer, Leucinodes orbonalis. J Econ Entomol 58(3):448–451
Latif MA, Rahman MM, Alam MZ (2010) Efficacy of nine insecticides against shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in eggplant. J Pest Sci 83(4):391–397
Leather SR (2018) Factors affecting fecundity, fertility, oviposition, and larviposition in insects. In: Insect reproduction. CRC Press, UK
Ma L, Wang X, Liu Y, Su MZ, Huang GH (2017) Temperature effects on development and fecundity of Brachmia macroscopa (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae). PLoS ONE 12(3):e0173065
Mannan MA, Begum A, Rahman MM, Hossain MM (2003) Screening of local and exotic brinjal varieties/cultivars for resistance to brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guen. Pak J Biol Sci 6(5):488–492
Mannan MA, Islam KS, Jahan M (2015a) Brinjal shoot and fruit borer infestation in relation to plant age and season. Bangladesh J Agric Res 40(3):399–407
Mannan MA, Islam KS, Jahan M, Tarannum N (2015b) Some biological parameters of brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis guenee (lepidoptera: pyralidae) on potato in laboratory condition. Bangladesh J Agric Res 40(3):381–390
Nguyen C, Bahar MH, Baker G, Andrew NR (2014) Thermal tolerance limits of diamondback moth in ramping and plunging assays. PLoS ONE 9(1):e87535
Onekutu A, Omoloye AA, Odebiyi JA (2013) Biology of the eggfruit and shoot borer (EFSB), Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee (Crambidae) on the garden egg, Solanum gilo Raddi. J Entomol 10(3):156–162
Qin JY, Liu YQ, Zhang L, Cheng YX, Luo LZ, Jiang XF (2018) Effects of temperatures on the development and reproduction of the armyworm, Mythimna roseilinea: analysis using an age-stage, two-sex life table. J Integr Agric 1(7):1506–1515
Shimazaki S, Ullah MS, Gotoh T (2019) Seasonal occurrence and development of three closely related Oligonychus species (Acari: Tetranychidae) and their associated natural enemies on fagaceous trees. Exp Appl Acarol https://doi.org/10.1007/s10493-019-00410-3 (online version), 79, 47, 68
Singla P, Bhullar MB, Kaur P (2018) Biological studies on brinjal shoot and fruit borer, Leucinodes orbonalis Guenee. J Entomol Zool Stud 6(1):161–165
Srinivasan R (2008) Integrated Pest management for eggplant fruit and shoot borer (Leucinodes orbonalis) in south and Southeast Asia: past, present and future. J Biopesticides 1(2):105–112
Tuan SJ, Yeh CC, Atlihan R, Chi H (2016) Linking life table and predation rate for biological control: a comparative study of Eocanthecona furcellata (Hemiptera: Pentatomidae) fed on Spodoptera litura (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae) and Plutella xylostella (Lepidoptera: Plutellidae). J Econ Entomol 109:13–24
Ullah MS, Lim UT (2015) Life history characteristics of Frankliniella occidentalis and F. intonsa (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in constant and fluctuating temperature. J Econ Entomol 108:1000–1009
Wang X, Song Y, Sun H, Zhu J (2016) Evaluation of the demographic potential of Aphelinus albipodus (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae) with Aphis glycines (Homoptera: Aphididae) as alternate host at various temperatures. Appl Entomol Zool 51:247–255
Acknowledgements
We sincerely thank Naznin Nahar, Ximena Cibils Stewart, Professor Hsin Chi and anonymous reviewers for their invaluable comments and careful perusal of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tarikul Islam designed the study. Tarikul Islam and A.H.M. Roknuzzaman executed the experiment and collected data. Tarikul Islam and Mohammad Shaef Ullah analysed data, and wrote the manuscript with Kamrul Hassan.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, T., Roknuzzaman, A., Hassan, K. et al. Temperature impacts on the eggplant shoot and fruit borer Leucinodes orbonalis: a life table approach. Int J Trop Insect Sci 40, 351–360 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-019-00086-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42690-019-00086-7