Abstract
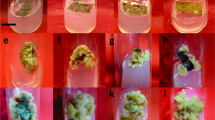
Glossonema varians is a rare and endemic plant species of arid and semiarid region of Rajasthan, used as edible plant in Thar Desert. The plant is facing serious threat of extinction from its natural habitat due to overexploitation and slow propagation in natural conditions. Moreover, plant is known for its nutritional values, hence present manuscript is focused on protein profiling of G. varians. The internodal shoot explants were taken from in vitro grown cultures and inoculated on Murashige and Skoog’s (MS) medium augmented with 25 mg each of citric acid, arginine, adenine and 50 mg of ascorbic acid with different concentrations of PGRs for initiation of callus culture. A combination of 2, 4-D (2, 4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid) and NAA (α-naphthalene acetic acid) was found to be suitable for optimum growth of callus. Regeneration of shoot buds was observed on MS medium augmented with a combination of BAP (6-benzylaminopurine), Kn (Kinetin), NAA and iP (N6-[2-isopentenyl] adenine). Comparative biochemical characterization of regenerative and non- regenerative callus has been done through in vitro quantification and protein profile has also been done by SDS-PAGE.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- BAP:
-
6-Benzylaminopurine
- NOA:
-
2-Naphthoxy acetic acid
- NAA:
-
α-Naphthalene acetic acid
- 2, 4-D:
-
2, 4-Dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog’s medium
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- PFD:
-
Photon flux density
References
Bhandari MM (1990) Flora of the Indian Desert. In: MPS Reports, Jodhpur, pp 197–198
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantization of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bulchandani N, Shekhawat GS (2018) Role of phytohormones and PGR’s in micropropagation of Anethum graveolens L. through axillary shoots and evaluation of NaCl effect on growth parameters. Vegetos 31(special):76–81
Dagla HR, Paliwal A, Shekhawat NS (2018) Micropropagation of Glossonema varians (Stocks) Benth. ex Hook.f.—a rare Asclepiadeae of Indian Thar Desert. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 54:637–641
Dhir R, Shekhawat GS (2012) Critical review on Tecomella undulata: a medicinally potent endangered plant species of Indian Thar Desert. Int J Curr Res 4(6):36–44
Dhir R, Shekhawat GS (2013) Production, storability and morphogenic response of alginate encapsulated axillary meristems and genetic fidelity evaluation of in vitro regenerated Ceropegia bulbosa: a pharmaceutically important threatened plant species. Ind Crop Prod 47:139–144
Dhir R, Shekhawat GS (2014a) Ecorehabilitation and biochemical studies of Ceropegia bulbosa Roxb.: a threatened medicinal succulent. Acta Physiol Plant 36(6):1335–1343
Dhir R, Shekhawat GS (2014b) In vitro propagation using thin cell layer cultures and homogeinity assessment in Ceropegia bulbosa Roxb. J Plant Growth Regul 33:820–830
Jana S, Shekhawat GS (2012) In vitro regeneration of Anethum graveolens, antioxidative enzymes during organogenesis and RAPD analysis for clonal fidelity. Biol Plant 56(1):9–14
Khan TI, Dular AK, Solomon DM (2003) Biodiversity conservation in the Thar Desert; with emphasis on endemic and medicinal plants. Environmentalist 23:137–144
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of Bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Mathur S, Shekhawat GS, Batra A (2002a) Micropropagation of Salvadora persica via cotyledonary nodes. J Biotechnol 1:197–200
Mathur S, Batra A, Shekhawat GS (2002b) An efficient in vitro method for mass propagation of Salvadora persica via apical meristem. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 11:125–112
Mathur S, Shekhawat GS, Batra A (2008) Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from cotyledon explants of Salvadora persica L. Phytomorphology 58(1–2):57–63
Mathur S, Bulchandani N, Parihar S, Shekhawat GS (2017) Critical review on steviol glycosides: pharmacological, toxicological and therapeutic aspects of high potency zero caloric sweetener. Int J Pharmacol 13(7):916–928
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Parihar S (2016) Caralluma edulis: an endemic, edible, medicinal and threatened plant species of Indian Thar Desert. Biotech Today 6(1):37–40
Parihar S (2017) In vitro conservation protocol of Ceropegia bulbosa: an important medicinal and threatened plant species of Western Rajasthan. Plant Sci Today 4(1):21–26
Parihar S (2018) In vitro biochemical characterization of Caralluma edulis (Edgew.) Benth. & Hook. f. and Caralluma adscendens (Roxb.) R. Br.: medicinally potent Indian plant species. Vegetos 31:142–146
Parihar S, Dwivedi NK (2019) Comprehensive analysis of liquid and semisolid culture system for in vitro propagation and conservation of Caralluma edulis: an appetite suppressant medicinal succulent of the indian thar desert. Plant Cell Biotechnol Mol Biol 20(21&22):1020–1031
Shekhawat GS, Mathur S, Batra A (2009) Role of phytohormones and various nitrogen inorganic and organic nutrients in induction of somatic embryogenesis in cell culture derived from leaflets of Azadirachta indica A. Juss. Biol Plant 53(4):707–710
Shekhawat GS, Parihar S, Mahawar L, Khator K, Bulchandani N (2019) Bilin metabolism in plants: structure, function and haem oxygenase regulation of bilin biosynthesis. eLS 2001:1–13
Singh AK (2004) Endangered economic species of Indian desert. Gen Res Crop Evol 51:371–380
Wray W, Boulikas T, Wray VP, Hancock R (1981) Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 118(1):197–203
Acknowledgements
The author is thankful to Prof. G.S. Shekhawat, Department of Botany, JNV University, Jodhpur, India for important comments and suggestions in the preparation of the manuscript. Author is also grateful to Prof. N. S. Shekhawat for providing laboratory facilities during this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parihar, S. Protein profiling of regenerative and non regenerative callus cultures of Glossonema varians: a rare, endemic and edible plant of Indian Thar Desert. Vegetos 33, 385–389 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-020-00120-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-020-00120-x