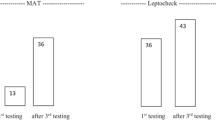
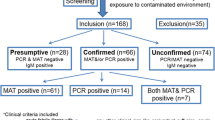
Abstract
Leptospirosis caused by Leptospira interrogans is a major health concern across the globe. It presents a wide range of clinical manifestations viz. fever, headache, nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain. If left untreated, it can lead to fatal complications. The current methods used for leptospirosis diagnosis are based on the detection of L. interrogans. The methods used for routine leptospirosis diagnosis and the agglutination test which is the gold standard method are time consuming and have shortcomings. Molecular methods such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) are considered quick, and better in terms of sensitivity and specificity. Keeping in view the importance of PCR in disease diagnosis and pathogen detection the present study is aimed at PCR based detection of Leptospira interrogans using LipL 32 gene specific primers. The primers used in this study amplified partial region of the LipL32 gene under specific conditions. The DNA amplicon of 392 bp confirmed partial amplification of LipL32 gene and showed no homology with any other organism when checked by BLAST. This method seems to be quick, specific and more sensitive as compared to other conventional methods.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- DNA:
-
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- bp:
-
Base pair
References
Ahmed SN, Shah S, Ahmad FMH (2005) Laboratory diagnosis of leptospirosis. J Postgrad Med 51:195–200
Ahmed SA, Sandai DA, Musa S, Hoe CH, Riadzi M, Lau KL et al (2012) Rapid diagnosis of leptospirosis by multiplex PCR. Malay J Med Sci 19:9
Atzingen MV, Barbosa AS, Brito DE (2008) Lsa21, a novel leptospiral protein binding adhesive matrix molecules and present during human infection. BMC Microbiol 2180:8–70
Barbosa AS, Abreu PA, Neves FO (2006) A newly identified leptospiral adhesion mediates attachment to laminin. Infect Immun 74:6356–6364
Bharti AR, Nally JE, Ricaldi JN, Matthias MA, Diaz M, Lovett MA et al (2003) Leptospirosis: a zoonotic disease of global importance. Lancet Infect Dis 3:757–771
Bhatia M, Umapathy BL, Navaneeth BV (2015) An evaluation of dark field microscopy, culture and commercial serological kits in the diagnosis of leptospirosis. Indian J Med Microbiol 33:416–421
Bomfim MR, Barbosa-Stancioli EF, Koury MC (2008) Detection of pathogenic leptospires in urine from naturally infected cattle by nested PCR. Vet J 178:251–256
Choy HA, Kelley MM, Chen TL, Moller AK, Matsunaga J, Haake DA (2007) Physiological osmotic induction of Leptospira interrogans adhesion: ligA and LigB bind extracellular matrix proteins and fibrinogen. Infect Immun 75:2441–2450
Ellis WA, Songer JG, Montgomery J, Cassells JA (1986) Prevalence of Leptospira interrogans serovar Hardjo in the genital and urinary tracts of non-pregnant cattle. Vet Rec 118:11–13
Haake DA, Chao G, Zuerner RL, Barnett JK, Barnett D, Mazel M et al (2000) The leptospiral outer membrane protein LipL32 is a lipoprotein expressed during the mammalian infection. Infect Immun 68:2276–2285
Khaki P (2016) Clinical laboratory diagnosis of human leptospirosis. Int J Enteric Pathog 4:1–7
Levett PN (2001) Leptospirosis. Clin Microbiol Rev 14:296–326
Marie L, Lisa L, Andrew ES (2000) The role of DNA amplification technology in the diagnosis of infectious diseases. CMAJ 63:301–309
Michael AG, Stanford TS (2004) Rapid diagnosis of pharyngitis caused by group A streptococci. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:571580
Mwachui MA, Crump L, Hartskeerl R, Zinsstag J, Hattendorf J (2015) Environmental and behavioural determinants of leptospirosis transmission: a systematic review. PLoS Neglect Trop Dis 9:e0003843
Nagraik R, Kaushal A, Gupta S, Dhar P, Sethi S, Kumar D (2019) Optimized DNA-based bioassay for Leptospira interrogans detection: a novel platform for leptospirosis diagnosis. 3 Biotech 9:284
Natarajaseenivasan K, Vijayachari P, Sharma S, Sugunan AP, Selvin J, Sehgal SC (2008) Serodiagnosis of severe leptospirosis: evaluation of ELISA based on the recombinant OmpL1 or LipL41 antigens of Leptospira interrogans serovar autumnalis. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 102:699–708
Niloofa R, Fernando N, de Silva NL, Karunanayake L, Wickramasinghe H, Dikmadugoda N et al (2015) Diagnosis of leptospirosis: comparison between microscopic agglutination test, IgM-ELISA and IgM rapid immunochromatography test. PLoS One 10:e0129236
Pereira JC, Chaves R, Bastos E, Leitão A, Guedes-Pinto H (2011) An efficient method for genomic DNA extraction from different molluscs species. Int J Mol Sci 12:8086–8095
Picardeau M (2013) Diagnosis and epidemiology of leptospirosis. Médecine et Maladies Infectieuses 43:1–9
Picardeau M, Bulach DM, Bouchier C, Zuerner RL, Zidane N, Wilson PJ et al (2008) Genome sequence of the saprophyte Leptospira biflexa provides insights into the evolution of Leptospira and the pathogenesis of leptospirosis. PLoS One 3:e1607
Ramadass P, Samuel B, Nachimuthu K (1999) A rapid latex agglutination test for detection of leptospiral antibodies. Vet Microbiol 70:137–140
Rao PS, Sridhar VS (2001) Serological evidence in suspected cases of leptospirosis in and around Manipal. Indian J Med Microbiol 19:32
Ristow P, Bourhy P, McBride FWC (2007) The OmpA-like protein Loa22 is essential for leptospiral virulence. PLoS Pathogens. 3:e97
Sehgal SC (2000) Leptospirosis in the horizon. Natl Med J India 13:228–230
Torgersen PR (2015) Global burden of leptospirosis: estimated in terms of disability adjusted life years. PLoS Neglect Trop Dis 9:e0004122
Vijayachari P, Sehgal SC (2006) Recent advances in the laboratory diagnosis of leptospirosis and characterisation of leptospires. Indian J Med Microbiol 24:320–322
Vijayachari P, Sugunan AP, Shriram AN (2008) Leptospirosis: an emerging global public health problem. J Biosci 33:557–569
Waitkins SA (1987) Leptospirosis. In: Manson-Bhor PEC, Bell DR (eds) Manson’s tropical diseases, 19th edn. Bailliére Tindall, London, pp 657–665
Wasinski B, Pejsak Z (2010) Occurrence of leptospiral infections in swine population in Poland evaluated by ELISA and microscopic agglutination test. Pol J Vet Sci 13:695–699
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to Prof. P.K. Khosla, Shoolini University, Solan (H.P) and Dr. Sunil Sethi, PGIMER, Chandigarh for providing facilities to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagraik, R., Kaushal, A., Gupta, S. et al. PCR based genetic marker for the detection of Leptospira interrogans causing leptospirosis. Vegetos 33, 21–25 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-019-00078-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42535-019-00078-5