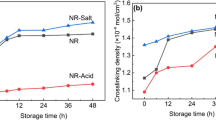
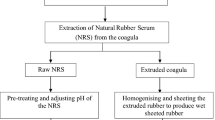
Abstract
With an objective to produce superior quality natural rubber (NR) for preparing tyre treads, various coagulation techniques were attempted for NR latex such as mechanical stirring and heating, steam-induced, salt-induced and freeze–thaw process, from which their efficiency was compared with formic acid-coagulated natural rubber. The effect of coagulation methods on molecular weight and thermo-oxidative ageing of resulting rubber was evaluated. The processing and cure characteristics, rubber–filler interaction and mechanical properties of NR were also evaluated. Rubber separated by mechanical stirring followed by heating and freeze–thaw coagulation showed better retention of molecular weight coagulated NR field latex. FTIR spectrum detected a high amount of nitrogenous materials in rubber compared to acid-coagulated natural rubber. Gel permeation chromatography (GPC), Mooney viscosity and black incorporation time were used to characterise the rubber separated by different methods. Different coagulation techniques adopted have very little effect on the glass transition temperature (Tg). Technological and morphological properties of rubber obtained by stirring and freeze–thaw processes are superior compared to other processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Ehabe E, Le Roux Y, Ngolemasango F, Bonfils F, Nkeng G, Nkouonkam B, Sainte-Beuve J, Gobina MS (2002) Effect of maturation on the bulk viscosity and molecular chain length of cuplump natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 86:703–708. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.10968
Fri PS, Nkeng GE, Ehabe EE (2007) Effect of natural coagula maturation on the processability, cure, and mechanical properties of unfilled vulcanizates of Hevea natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 103:2359–2363. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.25175
Toki S, Burger C, Hsiao BS, Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J, Tanaka Y (2008) Multi-scaled microstructures in natural rubber characterized by synchrotron X-ray scattering and optical microscopy. J Polym Sci, Part B: Polym Phys 46:2456–2464. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.21578
Karino T, Ikeda Y, Yasuda Y, Kohjiya S, Shibayama M (2007) Nonuniformity in natural rubber as revealed by small-angle neutron scattering, small-angle X-ray scattering, and atomic force microscopy. Biomacromol 8:693–699. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm060983d
Tanaka Y (2001) Structural characterization of natural polyisoprenes: solve the mystery of natural rubber based on structural study. Rubber Chem Technol 74:355–375. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547643
Suzuki T, Osaka N, Endo H, Shibayama M, Ikeda Y, Asai H, Higashitani N, Kokubo Y, Kohjiya S (2010) Nonuniformity in cross-linked natural rubber as revealed by contrast-variation small-angle neutron scattering. Macromolecules 43:1556–1563. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma9019416
Liao L-S, Liao J-H, Li Y-M, Chen Y-P, Zhao Y-F, He C-Z (2014) Curing kinetics and properties of natural rubber coagulated using microwave radiation. Rubber Chem Technol 87:43–52. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.13.87932
Sarath-Kumara SJ, Jansz ER, Mendis LP, Tillekedratne LMK, Wickremasinghe LKG (1987) Production of acid from cocoa sweatings and its use for coagulation of natural rubber latex. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 39:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1002/jctb.280390103
Ferreira VS, Rêgo INC, Pastore F, Mandai MM, Mendes LS, Santos KAM, Rubim JC, Suarez PAZ (2005) The use of smoke acid as an alternative coagulating agent for natural rubber sheets’ production. Biores Technol 96:605–609. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2004.06.008
Shell J, Wang T, Vejins V, MA B, Wong YL (2004) Liquid Phase NR/Carbon Black Composites in Vibration Isolation Applications. Automotive Elastomeric Conference Dearborn MI.
de Oliveira RG, Menut P, Bonfils F, Vaysse L, Hemar Y, Sanchez C (2015) Acid-induced aggregation and gelation of natural rubber latex particles. Colloids Surf, A 482:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2015.04.015
Krishnan S, Alex R, Kurian T (2014) HAF/silica/nanoclay “ternary” masterbatch and haf/silica binary masterbatch from fresh natural rubber latex. Rubber Chem Technol 87:250–263. https://doi.org/10.5254/rct.13.87908
Hirata Y, Kondo H, Ozawa Y (2014) 12 - Natural rubber (NR) for the tyre industry. In: Kohjiya S, Ikeda Y (eds) Chemistry, manufacture and applications of natural rubber. Woodhead Publishing, New Delhi, pp 325–352
Prasertkittikul S, Chisti Y, Hansupalak N (2013) Deproteinization of natural rubber using protease immobilized on epichlorohydrin cross-linked chitosan beads. Ind Eng Chem Res 52:11723–11731. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie400232r
Kumarn S, Churinthorn N, Nimpaiboon A, Sriring M, Ho C-C, Takahara A, Sakdapipanich J (2018) Investigating the mechanistic and structural role of lipid hydrolysis in the stabilization of ammonia-preserved hevea rubber latex. Langmuir 34:12730–12738. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02321
Ikeda Y, Yasuda Y, Ohashi T, Yokohama H, Minoda S, Kobayashi H, Honma T (2015) Dinuclear bridging bidentate zinc/stearate complex in sulfur cross-linking of rubber. Macromolecules 48:462–475. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma502063m
Gu Z, Song G, Liu W, Li P, Gao L, Li H, Hu X (2009) Preparation and properties of styrene butadiene rubber/natural rubber/organo-bentonite nanocomposites prepared from latex dispersions. Appl Clay Sci 46:241–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.08.010
Yunyongwattanakorn J, Sakdapipanich JT, Kawahara S, Hikosaka M, Tanaka Y (2007) Effect of gel on crystallization behavior of natural rubber after accelerated storage hardening test. J Appl Polym Sci 106:455–461. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.26507
Nimpaiboon A, Amnuaypornsri S, Sakdapipanich J (2013) Influence of gel content on the physical properties of unfilled and carbon black filled natural rubber vulcanizates. Polym Testing 32:1135–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.07.003
Gao T, Xie R, Zhang L, Gui H, Huang M (2015) Use of rubber process analyzer for characterizing the molecular weight parameters of natural rubber. Int J Poly Sci 2015:e517260. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/517260
Ng JW, Othman N, Yusof NH (2022) Various coagulation techniques and their impacts towards the properties of natural rubber latex from Hevea brasiliensis—a comprehensive review related to tyre application. Ind Crops Prod 181:114835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114835
Ehabe EE, Bonfils F, Sainte-Beuve J, Collet A, Schué F (2006) High-temperature mastication of raw natural rubber: changes in macrostructure and mesostructure. Polym Eng Sci 46:222–227. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.20433
Méndez-Hernández ML, Rivera-Armenta JL, Páramo-García U, Corona Galvan S, García-Alamilla R, Salazar-Cruz BA (2016) Synthesis of high cis-1,4-BR with neodymium for the manufacture of tires. Int J Polym Sci 2016:e7239540. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7239540
Bonfils F, Flori A, Sainte Beuve J (1999) Relations between Wallace plasticity and Mw for natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 74:3078–3087. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097-4628(19991220)74:13%3c3078::AID-APP10%3e3.0.CO;2-6
Le HH, Tiwari M, Ilisch S, RADUSCH H-J, (2005) Effect of molecular structure on carbon black dispersion in rubber compounds: characterization using the online measured electrical conductivity. KGK, Kautsch Gummi Kunstst 58:575–580
Sakdapipanich JT (2007) Structural characterization of natural rubber based on recent evidence from selective enzymatic treatments. J Biosci Bioeng 103:287–292. https://doi.org/10.1263/jbb.103.287
Mekkriengkrai D, Sakdapipanich JT, Tanaka Y (2006) Structural characterization of terminal groups in natural rubber: origin of nitrogenous groups. Rubber Chem Technol 79:366–379. https://doi.org/10.5254/1.3547942
Balani K, Verma V, Agarwal A, Narayan R (2015) Biosurfaces: a materials science and engineering perspective. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Hinchiranan N, Lertweerasirikun W, Poonsawad W, Rempel GL, Prasassarakich P (2009) Cure characteristics and mechanical properties of hydrogenated natural rubber/natural rubber blends. J Appl Polym Sci 111:2813–2821. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.29333
Sperling LH (2005) Introduction to physical polymer science. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken
Schollenberger CS, Dinbergs K (1979) Thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer molecular weight-property relations. Further studies. J Elastomers Plast 11:58–91. https://doi.org/10.1177/009524437901100104
Browning R, Sue H-J, Minkwitz R, Charoensirisomboon P (2011) Effects of acrylonitrile content and molecular weight on the scratch behavior of styrene-acrylonitrile random copolymers. Polym Eng Sci 51:2282–2294. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.22003
Xiao S, Sue H-J (2019) Effect of molecular weight on scratch and abrasive wear behaviors of thermoplastic polyurethane elastomers. Polymer 169:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2019.02.059
Kim D, Ahn B, Kim K, Lee J, Kim IJ, Kim W (2021) Effects of molecular weight of functionalized liquid butadiene rubber as a processing aid on the properties of ssbr/silica compounds. Polymers 13:850. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13060850
Nakade S, Kuga A, Hayashi M, Tanaka Y (1997) Highly purified natural rubber IV. Preparation and characteristics of gloves and condoms. J Nat Rubber Res 12:33–42
Othman AB, Murray GAW, Birley AW (1996) Stress relaxation behaviour of natural rubber vulcanisates containing non-rubber constituents. J Nat Rubber Res 11:183–199
Bristow GM (1990) Composition and cure behaviour of skim block natural rubber. J Natl Rubber Res 5:114–134
Omar NF, Othman N (2011) Effect of carbon black loading on curing characteristics and mechanical properties of waste tyre dust/carbon black hybrid filler filled natural rubber compounds. J Appl Polym Sci 121:1143–1150. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.33511
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Rubber Research Institute of India, Kottayam and Cochin University of Science and Technology for the technical support of this work.
Funding
The author(s) received no financial support for the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nambiathodi, V., Varghese, S. Sustainable coagulation approaches and their impacts towards the properties of natural rubber: a study related to tyre tread applications. J Rubber Res 27, 1–10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42464-023-00229-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42464-023-00229-z