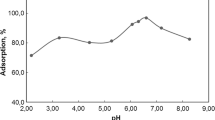
Abstract: Cesium-137 (137Cs) and europium-152+154 (152+154Eu) are the main species found in radioactive liquid wastes. Consequently, the study of their removal from wastewater was essential. For this purpose, hydroxyapatite (HA) nanoparticles were produced from calcium-rich bio-wastes (mussel shells) by a wet chemical precipitation technique. The physicochemical properties, morphology and thermal behaviour of the HA nanoparticles were examined by XRD, FT-IR, SEM/EDX, TGA/DTA. In addition, the surface area was estimated using a nitrogen adsorption desorption isotherm. Afterwards, the adsorptive removal capacity of HA nanoparticles for 137Cs and 152+154Eu within the pH range of 2−12 from aqueous solutions was determined, and the sorbent dose and contact time were also considered. The current work utilized cost effective HA nanoparticles as a planned barrier for the removal of nuclear ions originating from radio reactor liquid wastes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El-Bassyouni, G., Kenawy, S., Hassan, R. et al. Removal of 137Cs and 152+154Eu Using Hydroxyapatite Prepared from Mussel Shells. Interceram. - Int. Ceram. Rev. 68, 34–41 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42411-019-0049-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42411-019-0049-0