Abstract
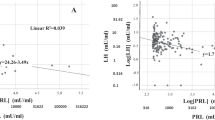
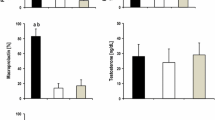
Sexual dysfunction (SD) and hyperprolactinemia are more prevalent in uremic men than in the general population. The aim of this study was to quantify the extent and degree of severity of both SD and hyperprolactinemia, and to investigate whether these two conditions are associated in a population of uremic men with CKD 3b-5d. In this cross-sectional study, we enrolled men aged 20–70 years with a creatinine clearance < 40 ml/min (non-dialysis-dependent patients (NDP)) or time on dialysis > 3 months (dialysis-dependent patients (DP)). Blood samples and a questionnaire including a Danish version of The International Index of Erectile Function (IIEF) were analyzed. Clinical information and medications were obtained from patient records. Seventy-seven patients (47 NDP and 30 DP) were enrolled in the study. Of these, 71% reported that they had sexual problems (NDP 62% and DP 87%, p=0.02). Erectile dysfunction was found in 87% (NDP 80% and DP 100%, p=0.04). Nocturnal erection was found in 32% (NDP 36% and DP 27%, p=0.42). Diminished frequency of sexual desire was found in 73% (NDP 67% and DP 83%, p=0.11). Low level of sexual desire was found in 72% (NDP 71% and DP 73%, p=0.83). Hyperprolactinemia was found in 21% (NDP 13% and DP 33%, p=0.03). Erectile dysfunction was significantly associated with prolactin (p=0.007). The prevalences for SD and hyperprolactinemia are high in uremic men, especially among dialysis patients. We have shown a significant correlation between erectile dysfunction and prolactin in a Danish population of uremic men.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Diemont WL, Vruggink PA, Meuleman EJH, Doesburg WH, Lemmens WAJG, Berden JHM. Sexual dysfunction after renal replacement therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 2000;35:845–51.
Shamloul R, Ghanem H. Erectile dysfunction. Lancet. 2013;381:153–65.
Rosen RC, Fisher WA, Eardley I, Niederberger C, Nadel A, Sand M. The multinational Men’s Attitudes to Life Events and Sexuality (MALES) study: I. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and related health concerns in the general population. Curr Med Res Opin. 2004;20:607–17.
Procci WR, Goldstein DA, Adelstein J, Massry SG. Sexual dysfunction in the male patient with uremia: a reappraisal. Kidney Int. 1981;19:317–23.
Palmer BF. Sexual dysfunction in men and women with chronic kidney disease and end-stage kidney disease. Adv Ren Replace Ther. 2003;10:48–60.
Palmer BF. Sexual dysfunction in uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10:1381–8.
Basaria S, Coviello AD, Travison TG, Storer TW, Farwell WR, Jette AM, et al. Adverse events associated with testosterone administration. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:109–22.
Carter JN, Tyson JE, Tolis G, Van Vliet S, Faiman C, Friesen HG. Prolactin-screening tumors and hypogonadism in 22 men. N Engl J Med. 1978;299:847–52.
Gomez F, De La Cueva R, Wauters JP, Lemarchand-Béraud T. Endocrine abnormalities in patients undergoing long-term hemodialysis. The role of prolactin. Am J Med. 1980;68:522–30.
Sievertsen GD, Lim VS, Nakawatase C, Frohman LA. Metabolic clearance and secretion rates of human prolactin in normal subjects and in patients with chronic renal failure. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1980;50:846–52.
Bommer J, Ritz E, Del Pozo E, Bommer G. Improved sexual function in male haemodialysis patients on bromocriptine. Lancet. 1979;2:496–7.
Carani C, Isidori AM, Granata A, Carosa E, Maggi M, Lenzi A, et al. Multicenter study on the prevalence of sexual symptoms in male hypo- and hyperthyroid patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90:6472–9.
Lo JC, Chertow GM, Go AS, Hsu C. Increased prevalence of subclinical and clinical hypothyroidism in persons with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2005;67:1047–52.
Rosen RC, Riley A, Wagner G, Osterloh IH, Kirkpatrick J, Mishra A. The international index of erectile function (IIEF): a multidimensional scale for assessment of erectile dysfunction. Urology. 1997;49:822–30.
Bartsch W. Interrelationships between sex hormone-binding globulin and testosterone, 5 alpha-dihydrotestosterone and oestradiol-17 beta in blood of normal men. Maturitas. 1980;2:109–18.
De Rosa M, Zarrilli S, Vitale G, et al. Six months of treatment with cabergoline restores sexual potency in hyperprolactinemic males: an open longitudinal study monitoring nocturnal penile tumescence. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2004;89:621–5.
Mesquita JF, Ramos TF, Mesquita FP, Netto JMB, Bastos MG, deFigueiredo AA. Prevalence of erectile dysfunction in chronic renal disease patients on conservative treatment. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2012;67:181–3.
Vecchio M, Palmer S, De Berardis G, et al. Prevalence and correlates of erectile dysfunction in men on chronic haemodialysis: a multinational cross-sectional study. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2012;27:2479–88.
Fugl-Meyer KS, Nilsson M, Hylander B, Lehtihet M. Sexual function and testosterone level in men with conservatively treated chronic kidney disease. Am J Mens Health. 2017;11:1069–76.
Xu ZH, Pan D, Liu TY, et al. Effect of prolactin on penile erection: a cross-sectional study. Asian J Androl. 2019;21:587–91.
Galdiero M, Pivonello R, Grasso LFS, Cozzolino A, Colao A. Growth hormone, prolactin, and sexuality. J Endocrinol Investig. 2012;35:782–94.
Muir JW, Besser GM, Edwards CRW, et al. Bromocriptime improves reduced libido and potency in men receiving maintenance hemodialysis. Clin Nephrol. 1983;20:308–3014.
Navaneethan SD, Vecchio M, Johnson DW, Saglimbene V, Graziano G, Pellegrini F, et al. Prevalence and correlates of self-reported sexual dysfunction in CKD: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;56:670–85.
Jannini EA, Granata AM, Hatzimiuratidis K, Goldstein I. Use and abuse of Rigiscan in the diagnosis of erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med. 2009;6:1820–9.
Finkelstein FO, Shirani S, Wuerth D, Finkelstein SH. Therapy Insight: sexual dysfunction in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nat Clin Pract Nephrol. 2007. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpneph0438.
Hatzimouratidis K, Giuliano F, Moncada I, Muneer A, Salonia A, Verze P. EAU Guidelines on errectile dysfunction, premature ejaculation, penile curvature and priapism. European association of Urology. 2016. uroweb.org/guideline/male-sexual-dysfunction/. Accessed 23 Jan 2021.
Krysiak R, Okopién B. Sexual functioning in hyperprolactinemic patients treated with cabergoline or bromocriptine. Am J Ther. 2019;26:e433–40. https://doi.org/10.1097/MJT.0000000000000777.
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Frost and M. Bjerregaard-Andersen for their support in using STATA for data management.
Funding
We thank the Research Council of Hospital Lillebaelt for funding this study (grant number 140-08/1-12-32).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Ann Helen Madsen, and Rikke Juul-Sandberg. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Ann Helen Madsen and all authors commented on later versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All the procedures performed in this study were performed in accordance with the principles of the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Approval was granted by the Ethical Committee of the Region of Southern Denmark (S-20120041).
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, A.H., Juul-Sandberg, R., Kjær Steffensen, G. et al. The Effect of Prolactin on Sexual Dysfunction in Uremic Men. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 3, 826–834 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-021-00807-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-021-00807-5