Abstract
Melanoma is a severe form of skin cancer arising from melanocytes. In recent years, immunotherapy in particular, immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI), has revolutionized the treatment of metastatic melanoma. Recent studies have explored the potential of treatment of metastatic melanoma using the combination of ICI with radiotherapy (RT). In present study, we systematically review available clinical studies involving the combination of RT with pembrolizumab. A systematic search using the electronic databases including PubMed, Scopus, and Embase was conducted to retrieve relevant clinical studies investigating the use of RT+ pembrolizumab on metastatic melanoma patients. Results showed that a total of 16 studies involving 612 metastatic melanoma patients were included. Furthermore, the treatment combination was generally safe with grade 3 or higher toxicities ranging from 1 to 11%. In conclusion, this therapeutic modality is promising. However, gray areas such as limited prospective studies and optimal timing will need to be addressed in future studies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chin L, Garraway LA, Fisher DE. Malignant melanoma: genetics and therapeutics in the genomic era. Genes Dev. 2006;20(16):2149–82.
Guy GP Jr, Thomas CC, Thompson T, Watson M, Massetti GM, Richardson LC. Vital signs: melanoma incidence and mortality trends and projections—United States, 1982–2030. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64(21):591.
Kamposioras K, Pentheroudakis G, Pectasides D, Pavlidis N. Malignant melanoma of unknown primary site. To make the long story short. A systematic review of the literature. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2011;78(2):112–26.
Soong SJ, Harrison RA, McCarthy WH, Urist MM, Balch CM. Factors affecting survival following local, regional, or distant recurrence from localized melanoma. J Surg Oncol. 1998;67(4):228–33.
Balch CM, Buzaid AC, Soong S-J, Atkins MB, Cascinelli N, Coit DG, et al. Final version of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for cutaneous melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 2001;19(16):3635–48.
Barth A, Wanek LA, Morton DL. Prognostic factors in 1,521 melanoma patients with distant metastases. J Am Coll Surg. 1995;181(3):193–201.
Eton O, Legha SS, Moon TE, Buzaid AC, Papadopoulos NE, Plager C, et al. Prognostic factors for survival of patients treated systemically for disseminated melanoma. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(3):1103–11.
Keilholz U, Conradt C, Legha SS, Khayat D, Scheibenbogen C, Thatcher N, et al. Results of interleukin-2-based treatment in advanced melanoma: a case record-based analysis of 631 patients. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(9):2921–9.
Manola J, Atkins M, Ibrahim J, Kirkwood J. Prognostic factors in metastatic melanoma: a pooled analysis of Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trials. J Clin Oncol. 2000;18(22):3782–93.
Schmidt H, Suciu S, Punt CJ, Gore M, Kruit W, Patel P, et al. Pretreatment levels of peripheral neutrophils and leukocytes as independent predictors of overall survival in patients with American Joint Committee on Cancer stage IV melanoma: results of the EORTC 18951 biochemotherapy trial. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(12):1562–9.
Jiang W, Chan CK, Weissman IL, Kim BY, Hahn SM. Immune priming of the tumor microenvironment by radiation. Trends Cancer. 2016;2(11):638–45.
Frey B, Rückert M, Deloch L, Rühle PF, Derer A, Fietkau R, et al. Immunomodulation by ionizing radiation—impact for design of radio-immunotherapies and for treatment of inflammatory diseases. Immunol Rev. 2017;280(1):231–48.
Son CH, Fleming GF, Moroney JW. Potential role of radiation therapy in augmenting the activity of immunotherapy for gynecologic cancers. Cancer Manag Res. 2017;9:553.
Lee Y, Auh SL, Wang Y, Burnette B, Wang Y, Meng Y, et al. Therapeutic effects of ablative radiation on local tumor require CD8+ T cells: changing strategies for cancer treatment. Blood. 2009;114(3):589–95.
Deng L, Liang H, Burnette B, Beckett M, Darga T, Weichselbaum RR, et al. Irradiation and anti–PD-L1 treatment synergistically promote antitumor immunity in mice. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(2):687–95.
Dovedi SJ, Adlard AL, Lipowska-Bhalla G, McKenna C, Jones S, Cheadle EJ, et al. Acquired resistance to fractionated radiotherapy can be overcome by concurrent PD-L1 blockade. Cancer Res. 2014;74(19):5458–68.
Alomari AK, Cohen J, Vortmeyer AO, Chiang A, Gettinger S, Goldberg S, et al. Possible interaction of anti–PD-1 therapy with the effects of radiosurgery on brain metastases. Cancer Immunol Res. 2016;4(6):481–7.
Nagasaka M, Zaki M, Kim H, Raza SN, Yoo G, Lin H-S, et al. PD1/PD-L1 inhibition as a potential radiosensitizer in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a case report. J Immunother Cancer. 2016;4(1):83.
Shi F, Wang X, Teng F, Kong L, Yu J. Abscopal effect of metastatic pancreatic cancer after local radiotherapy and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor therapy. Cancer Biol Ther. 2017;18(3):137–41.
Schoenhals JE, Seyedin SN, Tang C, Cortez MA, Niknam S, Tsouko E, et al. Preclinical rationale and clinical considerations for radiotherapy plus immunotherapy: going beyond local control. Cancer. 2016;22(2):130–7.
Haymaker CL, Kim D, Uemura M, Vence LM, Phillip A, McQuail N, et al. Metastatic melanoma patient had a complete response with clonal expansion after whole brain radiation and PD-1 blockade. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2017;5(2):100–5.
Improta G, Leone I, Donia M, Gieri S, Pelosi G, Fraggetta F. New developments in the management of advanced melanoma–role of pembrolizumab. Onco Targets Ther. 2015;8:2535.
Azad A, Lim SY, D'costa Z, Jones K, Diana A, Sansom OJ, et al. PD-L1 blockade enhances response of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma to radiotherapy. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(2):167–80.
Shaverdian N, Lisberg AE, Bornazyan K, Veruttipong D, Goldman JW, Formenti SC, et al. Previous radiotherapy and the clinical activity and toxicity of pembrolizumab in the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer: a secondary analysis of the KEYNOTE-001 phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(7):895–903.
Slovin S, Higano C, Hamid O, Tejwani S, Harzstark A, Alumkal J, et al. Ipilimumab alone or in combination with radiotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: results from an open-label, multicenter phase I/II study. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(7):1813–21.
Knisely JP, James BY, Flanigan J, Sznol M, Kluger HM, Chiang VL. Radiosurgery for melanoma brain metastases in the ipilimumab era and the possibility of longer survival. J Neurosurg. 2012;117(2):227–33.
Maity A, Mick R, Huang AC, George SM, Farwell MD, Lukens JN, et al. A phase I trial of pembrolizumab with hypofractionated radiotherapy in patients with metastatic solid tumours. Br J Cancer. 2018;119(10):1200.
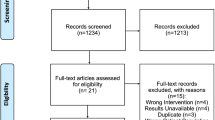
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med. 2009;151(4):264–9.
Sibaud V, David I, Lamant L, Resseguier S, Radut R, Attal J, et al. Acute skin reaction suggestive of pembrolizumab-induced radiosensitization. Melanoma Res. 2015;25(6):555–8.
Anderson E, Postow M, Young R, Chan T, Yamada Y, Beal K. Initial report on safety and lesion response of melanoma brain metastases after stereotactic radiosurgery or hypofractionated radiation therapy in patients receiving concurrent pembrolizumab. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016;96(2):E132.
Liniker E, Menzies A, Kong B, Cooper A, Ramanujam S, Lo S, et al. Activity and safety of radiotherapy with anti-PD-1 drug therapy in patients with metastatic melanoma. Oncoimmunology. 2016;5(9):e1214788.
Anderson ES, Postow MA, Wolchok JD, Young RJ, Ballangrud Å, Chan TA, et al. Melanoma brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiosurgery and concurrent pembrolizumab display marked regression; efficacy and safety of combined treatment. J Immunother Cancer. 2017;5(1):76.
Bang A, Wilhite TJ, Pike LR, Cagney DN, Aizer AA, Taylor A, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the tolerability of combined treatment with PD-1 and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors and palliative radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2017;98(2):344–51.
Fang P, Jiang W, Allen P, Glitza I, Guha N, Hwu P, et al. Radiation necrosis with stereotactic radiosurgery combined with CTLA-4 blockade and PD-1 inhibition for treatment of intracranial disease in metastatic melanoma. J Neuro-Oncol. 2017;133(3):595–602.
Kaidar-Person O, Zagar TM, Deal A, Moschos SJ, Ewend MG, Sasaki-Adams D, et al. The incidence of radiation necrosis following stereotactic radiotherapy for melanoma brain metastases: the potential impact of immunotherapy. Anti-Cancer Drugs. 2017;28(6):669–75.
Aboudaram A, Modesto A, Chaltiel L, Gomez-Roca C, Boulinguez S, Sibaud V, et al. Concurrent radiotherapy for patients with metastatic melanoma and receiving anti-programmed-death 1 therapy: a safe and effective combination. Melanoma Res. 2017;27(5):485–91.
Pike LR, Bang A, Ott P, Balboni T, Taylor A, Catalano P, et al. Radiation and PD-1 inhibition: favorable outcomes after brain-directed radiation. Radiother Oncol. 2017;124(1):98–103.
Nardin C, Mateus C, Texier M, Lanoy E, Hibat-Allah S, Ammari S, et al. Tolerance and outcomes of stereotactic radiosurgery combined with anti-programmed cell death-1 (pembrolizumab) for melanoma brain metastases. Melanoma Res. 2018;28(2):111–9.
Martin AM, Cagney DN, Catalano PJ, Alexander BM, Redig AJ, Schoenfeld JD, et al. Immunotherapy and symptomatic radiation necrosis in patients with brain metastases treated with stereotactic radiation. JAMA oncol. 2018;4(8):1123–4.
Du Four S, Janssen Y, Michotte A, Van Binst AM, Van den Begin R, Duerinck J, et al. Focal radiation necrosis of the brain in patients with melanoma brain metastases treated with pembrolizumab. Cancer Med. 2018;7(10):4870–9.
Blake Z, Marks DK, Gartrell RD, Hart T, Horton P, Cheng SK, et al. Complete intracranial response to talimogene laherparepvec (T-Vec), pembrolizumab and whole brain radiotherapy in a patient with melanoma brain metastases refractory to dual checkpoint-inhibition. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):25.
Chen L, Douglass J, Kleinberg L, Ye X, Marciscano AE, Forde PM, et al. Concurrent immune checkpoint inhibitors and stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases in non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, and renal cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018;100(4):916–25.
Murphy B, Walker J, Bassale S, Monaco D, Jaboin J, Ciporen J, et al. Concurrent radiosurgery and immune checkpoint inhibition. Am J Clin Oncol. 2019;42(3):253–7.
Kim HJ, Chang JS, Roh MR, Oh B-H, Chung K-Y, Shin SJ, et al. Effect of radiotherapy combined with pembrolizumab on local tumor control in mucosal melanoma patients. Front Oncol. 2019;9:835.
Kohutek ZA, Yamada Y, Chan TA, Brennan CW, Tabar V, Gutin PH, et al. Long-term risk of radionecrosis and imaging changes after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Neuro-Oncol. 2015;125(1):149–56.
Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, Hui R, Csőszi T, Fülöp A, et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1–positive non–small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(19):1823–33.
Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A, Grob JJ, Mortier L, et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(26):2521–32.
Kyriakopoulos C, Zarkavelis G, Andrianopoulou A, Papoudou-Bai A, Stefanou D, Boussios S, et al. Primary pulmonary malignant melanoma: report of an important entity and literature review. Case Rep Oncol Med. 2017;2017:8654326.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Medicine
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anahid, S.M., Afra, O. The Combination of Radiotherapy with Pembrolizumab in the Treatment of Metastatic Melanoma Patients: a Systematic Review. SN Compr. Clin. Med. 2, 432–438 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-020-00253-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-020-00253-9