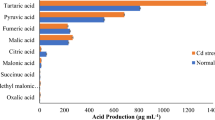
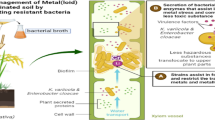
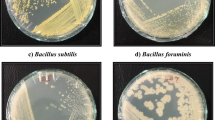
Abstract
Exposure to a high concentration of cadmium (Cd) is toxic to living organisms. The present study deals with the characterization of Cd resistant bacterial isolates, and analysis of the rhizoremediation of Cd using the metal resistant plant growth promoting (PGP) rhizobacteria applied through maize (Zea mays Sturt) rhizosphere. Cd resistant bacterial isolates were selected, analyzed for PGP attributes and applied in the rhizosphere of maize plants to study their effects on plant growth under metal stress, along with the Cd rhizoremediation potential. The bacterial isolates Serratia marcescens S2I7, S. marcescens BB-2B, Bacillus subtilis SR1 and Paenibacillus sp. S1I8 showed resistance to Cd and positive for PGP attributes, like phosphate-solubilization, production of indole acetic acid (IAA), and siderophore. The augmentation of the metal resistant bacteria caused 26% increase in the shoot length of the plants in Cd spiked soil. Under the stress of Cd, the activity of stress-responsive enzymes- glutathione S-transferase (GST), catalase (CAT), peroxidases (POD) of the treated plants were relatively higher. Augmentation of the bacterial isolates significantly reduced the activity of stress-responsive enzymes. The association of Z. mays-rhizobacteria played the most crucial role in the process of bioremediation, as it could remove up to 31% of Cd from soil after 30 days. The present study emphasizes the efficiency of plant–microbe interactions in the rhizosphere to remove metals from soil through the promotion of plant growth in contaminated sites.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The 16 s rDNA sequences of the isolates have been submitted to the National Centre for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) genebank database under the accession numbers MF992191 (B. subtilis SR1), KX602663 (Paenibacillus sp. S1I8), MF554655 (S. marcescens BB-2B), and KY744360 (S. marcescens S2I7).
References
Aladesanmi OT, Oroboade JG, Osisiogu CP, Osewole AO (2019) Bioaccumulation factor of selected heavy metals in Zea mays. J Health Pollut 9:24
Ali H, Khan E, Sajad MA (2013) Phytoremediation of heavy metals—Concepts and applications. Chemosphere 91:869–881
Bashir S, Hussain Q, Akmal M, Riaz M, Hu H, Ijaz SS, Iqbal M, Abro S, Mehmood S, Ahmad M (2018a) Sugarcane bagasse-derived biochar reduces the cadmium and chromium bioavailability to mash bean and enhances the microbial activity in contaminated soil. J Soils Sedim 18:874–886
Bashir S, Hussain Q, Shaaban M, Hu H (2018b) Efficiency and surface characterization of different plant-derived biochar for cadmium (Cd) mobility, bioaccessibility and bioavailability to Chinese cabbage in highly contaminated soil. Chemosphere 211:632–639
Becerra-Castro C, Prieto-Fernandez A, Alvarez-Lopez V, Monterroso C, Cabello-Conejo MI, Acea MJ, Kidd PS (2011) Nickel solubilizing capacity and characterization of rhizobacteria isolated from hyperaccumulating and non-hyperaccumulating subspecies of Alyssum serpyllifolium. Int J Phytoremediat 1:229–244
Belyaeva ON, Haynes RJ, Birukova OA (2005) Barley yield and soil microbial and enzyme activities as affected by contamination of two soils with lead, zinc or copper. Biol Fertil Soils 41(2):85–94
Bojorquez C, Voltolina D (2016) Removal of cadmium and lead by adapted strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Enterobacter cloacae. Rev Int Contam Ambie 32:407–412
Brunetti G, Farrag K, Rovira PS, Nigro F, Senesi N (2011) Greenhouse and field studies on Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn phytoextraction by Brassica napus from contaminated soils in the Apulia region, Southern Italy. Geoderma 160(3–4):517–523
Caregnato FF, Koller CE, MacFarlane GR, Moreira JCF (2008) The glutathione antioxidant system as a biomarker suite for the assessment of heavy metal exposure and effect in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1119–1127
Chibuike GU, Obiora SC (2014) Heavy metal polluted soils: effect on plants and bioremediation methods. Appl Environ Soil Sci 2:12
Dey S, Mazumder PB, Paul SB (2014) Accumulation of Cu at different concentration in tea plant (Camellia sinensis(L) OKuntze). IOSR J Agric Vet Sci 7(4):39–43
Diamandas A, Razon MR, Ramirez-Arcos S, Brassinga AKC (2021) The virulence of S marcescens strains isolated from contaminated blood roducts is divergent in the C. elegans infection model. Front Genet 12:667062. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.667062
Diao G, Wang Y, Wang C, Yang C (2011) Cloning and Functional Characterization of a Novel Glutathione S-Transferase Gene from Limonium bicolor. Plant Mol Biol Rep 29:77–87
Foyer CH, Lopez-Delgado H, Dat JF, Scott IM (1997) Hydrogen peroxide and glutathione-associated mechanisms of acclamatory stress tolerance and signalling. Physiol Plant 100:241–254
Głowacka K, Źróbek-Sokolnik A, Okorski A, Najdzion J (2019) The effect of cadmium on the activity of stress-related enzymes and the ultrastructure of pea roots. Plants (basel, Switzerland) 8(10):413. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants8100413
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases: the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Hameed A, Sheikh MA (2007) Changes in catalase, peroxidase activities and soluble proteins in wheat leaves on thiourea and H2O2 treatments. Biosci Res 4(1):21–27
Hasnat A, Rahman I, Pasha M (2013) Assessment of environmental impact for tannery industries in Bangladesh. Int J Environ Sci Dev 4(2):217–220
Hernandez LE, Villasante CO, Montero-Palmero MB, Escobar C, Carpena RO (2012) Heavy metal perception in a microscale environment: a model system using high doses of pollutants. In: Gupta DK, Sandalio LM (eds) Metal toxicity in plants: perception, signaling and remediation. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp 23–37. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-22081-4_2
Heshmatpure N, Rad MY (2012) The effect of PGPR (Plant-Growth-Promoting Rhizobacteria) on phytoremediation of cadmiums by canola, (Brassica napus L.) cultivars of Hyola. Ann Biol Res 2:5624–5630
Huang L, Pu X, Pan JF, Wang B (2013) Heavy metal pollution status in surface sediments of Swan Lake lagoon and Rongcheng Bay in the northern Yellow Sea. Chemosphere 93(9):1957–1964
Igiri BE, Okoduwa SIR, Idoko GO, Akabuogu EP, Adeyi AO, Ejiogu IK (2018) Toxicity and bioremediation of heavy metals contaminated ecosystem from tannery wastewater: a review. Hindawi J Toxicol 16:2
Irfan M, Ahmad A, Hayat S (2013) Effect of cadmium on the growth and antioxidant enzymes in two varieties of Brassica juncea. Saudi J Biol Sci 21:125–131
Khan AR, Park GS, Asaf S, Hong SJ, Jung BK, Shin JH (2017) Complete genome analysis of Serratia marcescens RSC-14: a plant growth-promoting bacterium that alleviates cadmium stress in host plants. PLoS ONE 12(2):0171534. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0171534
Kotoky R, Pandey P (2019) Rhizosphere mediated biodegradation of benzo(A)pyrene by surfactin producing soil bacilli applied through Melia azadirachta rhizosphere. Int J Phytorem. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2019.1663486
Kotoky R, Pandey P (2020) Rhizosphere assisted biodegradation of benzo(a)pyrene by cadmium resistant plant-probiotic Serratia marcescens S2I7, and its genomic traits. Sci Rep 10:5279. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62285-4
Kotoky R, Pandey P (2021) The genomic attributes of Cd-resistant, hydrocarbonoclastic Bacillus subtilis SR1 for rhizodegradation of benzo(a)pyrene under co-contaminated conditions. Genomics 113(1):613–623. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2020.09.0577
Kotoky R, Singha LP, Pandey P (2017a) Draft genome sequence of polyaromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacterium Bacillus subtilis SR1, which has plant growth-promoting attributes. Genome Announc 2:1–2
Kotoky R, Singha LP, Pandey P (2017b) Draft Genome Sequence of Heavy Metal- Resistant Soil Bacterium Serratia marcescens S2I7, Which Has the Ability To Degrade Polyaromatic Hydrocarbons. Genome Announc 2:1–2
Kotoky R, Nath S, Maheshwari DK, Pandey P (2019) Cadmium resistant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria Serratia marcescens S2I7 associated with the growth promotion of rice plant. Environ Sustain 2:135–144
Kuiper I, Bloemberg GV, Lugtenberg BJJ (2001) Selection of a plant-bacterium pair as a novel tool for rhizostimulation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 14:1197–1205
Kumar S, Stecher G, Li M, Knyaz C, Tamura K (2018) MEGA X: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol Biol Evol 35:1547–1549
Kumar V, Behl RK, Narula N (2001) Establishment of phosphate-solubilizing strains of azotobacter chroococcum in the rhizosphere and their effect on wheat cultivars under green house conditions. Microbiol Res 156 (1): 87–93 Retrieved http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0944501304700142.
Li M, Hu CW, Zhu Q, Chen L, Kong ZM, Liu ZL (2006) Copper and zinc induction of lipid peroxidation and effects on antioxidant enzyme activities in the micro-alga Pavlova viridis (Prymnesiophyceae). Chemosphere 62:65–572
Li H, Liu X, Wassie M et al (2020) Selenium supplementation alleviates cadmium-induced damages in tall fescue through modulating antioxidant system, photosynthesis efficiency, and gene expression. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9490–9502. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06628-3
Liu S, Liu H, Chen R, Ma Y, Yang B, Chen Z, Liang Y, Fang J, Xiao Y (2021) Role of two plant growth-promoting bacteria in remediating cadmium—contaminated soil combined with Miscanthus floridulus (Lab). Plants 10:912. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10050912
Ma Y, Rajkumar M, Freitas H (2009) Inoculation of plant growth promoting bacterium Achromobacter xylosoxidansstrain Ax10 for the improvement of copper phytoextraction by Brassica juncea. J Environ Manage 90:831–837
Madhaiyan M, Poonguzhali S, Torgmin SA (2007) Metal tolerating methylotrophic bacteria reduces nickel and cadmium toxicity and promotes plant growth of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum L.). Chemosphere 69(2):220–228
Marrs KA (1996) The functions and regulation of glutathione S-transferases in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 47:127–158
Mittler R, Vanderauwera S, Gollery M, Van Breusegem F (2004) Reactive oxygen gene network of plants. Trends Plant Sci 9:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2004.08.009
Moran MS, Depierre JW, Mannervik B (1979) Levels of glutathione, glutathionereductase and glutathione-S-transferase activities in rat lung and liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 582:67–78
Okolo VN, Olowolafe EA, Akawu I, Okoduwa SIR (2016) Effects of industrial effluents 581 on soil resource in challawa industrial area. J Glob Ecol Environ 5(1):10
Olaniran AO, Balgobind A, Pillay B (2013) Bioavailability of heavy metals in soil: impact on microbial biodegradation of organic compounds and possible improvement strategies. Int J Mol Sci 14(5):10197–10228
Osazee OJ, Obayagbona ON, Daniel EO (2013) Microbiological and physicochemical analyses of top soils obtained from four municipal waste dumpsites in Benin City, Nigeria. Int J Microbiol Mycol 1(1):23–30
Pal AK, Sengupta C (2019) Isolation of cadmium and lead tolerant plant growth promoting rhizobacteria: Lysinibacillusvarians and Pseudomonasputida from Indian agricultural soil. Soil Sedim Contam 28(7):601–629. https://doi.org/10.1080/15320383.2019.1637398
Patel M, Patel K, Al-Keridis LA, Alshammari N, Badraoui R, Elasbali AM, Al-Soud WA, Hassan MI, Yadav DK, Adnan M (2022) Cadmium-tolerant plant growth-promoting bacteria Curtobacterium oceanosedimentum improves growth attributes and strengthens antioxidant system in Chili (Capsicum frutescens). Sustainability 14:4335. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14074335
Pena LB, Barcia RA, Azpilicueta CE, Mendez AA, Gallego SM (2012) Oxidative post translational modifications of proteins related to cell cycle are involved in cadmium toxicity in wheat seedlings. Plant Sci 196:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2012.07.008
Piacentini D, Corpas FJ, D’Angeli S, Altamura MM, Falasca G (2020) Cadmium and arsenic-induced-stress differentially modulates Arabidopsis root architecture, peroxisome distribution, enzymatic activities and their nitric oxide content. Plant Physiol Biochem 148:312–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2020.01.026
Prasanna BM, Vasal SK, Kassahun B, Singh NN (2001) Quality protein maize. Curr Sci 81(10):1308–1319
Purkayastha GD, Mangar P, Saha A, Saha D (2018) Evaluation of the biocontrol efficacy of a Serratia marcescens strain indigenous to tea rhizosphere for the management of root rot disease in tea. PLoS ONE 13(2):e0191761. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0191761
Raja C, Selvam GS, Omine K (2009) Isolation, identification and characterization of heavy metal resistant bacteria from sewage. International joint symposium on Geodisaster prevention and geo-environment in Asia JS-Fukuoka, 205–209.
Rajkumar M, Ma Y, Freitas H (2008) Characterization of metal-resistant plant growth promoting Bacillus weihenstephanensis isolated from serpentine soil in Portugal. J Basic Microbiol 48:1–9
Rajkumari J, Choudhury Y, Bhattacharjee K, Pandey P (2021) Rhizodegradation of pyrene by a non-pathogenic klebsiella pneumoniae isolate applied with tagetes erecta l and changes in the rhizobacterial community. Front Microbiol 12:593023. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.593023
Reed MLE, Glick BR (2005) Growth of canola (Brassica napus) in the presence of plant growth-promoting bacteria and either copper or polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Can J Microbiol 51(12):1061–1069
Rehman M, Liua L, Bashirb S, Saleema MH, Chena C, Penga D, Siddiquec KHM (2019) Influence of rice straw biochar on growth, antioxidant capacity and copper uptake in ramie (Boehmeria nivea L.) grown as forage in aged copper contaminated soil. Plant Physiol Biochem 138:121–129
Rizvi A, Khan MS (2018) Heavy metal induced oxidative damage and root morphology alterations of maize (Zea mays L.) plants and stress mitigation by metal tolerant nitrogen fixing Azotobacter chroococcum. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 157:9–20
Rizwan M, Ali S, Adrees M, Rizvi H, Zia-ur-Rehman M, Hannan F, Qayyum MF, Hafeez F, Ok YS (2016) Cadmium stress in rice: toxic effects, tolerance mechanisms, and management: a critical review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(18):17859–17879
Romdhane L, Panozzo A, Radhouane L, Dal Cortivo C, Barion G, Vamerali T (2021) Characteristics and metal uptake of maize (Zea mays L.) under xtreme soil contamination. Agronomy 11:178. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11010178
Saha J, Sarkar M, Mandal P, Pal A (2022) Comparative study of heavy metal uptake and analysis of plant growth promotion potential of multiple heavy metal-resistant bacteria isolated from arable land. Curr Microbiol 79:7
Schulenburg H, Ewbank JJ (2004) Diversity and specificity in the interaction between Caenorhabditis elegans and the pathogen Serratia marcescens. BMC Evol Biol 2004(4):49. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-4-49
Shahzad A, Qin M, Elahie M, Naeem M, Bashir T, Yasmin H, Younas M, Areeb A, Irfan M, Billah M, Shakoor A, Zulfiqar S (2021) Bacillus pumilus induced tolerance of Maize (Zea mays L.) against Cadmium (Cd) stress. Sci Rep 11:17196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-96786-7
Sheng XF, Xia JJ (2006) Improvement of rape (Brassica napus) plant growth and cadmium uptake by cadmium-resistant bacteria. Chemosphere 64:1036–1042
Singh VP, Singh S, Kumar J, Prasad SM (2015) Investigating the roles of ascorbate-glutathione cycle and thiol metabolism in arsenate tolerance in ridged Luffa seedlings. Protoplasma 252:1217–1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-014-0753-6
Singh HN, Jayashree R, Narayan SL (2018) Heavy metal occurrence in the soil of high input tea agroecosystem of Southern Assam, Northeast India, Vegetos. Int J Plant Res 31(3):47–54. https://doi.org/10.5958/2229-4473.2018.00072.1
Singha P, Pandey P (2017) Glutathione and glutathione-S-transferase activity in Jatropha curcas in association with pyrene degrader Pseudomonas aeruginosa PDB1 in rhizosphere, for alleviation of stress induced by polyaromatic hydrocarbon for effective rhizoremediation L. Ecol Eng 102:422–432
Singha LP, Pandey P (2021) Rhizosphere assisted bioengineering approaches for the mitigation of etroleum hydrocarbons contamination in soil. Crit Rev Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/07388551.2021.1888066
Thakare M, Sarma H, Datar S, Roy A, Pawar P, Gupta K, Pandit S, Prasad R (2021) Understanding the holistic approach to plant-microbe remediation technologies for removing heavy metals and radionuclides from soil. Curr Res Biotechnol 3:84–98
Toth G, Hermann T, Da Silva MR, Montanarella L (2016) Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the European Union with implications for food safety. Environ Int 88:299–309
Van Assche F, Clijsters H (1990) Effects of metals on enzyme in plants. Plant Cell Environ 13:195–206
Xu X, Cao X, Zhao L, Wang H, Yu H, Gao B (2013) Removal of Cu, Zn, and Cd from aqueous solutions by the dairy manure-derived biochar. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:358–368
Yaouba A, Tatsadjieu N, Jazet DP, Mbofung CM (2012) Inhibition of fungal development in maize grains under storage condition by essential oils. Int J Biosci 2(6):41–48
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64(6):991–997
Zhang L, Chang X, Li Z, He Q (2010) Selective solid-phase extraction using oxidized activated carbon modified with triethylenetetramine for preconcentration of metal ions. J Mol Struct 964:58–62
Zhou L, Zhang L, He Y, Liu F, Li M, Wang Z, Ji G (2014) Isolation and characterization of bacterial isolates for biological control of clubroot on Chinese cabbage. Eur J Plant Pathol 140:159–168. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0451-4
Acknowledgements
BB and PP acknowledge the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Govt. of India for financial support, RK acknowledges the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt. of India for DST-INSPIRE fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhuyan, B., Kotoky, R., Maheshwari, D.K. et al. Rhizoremediation of Cd-contaminated soil using Zea mays Sturt, with heavy metal resistant rhizobacteria that alleviate Cd-induced stress in plant. Environmental Sustainability 5, 375–387 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-022-00241-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42398-022-00241-w