Abstract
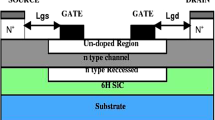
In this work, we have proposed a channel engineering technique for the performance enhancement of a short channel Laterally Diffused Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor (LDMOS) transistor for integrated low voltage power and RF applications. The technique involves a modification in the fabrication process flow of a conventional (CON) LDMOS to generate a device with a high graded doped channel. This device is labeled as Channel engineered (CE) LDMOS. Both devices are virtually fabricated in a process simulator with optimized implantation parameters. The impact of laterally grading the channel doping for a power device with a channel length of 0.1 µm is investigated through DC and AC device simulations. Important DC and AC performance parameters are extracted and compared with the CON device. It is seen that the CE device shows considerable improvement in transconductance (25.5%), saturated drain current (10%), output resistance (95.5%), intrinsic gain (143%), drain induced barrier lowering (53%), specific on-resistance (14%) and current on/off ratio without degrading the breakdown voltage. Small improvement is also observed in the transition frequency of the device.





















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Erlbacher, Lateral Power Transistors in Integrated Circuits (Springer, Cham, 2014)
F. van Rijs, in IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium, vol. 69 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/RWS.2008.4463430
S.J.C.H. Theeuwen, J.H. Qureshi, IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 60, 1755 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/TMTT.2012.2193141
S.J.C.H. Theeuwen, H. Mollee, R. Heeres, F. Van Rijs, in 13th European Microwave Integrated Circuits Conference (EuMIC), vol. 162, (2018) https://doi.org/10.23919/EuMIC.2018.8539904
M. Ahmed, X. Hue, M. Szymanowski, R. Uscola, J. Staudinger, J. Kitchen, IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 31, 881 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/LMWC.2021.3078699
M. Vigneau, M. Ercoli, S. Maroldt, Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 13, 543 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1017/S1759078721000131
T.V. Dinh et al., in: IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM), 25.2.1 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/IEDM19573.2019.8993471
Xu. Zhaozhao, D. Liu, Hu. Jun, F. Jin, X. Yang, W. Duan, W. Yue, Z. Fang, W. Qian, W. Kong, S. Zou, Microelectron. J. 88, 29 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mejo.2019.04.011
M. Zareiee, SILICON 11, 3011 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12633-019-0092-5
I. Cortes et al., Semicond. Sci. Technol. 23, 095024 (2008)
A.W. Ludikhuize, in: 12th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & ICs Proceedings, vol. 11, (2000). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPSD.2000.856763
M. Qiao, Y. Li, Z. Yuan, L. Liang, Z. Li, B. Zhang, IEEE Trans. Electron. Devices 16, 5605 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2020.3030872
M. Abouelatta-Ebrahim, A. Shaker, G.T. Sayah, C. Gontrand, A. Zekry, Ain Shams Eng. J. 6, 501 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2014.12.003
J. Wei, X. Luo, X. Shi, R. Tian, B. Zhang, Z. Li, in: IEEE 26th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices & IC's (ISPSD), vol. 127, (2014). https://doi.org/10.1109/ISPSD.2014.6855992
K. Hara, T. Kakegawa, S. Wada, T. Utsumi, T. Oda, in: 29th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and IC's (ISPSD), vol. 307, (2017). https://doi.org/10.23919/ISPSD.2017.7988965
S.Y. Chen et al., IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 69, 878 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2021.3131922
K.-Y. Na, K.-J. Baek, G.-W. Lee, Y.-S. Kim, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 60, 3515 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2013.2278974
M. Payal, Y. Singh, IETE Tech. Rev. 34, 246 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/02564602.2016.1166993
S. Chahar, G.M. Rather, H. Najeeb-ud-din, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 56, 585 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2018.2881918
F. Jie, W. Zhi-Gang, Z. Bo, L. Xiao-Rong, Chin. Phys. B 22, 048501 (2013)
K.-J. Baek, K.-Y. Na, Y.-S. Kim, Solid-State Electron. 100, 49 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sse.2014.07.004
X. Luo, Q. Tan, J. Wei, K. Zhou, G. Deng, Z. Li, Bo. Zhang, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 63, 2614 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2016.2555327
A. Saadat, M.L. Van De Put, H. Edwards, W.G. Vandenberghe, IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 8, 711 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2020.3008388
A. Saadat, M.L. Van de Put, H. Edwards, W.G. Vandenberghe, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 67, 4990 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2020.3019479
B. Yu, C.H. Wann, E.D. Nowak, K. Noda, C. Hu, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 44, 627 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1109/16.563368
D.G. Borse et al., IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 49, 1077 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2002.1003752
K. Narasimhulu, M.P. Desai, S.G. Narendra, V.R. Rao, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 51, 1416 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2004.833589
N.R. Mohapatra et al., in: Proceedings of 35th European Solid-State Device Research Conference, vol. 481, (2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/ESSDER.2005.1546689
K.N. Kaushal, N.R. Mohapatra, IEEE J. Electron Devices Soc. 9, 334 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1109/JEDS.2021.3059854
John Lin, United States Patent 6,900,101 B2, (2005)
Sentaurus User Guide, (Synopsys Inc., Mountain View, CA, USA 2019)
Y. Taur, T.H. Ning, Fundamentals of Modern VLSI Devices (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1998), pp.127–128
B.S. Kumar, M. Shrivastava, IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 65, 191 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1109/TED.2017.2777004
A.C.T Aarts, A. Tajic, MOS Model 20, Level 2002 (Philips Semiconductors PR-TN-2003/00301, 2004), https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/document?repid=rep1&type=pdf&doi=464292b7db9d1f5283ed73e58579c0e3520540b2
Integrated Power Devices and TCAD Simulation (CRC Press, 2014), pp. 224–225
B. Jayant Baliga, Fundamentals of Power Semiconductor Devices (Springer, US, 2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology for providing scholarship support during the research period.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fayaz, S., Hakim, Nud. & Rather, G.M. Applicability of Channel Doping Gradient in the Design of a Short Channel (0.1 µm) LDMOS Transistor for Integrated Power and RF Applications. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-024-00530-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-024-00530-7