Abstract
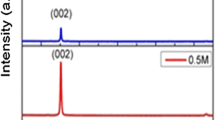
Zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films were deposited on glass substrates by using sol–gel spin coating technique. Zinc acetate dihydrate and 2-methoxyethanol were used as precursor with different molar concentrations, 0.2 M, 0.3 M and 0.6 M. The effect of precursor concentration on the structural and optical properties, transmission (T), reflection (R), optical bandgap (Eg), Urbach energy (EU), refractive index (n), extinction coefficient (k), single-oscillator energy (E0), dispersion energy (Ed), moments M−1 and M−3, dielectric constant (ε) and optical conductivity (σ), of the ZnO thin films was studied and investigated. Although, the transmittance, slightly, decreased and the reflectance increased, as the molar concentration increased, the measurements showed that all samples have high transparency and low reflectivity in the visible range which make them suitable for solar cells applications. It is also found that, as the molarity increased, the ZnO thin films exhibited lower Eg and EU and higher Ed, M−1 and M−3.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data of the research are available if the journal request.
References
H.S. Das, R. Das, P.K. Nandi, S. Biring, S.K. Maity, Influence of Ga-doped transparent conducting ZnO thin film for efficiency enhancement in organic light-emitting diode applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 127(4), 1–7 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04339-6
H. Liu, V. Avrutin, N. Izyumskaya, Ü. Özgr, H. Morkoç, Transparent conducting oxides for electrode applications in light emitting and absorbing devices. Superlattices Microstruct. 48(5), 458–484 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.spmi.2010.08.011
T.H. Seo et al., Graphene network on indium tin oxide nanodot nodes for transparent and current spreading electrode in InGaN/GaN light emitting diode. Appl. Phys. Lett. 98(25), 666–669 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3601462
Y. Wang et al., Solution-processed ITO thin-film transistors with doping of gallium oxide show high on-off ratios and work at 1 mV drain voltage. Appl. Phys. Lett. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5141140
T.E. Taouririt, A. Meftah, N. Sengouga, M. Adaika, S. Chala, A. Meftah, Effects of high- k gate dielectrics on the electrical performance and reliability of an amorphous indium–tin–zinc–oxide thin film transistor (a-ITZO TFT): an analytical survey. Nanoscale (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/C9NR03395E
Y.S. Shim et al., Transparent conducting oxide electrodes for novel metal oxide gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 160(1), 357–363 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2011.07.061
P.R. Ohodnicki, M. Andio, C. Wang, Optical gas sensing responses in transparent conducting oxides with large free carrier density. J. Appl. Phys. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4890011
S. Chala et al., Synthesis and characterization of ZnO thin film for modeling the effect of its defects on ZnO/Cu2O solar cell EQE. J. Nano- Electron. Phys. 13(1), 1–6 (2021). https://doi.org/10.21272/jnep.13(1).01009
M. García-Carrión et al., Hybrid solar cells with β- and γ- gallium oxide nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 261, 2–5 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.127088
F. Qin et al., Indium tin oxide (ITO)-free, top-illuminated, flexible perovskite solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 4(36), 14017–14024 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ta06657g
S. Chala, N. Sengouga, F. Yakuphanoglu, Modeling the effect of defects on the performance of an n-CdO/p-Si solar cell. Vacuum 120, 81–88 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vacuum.2015.05.019
A. Mallick, D. Basak, Revisiting the electrical and optical transmission properties of co-doped ZnO thin films as n-type TCOs. Prog. Mater. Sci. 96, 86–110 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2018.03.004
T.A. Harriman, Z. Bi, Q.X. Jia, D.A. Lucca, Frequency shifts of the E2high Raman mode due to residual stress in epitaxial ZnO thin films. Appl. Phys. Lett. 103(12), 121904 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4821222
N. Kumar, A. Dubey, B. Bahrami, S. Venkatesan, Q. Qiao, M. Kumar, Origin of high carrier mobility and low residual stress in RF superimposed DC sputtered Al doped ZnO thin film for next generation flexible devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 436, 477–485 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.11.274
C.-H. Chu, H.-W. Wu, J.-L. Huang, Effect of annealing temperature and atmosphere on aluminum-doped ZnO/Au/aluminum-doped ZnO thin film properties. Thin Solid Films 605, 121–128 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2015.11.043
J. Bruncko et al., Electrical and optical properties of thin ZnO shell layers on GaP nanorods grown by pulsed laser deposition. Thin Solid Films 725, 138634 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2021.138634
Y. Darma, S. Muhammady, Y.N. Hendri, E. Sustini, R. Widita, K. Takase, Tuning the point-defect evolution, optical transitions, and absorption edge of zinc oxide film by thermal exposure during molecular beam epitaxy growth. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 93, 50–58 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mssp.2018.12.030
G. Li, J. Zhang, X. Hou, Effects of excimer laser annealing on electrical properties of ZnO polycrystalline films deposited by sputtering. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 56(4), 906–910 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1002/mop
M. Godlewski et al., ZnO layers grown by atomic layer deposition: a new material for transparent conductive oxide. Thin Solid Films 518(4), 1145–1148 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2009.04.066
L.V. Podrezova, S. Porro, V. Cauda, M. Fontana, G. Cicero, Comparison between ZnO nanowires grown by chemical vapor deposition and hydrothermal synthesis. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 113(3), 623–632 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-013-7838-5
G. Sekicek, Z.B.B. Oral, Ca doped ZnO thin films by sol-gel dip coating method. AIP Conf. Proc. 2380(1), 40009 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0058237
N.S. Motlan, J.H. Panggabean, The Effect of Spin Coating Speed on Structural and Optical Properties of ZnO and ZnO/Dye Thin Films Synthesized by Sol-Gel Spin Coating Method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1819/1/012050
M.I. Khan, K.A. Bhatti, R. Qindeel, N. Alonizan, H.S. Althobaiti, Characterizations of multilayer ZnO thin films deposited by sol-gel spin coating technique. Results Phys. 7, 651–655 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2016.12.029
R. Amari, B. Deghfel, A. Mahroug, A.A. Mohamad, A. Boukhari, N. Selmi, Effects of Mn doping on the structural, morphological, electronic and optical properties of ZnO thin films by sol-gel spin coating method: an experimental and DFT+U study. Phys. B Condens. Matter (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physb.2019.411766
A. Ratkovich, R.L. Penn, Zinc oxide nanoparticle growth from homogenous solution: Influence of Zn:OH, water concentration, and surfactant additives. Mater. Res. Bull. 44(5), 993–998 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2008.11.012
K. Lin, P. Tsai, Parametric study on preparation and characterization of ZnO: Al films by sol-gel method for solar cells. Mater. Sci. Eng. B Solid State Mater. Adv. Technol. 139(1), 81–87 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mseb.2007.01.050
I.B. Mursal, Z. Jalil, Structural and optical properties of zinc oxide (ZnO) based thin films deposited by sol-gel spin coating method. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/1116/3/032020
M. Smirnov, C. Baban, G.I. Rusu, Structural and optical characteristics of spin-coated ZnO thin films. Appl. Surf. Sci. 256(8), 2405–2408 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.10.075
J.G. Lu et al., Structural, optical, and electrical properties of (Zn, Al)O films over a wide range of compositions. J. Appl. Phys. (2006). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2357638
S. Chala, N. Sengouga, F. Yakuphanoğlu, S. Rahmane, M. Bdirina, İ Karteri, Extraction of ZnO thin film parameters for modeling a ZnO/Si solar cell. Energy (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.ENERGY.2018.09.035
M. Baneto, A. Enesca, Y. Lare, K. Jondo, K. Napo, A. Duta, Effect of precursor concentration on structural, morphological and opto-electric properties of ZnO thin films prepared by spray pyrolysis. Ceram. Int. 40(6), 8397–8404 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.048
M. Salem, Z.Y. Alami, B. Bessais, A. Chahboun, M. Gaidi, Structural and optical properties of ZnO nanoparticles deposited on porous silicon for mc-Si passivation. J. Nanoparticle Res. 17(3), 1–20 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-015-2944-2
Z.Y. Alami, M. Salem, M. Gaidi, Effect of Zn concentration on structural and optical proprieties of ZNO thin films deposited by spray pyrolysis. Adv. Energy An Int. J. 2(4), 11–24 (2015). https://doi.org/10.5121/aeij.2015.2402
U. Chaitra, D. Kekuda, K.M. Rao, Dependence of solution molarity on structural, optical and electrical properties of spin coated ZnO thin films. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(7), 7614–7621 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-016-4745-5
J.I. Pankove, Optical Processes in Semiconductors (Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, 1971)
F. Yakuphanoglu, A. Cukurovali, I. Yilmaz, Refractive index and optical absorption properties of the complexes of a cyclobutane containing thiazolyl hydrazone ligand. Opt. Mater. (Amst) 27, 1363–1368 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2004.09.021
M.R. Islam, J. Podder, Optical properties of ZnO nano fiber thin films grown by spray pyrolysis of zinc acetate precursor. Cryst. Res. Technol. 44, 286–292 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1002/crat.200800326
S.H. Wemple, M. Didomenico, Theory of the elasto-optic effect in nonmetallic crystals. Phys. Rev. B 1(1), 193–202 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevB.1.193
M.A. Omar, Elementary Solid State Physics (Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, NY, 1993)
N.F. Mott, E.A. Davis, Electronic Processes in Non-Crystalline Materials (Clarendon Press, NY, 1979)
Acknowledgements
Slimane Chala would like to thank the Laboratory of Metallic and Semiconducting Materials (LMSM), University of Biskra, and the Algerian General Directorate of Scientific Research and Technological Development (DGRSDT) for their scientific and academic support.
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
This manuscript has not been published and is not under consideration for publication elsewhere.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chala, S., Bdirina, M., Elbar, M. et al. Dependence of Structural and Optical Properties of ZnO Thin Films Grown by Sol–Gel Spin-Coating Technique on Solution Molarity. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 23, 544–551 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-022-00386-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-022-00386-9