Abstract
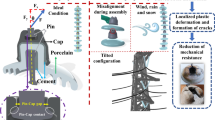
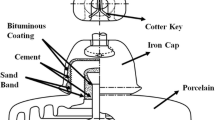
Corrosion of porcelain insulators has become a consequential threat to the secure and steady performance of power utilities. The losses due to corrosion have been calculated to be approximately 2–5% of the gross national product of any country. Under the influence of various contaminated environment, space between lower surface of iron cap and porcelain surface bridged by water which supports corrosion in iron cap and pin because of electrolytic process. Investigations validate corrosion found within metal part of insulators can worsen the bond between metal part and other accessories surrounding it and degrade its electrical and mechanical characteristics. These issues can be suppressed partially by utilizing various approaches such as washing and greasing of insulators, utilizing corrosion resistant metals and nonmetallic pins, zinc sleeve concept and U-shaped zinc ring etc. This paper highlights principle of corrosion mechanism especially focusing on corrosion occurs in metal part of insulators, causes of corrosion, dominance of pin and iron cap corrosion on mechanical and electrical characteristics of insulators. Furthermore, various approaches for suppression of corrosion in metal part of suspension insulators have been reviewed.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. Zhang, Yu. Yongqing, G. Li, J. Fan, S. Zhiyi, L. Jiayu, B. Li, Proc. CSEE 27, 7 (2007)
T. Taniguchi, M. Watanabe, Y. Watanabe, IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 6, 3 (1991)
K. Naito, K. Sakanishi, Y. Suzuki, M. Ito, Trans. IEE Jpn. 100, 9 (1980)
J.J. Taylor, A.D. Lantz Jr., CIGRE 211, 7 (1960)
Visual Inspection of Porcelain and Glass Disc Insulators, Project 3002005628, Electric Power Research. Institute Report, November 2015
L. Luo, L. Wang, H. Mei, Z. Guan, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23, 1 (2016)
V.I. Galanov, L.A. Koshcheev, V.L. Dimitrev, Research center of HVDC transmission technology, the former Soviet Union
A.W. Bardeen, J.M. Sheadel, A.I.E.E. Trans, Power Apparatus Syst. 3, 491–501 (1956)
X. Jiang, B. Dong, H. Qin, F. Yin, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 20, 2 (2013)
K.C. Holte, D.E. Alexander, D.M. Baker, IEEE Trans. Power Apparatus Syst. 98, 5 (1979)
I.M. Crabtree, K.J. Mackey, K. Kito, IEEE Trans. Power Apparatus Syst. 3, 645–654 (1985)
K. Kito, S. Kosaka, K. Sakanishi, NGK Rev. 43, 21–28 (1982)
L. Luo, L. Wang, Z. Guan, Electrical Insulation Conference (IEEE, 2014)
L. Luo, L. Wang, Z. Guan, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 22, 4 (2015)
L. Luo, L. Wang, Z. Guan, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 21, 6 (2014)
P. Bresesti, W.L. Kling, R.L. Hendriks, IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 22, 1 (2007)
C.A.O. Peixoto, L. Pargamin, IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 3, 2 (1988)
S.U. Zhiyi, Proc. CSEE 7, 6 (2007)
J.H. Mason, F.R. Silva, Fifth International Conference on Dielectric Materials, Measurements and Applications (IEEE, 1988)
S.M. Gubanski, IEEE Electr. Insul. Mag. 21, 6 (2005)
X. Wang, X. Man, X. Cao, Fifth International Conference on Properties & Applications of Dielectric Materials (IEEE, 2006)
J.S. Forrest, P.J. Lambeth, Inst. Electr. Eng. 107, 32 (1959)
R.B. Comizzoli, R.P. Frankenthal, Science 234, 4774 (1986)
Z. Yang, X. Jiang, Z. Zhang, D. Zhang, IEEE Trans. Dielectr. Electr. Insul. 23, 6 (2016)
T. Ito, Y. Morishima, IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 4, 422–424 (2009)
T. Ito, Y. Morishima, IEEJ Trans. Electr. Electron. Eng. 3, 313–316 (2008)
Grantw13, Electrical Insulator Flashover (Wikipedia, 2012), https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Electrical_insulator_flashover_from_volcanic_ash.jpg
J.W. Osenbach, Semicond. Sci. Technol. 11, 7 (1998)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanyal, S., Kim, T., Jeon, S. et al. Influence of Corrosion on Electrical and Mechanical Properties of Porcelain Suspension Insulators: An Overview. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 21, 543–549 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-020-00239-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42341-020-00239-3