Abstract
Background
Metformin hydrochloride is a common anti-diabetic medication, frequently prescribed in fixed-dose combinations for diabetes treatment. Various analytical methods, such as RP-HPLC and HPTLC, are employed to ensure the quality of these fixed-dose combinations. However, many of these methods utilized harmful organic solvents with potential environmental consequences. Consequently, there is a growing demand for greener and safer chromatographic methods. A recent concept of white analytical chemistry, emphasizes the development and assessment of chromatographic techniques based on validation, cost, time, and environmental sustainability.
Objectives
In line with this concept, an RP-HPLC method has been developed for the synchronous estimation of multiple fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) of metformin hydrochloride, utilizing low-toxic and economical solvents under a single chromatographic condition.
Methods
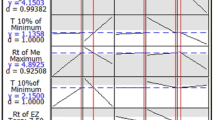
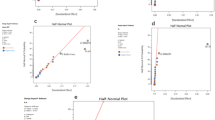
The RP-HPLC method was developed using the AQbD approach, which integrates analytical quality risk assessment and DoE principles. The goal was to reduce organic waste and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. The method was subsequently rigorously validated following ICH Q2 (R1) guidelines.
Results
The chromatographic separation of metformin and other drugs have been carried out using a Shim-Pack C18 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm, 5.0 µm) as stationary phase and the mobile phase, composed of ethanol: water (70 + 30, v/v) at pH 3.0 (adjusted using glacial acetic acid). The developed method was found to be specific, accurate, precise, robust and sensitive for estimation of multiple FDCs of metformin. The method was applied effectively to various metformin hydrochloride fixed-dose combinations, confirming label claim compliance. This method was also compared with published RP-HPLC methods, which were evaluated based on white analytical chemistry principles.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the proposed white analytical chemistry-driven RP-HPLC method offers a safe, cost-effective, and eco-friendly alternative to existing techniques for quality control and routine analysis of multiple fixed-dose combinations of metformin hydrochloride in the pharmaceutical industry.







Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of Data and Material
The data will be availed by corresponding author of manuscript on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ICH:
-
International council for harmonization
- RP-HPLC:
-
Reversed-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography
- IP:
-
Indian Pharmacopoeia
- PDE:
-
Permitted daily exposure
- WAC:
-
White analytical chemistry
- AQbD:
-
Analytical quality by design
- AQRM:
-
Analytical quality risk management
- DoE:
-
Design of experiments
- CPPs:
-
Critical procedure parameters
- CMPAs:
-
Critical method performance attributes
- GAC:
-
Green analytical chemistry
- QRM:
-
Quality risk management
- MET:
-
Metformin hydrochloride
- NATE:
-
Nateglinide
- DGZ:
-
Dapagliflozin
- GLB:
-
Glyburide
- REPA:
-
Repaglinide
- RSM:
-
Response surface modeling
- AGREE:
-
Analytical greenness
- GAPI:
-
Green analytical procedure index
- NEMI:
-
National environmental method index
- FDCs:
-
Fixed-dose combinations
- APIs:
-
Active pharmaceutical ingredients
References
Nowak MP, Weitecha-Posluszny R, Pawliszyn J (2021) White analytical chemistry: an approach to reconcile the principles of green analytical chemistry and functionality. Trends Anal Chem 138:116223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2021.116223
(2016) International Council for Harmonization Q3C (R6) guideline, impurities: a guideline for residual solvent. pp 1–40
Indian Pharmacopoeia 2018, Volume I, residual solvents, the Indian Pharmacopeia Commission, pp 987
Byrne FP, Jin S, Paggiola G, Petchey THM, Clark JH, Farmer TJ, Hunt AJ, McElroy CR, Sherwood J (2016) Tools and techniques for solvent selection: green solvent selection guides. Sustain Chem Process 4(7):1–24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40508-016-0051-z
Stojanovic J, Krmar J, Otasevic B, Protic A (2023) Resource management in HPLC: Unveiling a green face of pharmaceutical analysis. Arhiv Za Farmaciju 73(2):146–171. https://doi.org/10.5937/arhfarm73-43479
Kannaiah KP, Chanduluru HK, Obaydo RH, Lotfy HM, Erk N, Krishnan M, El Hamd MA (2023) Application of advanced environmentally benign assessment tools in determining ternary cardiovascular drug combination by RP-HPLC with analytical quality by design: application to stability indicating method evaluation. Sustain Chem Pharm 35:101197
Patel A, Shah SA (2021) DoE-based analytical quality risk management for enhanced AQbD approach to economical and eco-friendly RP-HPLC method for synchronous estimation of multiple FDC products of antihypertensive drugs. J Chromatogr Sci 60(8):786–799. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmab123
Mistry KY, Shah SA (2022) DoE-based analytical failure modes critical effect analysis (AFMCEA) to a multipurpose-RP-HPLC method for the estimation of multiple FDC products of metformin hydrochloride using an analytical quality by design approach. J AOAC Int 105(4):986–998. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsac025
Patel AS, Shah SA (2023) Simultaneous estimation of telmisartan, chlorthalidone, amlodipine besylate and atorvastatin by RP-HPLC method for synchronous assay of multiple FDC products using analytical FMCEA-based AQbD approach. J Chromatogr Sci 61(2):160–171. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmac030
Shahi A, Acharya A, Shah SA (2023) Chemometric and design of experiments based analytical quality by design and green chemistry approaches to the multipurpose high-pressure liquid chromatographic method for synchronous estimation of multiple fixed-dose combinations of azilsartan medoxomil. J AOAC Int 106(1):250–260. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsac086
Prajapati B, Pulusu V, Shah S (2023) Multivariate analysis and response surface modeling to green analytical chemistry-based RP-HPLC-PDA method for chromatographic analysis of vildagliptin and remogliflozin etabonate. J AOAC Int 106(03):601–612. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsad013
Jariwala H, Prajapati B, Salunkhe M, Pulusu V, Shah S (2023) Application of principal component analysis and DoE driven green analytical chemistry concept to liquid chromatographic method for estimation of co-formulated anti-hypertensive drugs. J AOAC Int. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsad016
Patel A, Shah SA (2022) DoE-based analytical-FMCEA for enhanced AQbD approach to MEER-RP-HPLC method for synchronous estimation of fifteen antihypertensive pharmaceutical dosage forms. J AOAC Int 105(1):34–45. https://doi.org/10.1093/jaoacint/qsab097
Drug data bank of metformin hydrochloride/dapagliflozin/nateglinide/glyburide/ repaglinide, https://go.drugbank.com/salts/DBSALT000114/DB06292/DB00731, DB01016/DB00912. Accessed 22 May 2023
Urooj A, Sundar PS, Vasanthi R, Raja MA, Dutt KR, Rao KNV, Ramana H (2017) Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of dapagliflozin and metformin in bulk and synthetic mixture. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(7):2139–2150
Edla S, Sundhar BS (2014) New analytical method development and validation for the simultaneous estimation of metformin and glibenclamide in bulk and tablet dosage form using RP-HPLC. Rasayan J Chem 7(1):55–63
De AK, Dey AK, Biswas A (2012) Simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride and glibenclamide by RP-HPLC method from combined tablet dosage form. Int J Sci Invent Today 1(2):98–105
Chengalva P, Parameswari A, Gingawar A (2016) Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for metformin hydrochloride and nateglinide in bulk and combined dosage forms. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 8(4):267–271
Soni LK, Narsinghani T, Jain M (2012) Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride and repaglinide in the tablet dosage form. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 35(3):385–392
Jain M, Sharma A, Soni LK, Kabra M (2013) Method development and simultaneous estimation of metformin hydrochloride and repaglinide in the tablet dosage form. Asian J Pharm Res Dev 1(3):108–114
Acknowledgements
The Maliba Pharmacy College’s Principal and the Uka Tarsadia University’s Provost are thanked by the authors for their enormous help in providing the necessary infrastructure and instrumentation equipment to carry out the research endeavor. Their contributions were crucial to the accomplishment of this investigation.
Funding
No funding support from any agency.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr PP—drafting, conceptualization, supervision, review. BR—methodology and writing. VSP—review, software analysis handling and drafting. AM—supervision and review support.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors of the manuscript already declared that they do not have any conflicts of interest for the publication of the manuscript.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Our research work does not include use of animal and human being. The manuscript has been solely submitted for publication in the future journal of pharmaceutical sciences. The authors of manuscript have declared that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Consent for Publication
Our research work does not include any human study. The manuscript entitles ‘Innovative RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Fixed-Dose Combinations of Anti-diabetic Drugs: Integrating Green, Economical, and Robust Approaches with Design of Experiments and White Analytical Chemistry’ has been solely submitted to Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prajapati, P., Rana, B., Pulusu, V.S. et al. Multipurpose RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Fixed-Dose Combinations of Anti-diabetic Drugs: Integrating Green, Economical, and Robust Approaches with Design of Experiments and White Analytical Chemistry. Chemistry Africa 7, 1385–1400 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00835-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42250-023-00835-9