Abstract
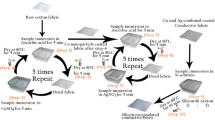
Metallizing insulating textile yarns can create flexibility to embed conductive patterns in textile products. However, fabricating a conductive yarn with keeping its inherent soft material’s properties in a scalable manufacturing process is very challenging. In this paper, we present a simple, yet effective multilayered deposition process of the coating conductive silver particle on cotton yarn to impart electrical conductivity. The process includes sequential dip coating and drying process of raw cotton yarn in the silver salt and reducing agent solutions. The result shows that repeating a similar process can enhance the electrical conductivity of the yarn and the resistance can get down up to 30 Ω/inch after 7 consecutive cycles of the coating process. The SEM image shows that the particle aggregates on top of each other and clusters around the fiber. The conductive fabric may withstand up to ten agitated washing cycles. The resistance of the sample steadily increased as a result of washing, bending, and elongation. The stiffness value of conductive fabric was greater while the air permeability value was lower compared to raw cotton fabric due to the deposition of metallic particles on the fabric surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Shahariar, H. Soewardiman, J.S. Jur, Fabrication and packaging of flexible and breathable patch antennas on textiles. SoutheastCon 2017 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1109/secon.2017.7925306
H. Shahariar, H. Soewardiman, C.A. Muchler, J.J. Adams, J.S. Jur, Porous textile antenna designs for improved wearability. Smart Mater. Struct. 27(4), 045008 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665x/aaaf91
H. Shahariar, J.S. Jur, Correlation of printing faults with the RF characteristics of coplanar waveguides (CPWs) printed on nonwoven textiles. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 273, 240–248 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2018.02.043
Y.L. Yang, M.C. Chuang, S.L. Lou, J. Wang, Thick-film textile-based amperometric sensors and biosensors. Analyst 135(6), 1230 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1039/b926339j
E. Lee, G. Cho, Polyurethane nanoweb-based textile sensors treated with single-walled carbon nanotubes and silver nanowire. Text. Res. J. 89(14), 2938–2951 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/0040517518805382
I. Kim, G. Cho, Polyurethane nanofiber strain sensors viain situpolymerization of polypyrrole and application to monitoring joint flexion. Smart Mater. Struct. 27(7), 075006 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-665x/aac0b2
E. Lee, I. Kim, H. Liu, G. Cho, Exploration of AgNW/PU nanoweb as ECG textile electrodes and comparison with Ag/AgCl electrodes. Fibers Polym. 18(9), 1749–1753 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-017-7410-6
R. Xu, A. Lei, C. Dahl-Petersen, K. Hansen, M. Guizzetti, K. Birkelund, E. Thomsen, O. Hansen, Screen printed PZT/PZT thick film bimorph MEMS cantilever device for vibration energy harvesting. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 188, 383–388 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2011.12.035
T. Linz, C. Kallmayer, R. Aschenbrenner, H. Reichl, Embroidering Electrical Interconnects with Conductive Yarn for the Integration of Flexible Electronic Modules into Fabric (Ninth IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC’05), 2005). https://doi.org/10.1109/iswc.2005.19
T.M. Brown, F. De Rossi, F. Di Giacomo, G. Mincuzzi, V. Zardetto, A. Reale, A. Di Carlo, Progress in flexible dye solar cell materials, processes and devices. J. Mater. Chem. A 2(28), 10788–10817 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta00902a
Y. Ouyang, W. Chappell, High frequency properties of electro-textiles for wearable antenna applications. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 56(2), 381–389 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1109/tap.2007.915435
J. Berzowska, M. Coelho, Kukkia and Vilkas: Kinetic Electronic Garments (Ninth IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC’05), n.d.). https://doi.org/10.1109/iswc.2005.29
K. Koski, E. Koski, T. Bjorninen, A.A. Babar, L. Ukkonen, L. Sydanheimo, Y. Rahmat-Samii, Practical Read Range Evaluation of Wearable Embroidered UHF RFID Tag (Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation, 2012). https://doi.org/10.1109/aps.2012.6349382
C. Mattmann, F. Clemens, G. Tröster, Sensor for measuring strain in textile. Sensors 8(6), 3719–3732 (2008). https://doi.org/10.3390/s8063719
J. Berzowska, Electronic textiles: wearable computers, reactive fashion, and soft computation. Textile 3(1), 58–75 (2005). https://doi.org/10.2752/147597505778052639
S. Coyle, D. Morris, K.T. Lau, D. Diamond, N. Moyna, Textile-Based Wearable Sensors for Assisting Sports Performance (2009 Sixth International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks, 2009). https://doi.org/10.1109/bsn.2009.57
A. Das, J. Krishnasamy, R. Alagirusamy, A. Basu, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of SS/PET hybrid yarn incorporated woven fabrics. Fibers Polym. 15(1), 169–174 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-014-0169-0
S. Lam Po Tang, G.K. Stylios, An overview of smart technologies for clothing design and engineering. Int. J. Cloth. Sci. Technol. 18(2), 108–128 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1108/09556220610645766
Y.A. Samad, Y. Li, S.M. Alhassan, K. Liao, Non-destroyable graphene cladding on a range of textile and other fibers and fiber mats. RSC Adv. 4(33), 16935–16938 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra01373e
S. Tsukada, H. Nakashima, K. Torimitsu, Conductive polymer combined silk fiber bundle for bioelectrical signal recording. PLoS One 7(4), e33689 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033689
H. Cheng, Z. Dong, C. Hu, Y. Zhao, Y. Hu, L. Qu, N. Chen, L. Dai, Textile electrodes woven by carbon nanotube–graphene hybrid fibers for flexible electrochemical capacitors. Nanoscale 5(8), 3428 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr00320e
L. An, X. Yang, C. Chang, On contact resistance of carbon nanotubes. Int. J. Theor. Appl. Nanotechnol. (2013). https://doi.org/10.11159/ijtan.2013.004
K. Nagashio, T. Nishimura, K. Kita, A. Toriumi, Systematic investigation of the intrinsic channel properties and contact resistance of monolayer and multilayer graphene field-effect transistor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 49(5R), 051304 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1143/jjap.49.051304
P. Xue, K. Park, X. Tao, W. Chen, X. Cheng, Electrically conductive yarns based on PVA/carbon nanotubes. Compos. Struct. 78(2), 271–277 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.10.016
K. Kawano, R. Pacios, D. Poplavskyy, J. Nelson, D.D. Bradley, J.R. Durrant, Degradation of organic solar cells due to air exposure. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 90(20), 3520–3530 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solmat.2006.06.041
D. Knittel, E. Schollmeyer, Electrically high-conductive textiles. Synth. Met. 159(14), 1433–1437 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2009.03.021
A.S. Barnard, Modelling of the reactivity and stability of carbon nanotubes under environmentally relevant conditions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 14(29), 10080 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cp40862g
A. Murray, E. Kisin, S. Leonard, S. Young, C. Kommineni, V. Kagan, V. Castranova, A. Shvedova, Oxidative stress and inflammatory response in dermal toxicity of single-walled carbon nanotubes. Toxicology 257(3), 161–171 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2008.12.023
H. Dong, D. Wang, G. Sun, J.P. Hinestroza, Assembly of metal nanoparticles on electrospun nylon 6 nanofibers by control of interfacial hydrogen-bonding interactions. Chem. Mater. 20(21), 6627–6632 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1021/cm801077p
B.H. Dong, J.P. Hinestroza, Metal nanoparticles on natural cellulose fibers: electrostatic assembly and in situ synthesis. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1(4), 797–803 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/am800225j
H. Liu, W.P. Goh, T.B. Norsten, Aqueous-based formation of gold nanoparticles on surface-modified cotton textiles. J. Mol. Eng. Mater. 1(1), 1250001 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1142/s2251237312500013
P. Kanninen, C. Johans, J. Merta, K. Kontturi, Influence of ligand structure on the stability and oxidation of copper nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 318(1), 88–95 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2007.09.069
M. Momtaz Islam, M.A. Reza, D.M. Ahmed, M.A.A. Mamun, H. Shahariar, Facile metallization technique of textiles for electronic textile applications. Funct. Textiles Cloth. 91–99 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-7721-1_8
M.A.A. Mamun, M.T. Islam, M.M. Islam, K. Sowrov, M.A. Hossain, D.M. Ahmed, H. Shahariar, Scalable process to develop durable conductive cotton fabric. Adv. Fiber Mater. 2(6), 291–301 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-020-00051-x
I. Perelshtein, G. Applerot, N. Perkas, G. Guibert, S. Mikhailov, A. Gedanken, Sonochemical coating of silver nanoparticles on textile fabrics (nylon, polyester and cotton) and their antibacterial activity. Nanotechnology 19(24), 245705 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/19/24/245705
C.H. Xue, J. Chen, W. Yin, S.T. Jia, J.Z. Ma, Superhydrophobic conductive textiles with antibacterial property by coating fibers with silver nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258(7), 2468–2472 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.10.074
N. Durán, P.D. Marcato, G.I.H. De Souza, O.L. Alves, E. Esposito, Antibacterial effect of silver nanoparticles produced by fungal process on textile fabrics and their effluent treatment. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 3(2), 203–208 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2007.022
S.T. Dubas, P. Kumlangdudsana, P. Potiyaraj, Layer-by-layer deposition of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles on textile fibers. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 289(1–3), 105–109 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2006.04.012
M. Rai, A. Yadav, A. Gade, Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 27(1), 76–83 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002
H. Sun, J. Chao, X. Zuo, S. Su, X. Liu, L. Yuwen, C. Fan, L. Wang, Gold nanoparticle-decorated MoS 2 nanosheets for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. RSC Adv. 4(52), 27625–27629 (2014)
J. Polte, T.T. Ahner, F. Delissen, S. Sokolov, F. Emmerling, A.F. Thünemann, R. Kraehnert, Mechanism of gold nanoparticle formation in the classical citrate synthesis method derived from coupled in situ XANES and SAXS evaluation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 132(4), 1296–1301 (2010)
A. Ambrosi, A. Morrin, M.R. Smyth, A.J. Killard, The application of conducting polymer nanoparticle electrodes to the sensing of ascorbic acid. Anal. Chim. Acta 609(1), 37–43 (2008)
S. Patra, D. Sen, A.K. Pandey, J. Bahadur, S. Mazumder, S.V. Ramagiri, J.R. Bellare, S.V. Roth, G. Santoro, S. Yu, A. Goswami, Time resolved growth of membrane stabilized silver NPs and their catalytic activity. RSC Adv. 4(103), 59379–59386 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ra10400e
D. Doganay, S. Coskun, S.P. Genlik, H.E. Unalan, Silver nanowire decorated heatable textiles. Nanotechnology 27(43), 435201 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1088/0957-4484/27/43/435201
A. Hebeish, M. El-Rafie, F. Abdel-Mohdy, E. Abdel-Halim, H. Emam, Carboxymethyl cellulose for green synthesis and stabilization of silver nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 82(3), 933–941 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2010.06.020
Z. Li, M. Li, Q. Fan, X. Qi, L. Qu, M. Tian, Smart-fabric-based supercapacitor with long-term durability and waterproof properties toward wearable applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 13(12), 14778–14785 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c02615
G. Hossain, I.Z. Hossain, G. Grabher, Piezoresistive smart-textile sensor for inventory management record. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 315, 112300 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2020.112300
H.L.O. Júnior, R.M. Neves, F.M. Monticeli, L. Dall Agnol, Smart fabric textiles: recent advances and challenges. Textiles 2(4), 582–605 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles2040034
S.M. Sharaf, Smart conductive textile. Adv. Funct. Protective Textiles 141–167 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-820257-9.00007-2
S. Faquiri, A. Kuijper, Performance Comparison of E-Textile Electrode Properties in a Capacitive Proximity Sensing Setting (Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, 2022). https://doi.org/10.1145/3529190.3529215
B.F. Iliescu, V.N. Mancasi, I.D. Ilie, I. Mancasi, B. Costachescu, D.I. Rotariu, Design principle and proofing of a new smart textile material that acts as a sensor for immobility in severe bed-confined patients. Sensors 23(5), 2573 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23052573
G. Mariani, J. Taborri, I. Mileti, G. Bagordo, E. Palermo, F. Patane, S. Rossi, Design and Characterization of a Smart Fabric Sensor to Recognize Human Intention for Robotic Applications (2022 IEEE International Workshop on Metrology for Industry 4.0 & IoT (MetroInd4.0&IoT), 2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/metroind4.0iot54413.2022.9831554
R.G. Ovejero, J.T. González, L.R. Izquierdo, J.A.G. Valencia, E.S. Hernández, V.R.Q. Leithardt, Influence of air temperature and relative humidity on the electrical behaviour of smart textiles. Adv. Intell. Syst. Comput. 244–253 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-14859-0_22
J.K. Kim, S. Park, H.S. Cho, J.H. Yang, S.H. Lee, J. Lee, Conditions for textile electrode sensors to monitor cardiac activity in daily life. J. Electrical Eng. Technol. 17(5), 3045–3055 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42835-022-01156-6
S. Veeralingam, A. Gandrothula, S. Badhulika, Tungsten oxysulfide nanoparticles interspersed nylon based e-textile as a low cost, wearable multifunctional platform for ultra-sensitive tactile sensing and breath sensing applications. Mater. Res. Bull. 160, 112133 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2022.112133
F. Alshabouna, H.S. Lee, G. Barandun, E. Tan, Y. Cotur, T. Asfour, L. Gonzalez-Macia, P. Coatsworth, E. Núnez-Bajo, J.S. Kim, F. Güder, PEDOT:PSS-modified cotton conductive thread for mass manufacturing of textile-based electrical wearable sensors by computerized embroidery. Mater. Today 59, 56–67 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mattod.2022.07.015
B. Zhao, Z. Dong, H. Cong, A wearable and fully-textile capacitive sensor based on flat-knitted spacing fabric for human motions detection. Sensors Actuators A Phys. 340, 113558 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2022.113558
Y. Pang, X. Xu, S. Chen, Y. Fang, X. Shi, Y. Deng, Z.L. Wang, C. Cao, Skin-inspired textile-based tactile sensors enable multifunctional sensing of wearables and soft robots. Nano Energy 96, 107137 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nanoen.2022.107137
J. Yin, J. Li, V.S. Reddy, D. Ji, S. Ramakrishna, L. Xu, Flexible textile-based sweat sensors for wearable applications. Biosensors 13(1), 127 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010127
M.A.A. Rumon, G. Cay, V. Ravichandran, A. Altekreeti, A. Gitelson-Kahn, N. Constant, D. Solanki, K. Mankodiya, Textile knitted stretch sensors for wearable health monitoring: design and performance evaluation. Biosensors 13(1), 34 (2022). https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010034
M. Wagih, A. Komolafe, A.S. Weddell, S. Beeby, Broadband compact substrate-independent textile wearable antenna for simultaneous near- and far-field wireless power transmission. IEEE Open J. Antennas Propag. 3, 398–411 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/ojap.2022.3167089
U. Pandey, P. Singh, R. Singh, Review on miniaturized flexible wearable antenna with SAR measurement for body area network. Mater. Today: Proc. 66, 3667–3674 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.07.344
N. Atanasov, G. Atanasova, B. Atanasov, M. Avramov, N. Hristov, Numerical and Experimental Evaluation of a Textile Wearable Antenna for on-body Communications (2022 13th National Conference With International Participation (ELECTRONICA), 2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/electronica55578.2022.9874421
A. Tsolis, S. Bakogianni, C. Angelaki, A.A. Alexandridis, A review of clothing components in the development of wearable textile antennas: design and experimental procedure. Sensors 23(6), 3289 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3390/s23063289
V. Jain, B.S. Dhaliwal, A. Kumar, A.K. Vats, S. Pattnaik, Experimental investigations on the effect of textile substrate nanomaterial coating on wearable antenna performance. Natl. Acad. Sci. Lett. (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40009-023-01238-7
M.M.H. Mahfuz, M.R. Islam, C.W. Park, E.A.A. Elsheikh, F.M. Suliman, M.H. Habaebi, N.A. Malek, N. Sakib, Wearable textile patch antenna: challenges and future directions. IEEE Access 10, 38406–38427 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2022.3161564
J. Xu, B. Xin, X. Du, C. Wang, Z. Chen, Y. Zheng, M. Zhou, Flexible, portable and heatable non-woven fabric with directional moisture transport functions and ultra-fast evaporation. RSC Adv. 10(46), 27512–27522 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1039/d0ra03867a
H. Souri, D. Bhattacharyya, Wool fabrics decorated with carbon-based conductive ink for low-voltage heaters. Mater. Adv. 3(9), 3952–3960 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1039/d1ma00981h
N. Maheshwari, M. Abd-Ellah, I.A. Goldthorpe, Transfer printing of silver nanowire conductive ink for e-textile applications. Flexible and Printed. Electronics 4(2), 025005 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1088/2058-8585/ab2543
M.T. Islam, M.A.A. Mamun, M.T. Hasan, H. Shahariar, Scalable coating process of AgNPs-silicone on cotton fabric for developing hydrophobic and antimicrobial properties. J. Coat. Technol. Res. 18(3), 887–898 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-020-00451-z
N. Jarach, D. Meridor, M. Buzhor, D. Raichman, H. Dodiuk, S. Kenig, E. Amir, Hybrid antibacterial and electro-conductive coating for textiles based on cationic conjugated polymer. Polymers 12(7), 1517 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym12071517
X. Yan, C.R. Bowen, C. Yuan, Z. Hao, M. Pan, Carbon fibre based flexible piezoresistive composites to empower inherent sensing capabilities for soft actuators. Soft Matter 15(40), 8001–8011 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9sm01046g
Y. Wang, J. Guo, D. Xu, Z. Gu, Y. Zhao, Micro-/nano-structured flexible electronics for biomedical applications. Biomed. Tech. 2, 1–14 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmt.2022.11.013
D. Zhang, R. Yin, Y. Zheng, Q. Li, H. Liu, C. Liu, C. Shen, Multifunctional MXene/CNTs based flexible electronic textile with excellent strain sensing, electromagnetic interference shielding and Joule heating performances. Chem. Eng. J. 438, 135587 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.135587
X. Sun, J.H. Fu, C. Teng, M. Zhang, T. Liu, M. Guo, P. Qin, F. Zhan, Y. Ren, H. Zhao, L. Wang, J. Liu, Superhydrophobic E-textile with an Ag-EGaIn conductive layer for motion detection and electromagnetic interference shielding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 14(29), 33650–33661 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c09554
V.S. Siavashani, N.C. Gursoy, M. Montazer, P. Altay, Stretchable electromagnetic interference shielding textile using conductive polymers and metal nanoparticles. Fibers Polym. 23(10), 2748–2759 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-022-4492-6
D. Yao, Z. Tang, Z. Liang, L. Zhang, Q.J. Sun, J. Fan, G. Zhong, Q.X. Liu, Y.P. Jiang, X.G. Tang, V.A. Roy, J. Ouyang, Adhesive, multifunctional, and wearable electronics based on MXene-coated textile for personal heating systems, electromagnetic interference shielding, and pressure sensing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 630, 23–33 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2022.09.003
S. Verma, M. Dhangar, S. Paul, K. Chaturvedi, M.A. Khan, A.K. Srivastava, Recent advances for fabricating smart electromagnetic interference shielding textile: a comprehensive review. Electron. Mater. Lett. 18(4), 331–344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13391-022-00344-w
X. Peng, X. Meng, B. Yu, H. Chen, Z. Liu, M. Tang, Y. Zheng, Y. Sun, W. Lu, Y. Dai, Graphitized and flexible porous textile updated from waste cotton for wearable electromagnetic interference shielding. Carbon 207, 144–153 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2023.02.044
M.Z. Islam, H. Deb, M.K. Hasan, N.A. Khoso, M.K. Hossain, Y. Wentong, X. Qi, Y. Dong, Y. Zhu, Y. Fu, A facile one-pot scalable production of super electromagnetic shielding conductive cotton fabric by hierarchical graphene-composites. J. Mater. Sci. 57(32), 15451–15463 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-022-07411-5
Acknowledgements
The Bangladesh University of Textiles in Dhaka, Bangladesh, has been recognized by the writers as a supporter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Islam, M.M., Ahmed, D.M. & Shahariar, H. An approach to develop electrically conductive cotton yarn by facile multilayered deposition of silver particles. emergent mater. 6, 1027–1036 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00505-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00505-z