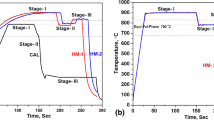
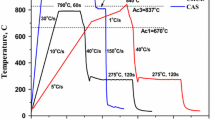
Abstract
The conventional melting methods were used to obtain in situ TiC particle-reinforced dual-phase steel, followed by hot rolling and heat treatment processes. The aim was to investigate the effect of TiC particles on the fracture behavior of dual-phase steel at different annealing temperatures, by analyzing the microstructure and tensile behavior of the multiscale TiC particle-reinforced dual-phase steel. The results showed that TiC particles precipitated in the as-cast microstructure of dual-phase steel were distributed along the grain boundaries. During hot rolling, the grain boundary-like morphology of the micron-sized TiC particles was disrupted, and the particles became more refined and evenly distributed in the matrix. The tensile tests revealed that the strength of the TiC particle-reinforced dual-phase steel increased with increasing martensite content, while the elongation decreased. These results were similar to those of conventional steel. The addition of 1 vol.% multiscale TiC particles improved the strength of the dual-phase steel but did not affect elongation of the steel. Cracks and holes were primarily concentrated around the TiC particles rather than at the interface of martensite and ferrite. The main causes of crack sprouting were TiC particle interface cracking and TiC particle internal fragmentation. Overall, the study demonstrated the potential of multiscale TiC particle-reinforced dual-phase steel as a strong and tough material. The refined distribution of TiC particles in the matrix improved the strength of the material without compromising its elongation. The results also highlighted the importance of careful selection of reinforcement particles to avoid detrimental effects on the fracture behavior of the material.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.O. Rocha, T.M.F. Melo, E.V. Pereloma, D.B. Santos, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 391 (2005) 296–304.
N. Peranio, Y.J. Li, F. Roters, D. Raabe, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 527 (2010) 4161–4168.
X. Zheng, H. Ghassemi-Armaki, A. Srivastava, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 774 (2020) 138924.
M. Asadi, B.C. De Cooman, H. Palkowski, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 538 (2012) 42–52.
S. Sun, M. Pugh, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 335 (2002) 298–308.
J. Liao, J.A. Sousa, A.B. Lopes, X. Xue, F. Barlat, A.B. Pereira, Int. J. Plast. 93 (2017) 269–290.
Y.L. Kang, Q.H. Han, X.M. Zhao, M.H. Cai, Mater. Des. 44 (2013) 331–339.
C.N. Li, G. Yuan, F.Q. Ji, D.S. Ren, G.D. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 665 (2016) 98–107.
J. Wang, W. Li, X. Zhu, L. Zhang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 832 (2022) 142424.
K.J. Kim, C.G. Lee, S. Lee, Scripta Mater. 38 (1997) 27–32.
A. Bag, K.K. Ray, E.S. Dwarakadasa, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30 (1999) 1193–1202.
D. Das, P.P. Chattopadhyay, J. Mater. Sci. 44 (2009) 2957–2965.
H. Ashrafi, M. Shamanian, R. Emadi, N. Saeidi, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 680 (2017) 197–202.
H.S. Wang, G. Yuan, J. Kang, G.M. Cao, C.G. Li, R.D.K. Misra, G.D. Wang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 703 (2017) 486–495.
M.P. Rao, V.S. Sarma, S. Sankaran, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45 (2014) 5313–5317.
K. Park, M. Nishiyama, N. Nakada, T. Tsuchiyama, S. Takaki, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 604 (2014) 135–141.
Q. Wang, X. Deng, L. Huang, T. Fu, Y. Jia, C. Li, Z. Wang, ISIJ Int. 61 (2021) 985–992.
L. Huang, X. Deng, Y. Jia, C. Li, Z. Wang, Wear 410–411 (2018) 119–126.
L. Huang, X. Deng, C. Li, Y. Jia, Q. Wang, Z. Wang, Wear 434–435 (2019) 202971.
Y.I. Son, Y.K. Lee, K.T. Park, C.S. Lee, D.H. Shin, Acta Mater. 53 (2005) 3125–3134.
H. Xiong, Z. Li, K. Zhou, Ceram. Int. 42 (2016) 6858–6867.
H. Ashrafi, S. Sadeghzade, R. Emadi, M. Shamanian, Steel Res. Int. 88 (2017) 1600213.
H. Mirzadeh, M. Alibeyki, M. Najafi, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 48 (2017) 4565–4573.
F. Jamei, H. Mirzadeh, M. Zamani, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 750 (2019) 125–131.
Q.H. Han, Y.L. Kang, X.M. Zhao, C. Lu, L.F. Gao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 5, 52–58.
S. Wang, Y. Li, J. Wang, T. Luo, K. Zheng, Z. Zheng, J. Long, Y. Lin, Mater. Chem. Phys. 287 (2022) 126376.
H.W. Yen, C.Y. Chen, T.Y. Wang, C.Y. Huang, J.R. Yang, Mater. Sci. Technol. 26 (2010) 421–430.
C.L. Tu, X.D. Sun, J. Li, H.G. Zhu, X.D. Li, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28 (2021) 1471–1480.
C. Zhao, H. Zhu, Z. Xie, Intermetallics 140 (2022) 107398.
F. Ma, J. Zhou, P. Liu, W. Li, X. Liu, D. Pan, W. Lu, D. Zhang, L. Wu, X. Wei, Mater. Charact. 127 (2017) 27–34.
Z. Zhang, D. Chen, Scripta Mater. 54 (2006) 1321–1326.
J.H. Zhou, Y.F. Shen, Y.Y. Hong, W.Y. Xue, R.D.K. Misra, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 769 (2020) 138471.
T. Lu, C. Chen, P. Li, C. Zhang, W. Han, Y. Zhou, C. Suryanarayana, Z. Guo, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 799 (2021) 140161.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge support from the National Basic Research Program, China (No. 2022YFB3705300), National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 52274380, 51874089, and U1960112), and LiaoNing Revitalization Talents Program (XLYC2007030).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Xiang-tao Deng is the youth editorial board member for Journal of Iron and Steel Research International and was not involved in the editorial review or the decision to publish this article. The authors declare there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, Y., Deng, Xt., Wang, Q. et al. Synergistic effects of multiscale TiC and dual-phase structure on tensile properties of particle-reinforced steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 31, 1232–1245 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01110-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01110-4