Abstract
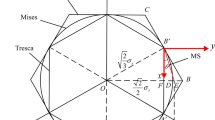
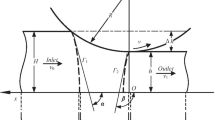
For the sake of solving the problem that it is difficult to be integrated for the Mises specific plastic power due to its nonlinearity, a new linear criterion, named the globally optimal approximation criterion, is constructed by the polygonal approximation to the Mises circle. The new criterion is proved to be the linear function of the principal stress components σ1, σ2 and σ3 and the trajectory of it on the π-plane is a non-equiangular but equilateral dodecagon intersecting the Mises circle. The theoretical results of the current criterion described by the Lode stress parameters are in excellent accordance with the experimental results. Meanwhile, according to the trend that the metallic flow velocity between rollers aggrandizes gradually from the inlet to the outlet during the hot rolling of a thick plate, a biomimetic velocity field is proposed in which the horizontal velocity component fits the egg-circular curve distribution. The velocity field and its simulated results agree quite well. Subsequently, using the determined linear criterion, energy analysis of the constructed velocity field is utilized to obtain the interior deformation power, while the vector decomposition approach is utilized to obtain the frictional power and shear power. On this basis, the overall power is obtained and the analytical solutions are generated for the rolling torque, rolling force and the coefficient of the stress state under different egg curves by minimizing the neutral angle. Furthermore, the parameter optimization of the characteristic parameter ρ which affects the slope of the egg-circular curve is carried out and the best egg-circular curve which can minimize the energy consumption is determined. The best agreement between the theoretical and observed values of rolling force and rolling torque is under this curve, and the mean relative errors of the rolling torque and rolling force are no more than 2.93%, while the maximum error is no more than 8.35%.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Tresca, Comptes-rendus de l’académie des sciences 59 (1864) 754–758.
R.V. Mises, N. von der Gesellschaft der Wissenschaften zu Göttingen, Mathematisch-Physikalische Klasse 1913 (1913) 582–592.
R.V. Mises, Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 8 (1928) 161–185.
M.H. Yu, L.N. He, L.Y. Song, Sci. Sin. 28 (1985) 1174–1183.
X.R. Hu, M.H. Yu, Engineering Mechanics 23 (2006) No. 4, 6–11.
L. Deng, S.H. Zhang, S.H. Qin, X.Y. Liu, Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics 6 (2021) 763–769.
X.R. Jiang, S.H. Zhang, C.J. Wang, Y.X. Li, W.H. Tian, J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 52 (2020) No. 56, 41–48.
S.E. Lundberg, T. Gustafsson, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2 (1993) 873–879.
Y.M. Hwang, H.H. Hsu, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 88 (1999) 97–104.
J.L. Zhang, Z.S. Cui, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 18 (2011) No. 7, 20–27.
J.Z. Cao, D.W. Zhao, S.H. Zhang, W. Peng, S.Z. Chen, D.H. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 (2014) 295–299.
S. Seuren, J. Seitz, A. Krämer, M. Bambach, G. Hirt, Prod. Eng. 8 (2014) 17–24.
G.S. Ma, Y.M. Liu, W. Peng, F.C. Yin, J.G. Ding, D.W. Zhao, H.S. Di, D.H. Zhang, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 39 (2017) 523–530.
D.H. Zhang, Y.M. Liu, J. Sun, D.W. Zhao, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 84 (2016) 843–850.
Y.F. Zhang, H.S. Di, X. Li, D.W. Zhao, D.H. Zhang, Journal of Plasticity Engineering 27 (2020) 153–158.
Y.Y. Wei, T. Zhen, J.B. Huang, H. Li, P. Wang, L.Y. Jiang, Heavy Machinery (2021) No. 1, 52–56.
L.Y. Jiang, T. Zhen, J.B. Huang, Y.Y. Wei, Journal of Plasticity Engineering 28 (2021) 249–256.
Z.H. Wang, Y.M. Liu, T. Wang, J. Sun, D.H. Zhang, Iron and Steel 57 (2022) No. 9, 95–102.
L. Deng, S.H. Zhang, J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 53 (2021) No. 8, 116–124.
S.H. Zhang, S.W. Gao, G.J. Wu, J. Cao, D.W. Zhao, J. Manuf. Process. 28 (2017) 243–252.
W. Lode, Z. Phys. 36 (1926) 913–939.
J.M. Lessells, C.W. MacGregor, J. Frankl. Inst. 230 (1940) 163–181.
W.A. Maxey, in: Proceedings of the Fifth Symposium on Line Pipe Research, Houston, Texas, USA, 1974, pp. 20–22.
P.M. Naghdi, F. Essenburg, W. Koff, J. Appl. Mech. 25 (1958) 201–209.
Z.L. Liu, Research on nonlinear stability of egg circular curved single-layer reticulated shell, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2018.
S.H. Zhang, L. Deng, W.H. Tian, L.Z. Che, Y. Li, Comput. Math. Appl. 109 (2022) 58–73.
J.N. Harris, Mechanical working of metals: theory and practice, Elsevier, Amsterdam, USA, 2014.
S.H. Zhang, W.H. Tian, L. Deng, J. Braz. Soc. Mech. Sci. Eng. 43 (2021) 1–11.
S.H. Zhang, Linearization of yield criterion and its engineering applications, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2018.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to extend their thanks to the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 52074187, U1960105 and 52274388) and the Undergraduate Training Program for Innovation and Entrepreneurship, Soochow University, China (Grant No. 202210285158Y). The valuable suggestions from reviewers are also gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Sh., Zhang, Y., Tian, Wh. et al. An analytical model of hot rolling force for a thick plate by combining globally optimal approximation yield criterion and egg-circular velocity field. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 31, 647–659 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01099-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-023-01099-w