Abstract
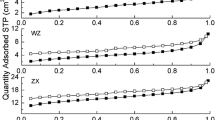
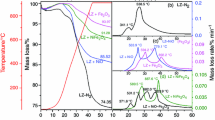
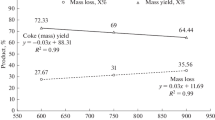
Substantial semi-coke has been produced through the industrialized low-temperature pyrolysis process, which has great potential as an alternative fuel for pulverized coal injection (PCI) and iron ore sintering. X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscope, and thermal analysis were used to compare the carbon chemical structure and combustion reactivity of semi-coke, pulverized coal, and coke breeze. The results show that the average volatile matter content in 46 types of semi-cokes is 8.94 wt.%. The fluctuation range of the characteristic parameters of the semi-coke chemical structure is d002 = (0.352–0.379) nm and AD1/AG = (2.51–7.92), while the fluctuation range of the characteristic parameters of pulverized coal is d002 = (0.348–0.373) nm and AD1/AG = (1.71–9.03) (where d002 means the interlayer spacing between the aromatic planes, and AD1/AG is an index that characterizes the degree of disorder of the char structure through the area ratio of the defect peak band D1 to the perfect graphite peak band G); the overlap between these ranges is relatively high. Contrarily, the fluctuation range of the characteristic parameters of coke breeze is d002 = (0.343–0.350) nm and AD1/AG = (0.75–2.51), which is markedly different from that of semi-coke. Semi-coke combustion reactivity is close to that of pulverized coal, but considerably better than that of coke breeze. In terms of chemical structure and combustion reactivity, semi-coke can be used as an alternative fuel for PCI; however, when used for sintering alternative fuel, matching of the heat supply and demand in the later sintering stage must be scrupulously analyzed.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.M. Sun, X.J. Ning, J.L. Zhang, K.J. Li, G.W. Wang, H.Y. Wang, China Metallurgy 28 (2018) No. 3, 1–8.
J.H. Kim, R.G. Kim, G.B. Kim, C.H. Jeon, Exp. Thermal Fluid Sci. 79 (2016) 266–274.
L.M. Lu, V. Sahajwalla, D. Harris, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 32 (2001) 811–820.
Y. Wang, Z.L. Zhang, Coal Quality Technol. (2018) No. 2, 1–5.
A.D.S. Machado, A.S. Mexias, A.C.F. Vilela, E. Osorio, Fuel 114 (2013) 224–228.
J.Y. He, C. Zou, J.X. Zhao, C. Ma, X.R. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 26 (2019) 1273–1284.
C.Y. Tsai, A.W. Scaroni, Fuel 66 (1987) 1400–1406.
B. Wang, L. Sun, S. Su, J. Xiang, S. Hu, H. Fei, Energy Fuels 26 (2012) 1565–1574.
C.D. Sheng, Fuel 86 (2007) 2316–2324.
B. Tian, Y.Y. Qiao, Y.Y. Tian, Q. Liu, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 121 (2016) 376–386.
C. Ma, C. Zou, J.X. Zhao, R.M. Shi, X.M. Li, J.Y. He, X.R. Zhang, Energy Fuels 33 (2019) 6098–6112.
Y. Liu, X.F. He, F.S. Yang, Y.G. Zhang, X.B. Ren, A.N. Zhou, J. China Coal Soc. 40 (2015) 497–504.
X.Y. Zhang, B.X. Zhou, D.H. An, L. Cui, Y. Zheng, Y. Dong, J. China Coal Soc. 44 (2019) 604–610.
A. Yoshida, Y. Kaburagi, Y. Hishiyama, Carbon 44 (2006) 2333–2335.
C. Zou, J.Y. He, J.X. Zhao, X.M. Li, R.M. Shi, C. Ma, Y. Kang, X.R. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50 (2019) 2304–2318.
G. Rantitsch, A. Bhattacharyya, J. Schenk, N.K. Lünsdorf, Int. J. Coal Geol. 130 (2014) 1–7.
H. Takagi, K. Maruyama, N. Yoshizawa, Y. Yamada, Y. Sato, Fuel 83 (2004) 2427–2433.
M.F. Li, F.G. Zeng, F.H. Qi, B.L. Sun, Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis 29 (2009) 2446–2449.
X.H. Liu, Y. Zheng, Z.H. Liu, H.R. Ding, X.H. Huang, C.G. Zheng, Fuel 157 (2015) 97–106.
Q.H. Wang, R. Zhang, Z.Y. Luo, M.X. Fang, K.F. Cen, Energy Technol. 4 (2016) 543–550.
H.J. Seong, A.L. Boehman, Energy Fuels 27 (2013) 1613–1624.
B. Hu, C. Zou, J.X. Zhao, C. Ma, J.Y. He, X.M. Li, Coal Conversion 41 (2018) No. 1, 1–6.
L. He, W.Z. Shang, J.L. Liu, J.L. Hou, Y. Ma, S.Y. Li, Clean Coal Technol. 21 (2015) No. 6, 59–62.
Q. Xie, D.C. Liang, M. Tian, J.T. Dang, J.C. Liu, M.S. Yang, J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 43 (2015) 798–805.
X.J. Ning, W. Liang, J.L. Zhang, G.W. Wang, Y.J. Li, C.H. Jiang, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 26 (2019) 973–982.
Q.L. Shi, B.T. Qin, Q. Bi, B. Qu, Fuel 226 (2018) 307–315.
S. Dong, N. Paterson, S.G. Kazarian, D.R. Dugwell, R. Kandiyoti, Energy Fuels 21 (2007) 3446–3454.
G.W. Liu, P. Dong, Y.F. Han, R.S. Bie, J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 43 (2011) No. 1, 104–108.
R.H. Essenhigh, M.K. Misra, S.W. Shaw, Combust. Flame 77 (1989) 3–30.
X.N. Zhao, L. Ding, Q.H. Guo, B. Dong, D.H. Wu, Clean Coal Technol. 22 (2016) No. 6, 52–55.
W.K. Zhu, W.L. Song, W.G. Lin, Energy Fuels 22 (2008) 2482–2487.
M. Zhong, S.Q. Gao, Z.K. Zhang, J.R. Yue, G.W. Xu, Chin. J. Process Eng. 12 (2012) 231–238.
V. Suresh Babu, M.S. Seehra, Carbon 34 (1996) 1259–1265.
W. Huo, S.Q. Zhong, Coal Conversion 40 (2017) No. 1, 8–12.
C. Zou, Y. She, R.M. Shi, Fuel Process. Technol. 190 (2019) 1–12.
Y.M. Yang, J.Z. Liu, J. Wang, J. Cheng, Z.H. Wang, K.F. Cen, Energy Fuels 32 (2018) 1297–1308.
X.R. Zhang, C. Zou, J.X. Zhao, C. Ma, B. Hu, S.W. Liu, J.Y. He, J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 47 (2019) 1288–1297.
J.G. Zhang, Z.G. Sun, Q. Guo, X.J. Wang, G.S. Yu, H.F. Liu, F.C. Wang, J. Fuel Chem. Technol. 45 (2017) 129–137.
D.D. Liu, J.H. Gao, S.H. Wu, Y.K. Qin, J. Harbin Inst. Technol. 48 (2016) No. 7, 39–45.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51374166 and 51704224) for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, Jy., Zou, C., Zhao, Jx. et al. Comparison of semi-coke with traditional pulverized coal injection and iron ore sintering fuels based on chemical structure and combustion behavior. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29, 725–740 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00726-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00726-8