Abstract
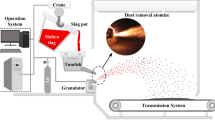
To solve the problem of difficult utilization of steel slag, the liquid steel slag was modified and the air-quenching granulation process was carried out to make steel slag into a value-added end product: air-quenching granulated steel slag. The granulated slag was tested to analyze the variation rule of slag properties under different modification conditions. Based on the phase diagram of CaO–Si2O–FeO–MgO–Al2O3 slag system, the feasibility of blast furnace (BF) slag as modifier was determined. When the addition of BF slag was increased from 0% to 35%, following results were obtained. The slag fluidity was improved, and the air-quenching temperature range was expanded. Then, the yield of air-quenched steel slag increased, while the granulation rate, the degree of sphericity, the compactness were decreased. Furthermore, the air-quenching granulation process could substantially improve the stability and the amorphous content of steel slag. The maximum removal rate of free CaO was above 80% and the amorphous content was up to 95%. Taking the factors of yield and properties of granulated steel slag into full consideration, the optimum proportion of BF slag is around 15%.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y. Jiang, T.C. Ling, C.J. Shi, S.Y. Pan, Resour. Conserv. Recy. 136 (2018) 187–197.
H.B. Dong, Y. Liu, L.J. Wang, X.C. Li, Z.L. Tian, Y.X. Huang, C. McDonald, Ironmak. Steelmak. 46 (2019) 922–927.
J.L. Guo, Y.P. Bao, M. Wang, Waste Manage. 78 (2018) 318–330.
L.V. Fisher, A.R. Barron, Resour. Conserv. Recy. 146 (2019) 244–255.
Y. Zhang, J. Zhang, T.Y. Zhang, Y.M. Liu, Z.B. Han, China Metallurgy 24 (2014) No. 8, 33–37.
J. Zhang, D.L. Yan, Y.H. Qi, P.F. Shen, H.J. Xu, J.J. Gao, Iron and Steel 55 (2020) No. 1, 1–5.
Y. Kang, C. Liu, Y.Z. Zhang, H.W. Xing, Crystals 10 (2020) 30.
L.L. Wang, Y.Z. Zhang, Y. Long, H.B. Ke, Appl. Therm. Eng. 181 (2020) 115850.
Y. Kang, C. Liu, Y.Z. Zhang, H.W. Xing, M.F. Jiang, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 500 (2018) 453–459.
H. Wang, W. Zhang, C. Wang, T.L. Tian, H.W. Xing, Y.Z. Zhang, Ironmak. Steelmak. 47 (2020) 432–436.
H.G. Wang, B. Peng, C.S. Yue, L. Wu, G.B. Qiu, Z.T. Bai, M. Zhang, M. Guo, Environ. Eng. 38 (2020) No. 5, 133–137.
X. Yin, C.M. Zhang, G.C. Wang, Y.H. Cai, C.M. Zhao, Metall. Res. Technol. 115 (2018) 414.
Y.X. Jiang, Iron and Steel 46 (2011) No. 5, 89–92.
J.J. Pei, J.H. Wu, W.Q. Huo, Y.Z. Zhang, H.W. Xing, Q.Q. Ren, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28 (2021) 383–390.
J.M. Kim, S.H. Cho, E.G. Kwak, KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 19 (2015) 1548.
T.S. Naidu, G.M. Sheridan, L.D. van Dyk, Miner. Eng. 149 (2020) 106234.
M. Barati, S. Jahanshahi, J. Sustain. Metall. 6 (2020) 191–206.
L.B. Deng, S. Wang, Z. Zhang, Z.H. Li, R.D. Jia, F. Yun, H. Li, Y.H. Ma, W.C. Wang, Mater. Chem. Phy. 251 (2020) 123159.
C.W. Liu, S.G. Huang, B. Blanpain, M.X. Guo, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 50 (2019) 271–281.
R.D. Jia, L.B. Deng, F. Yun, H. Li, X.F. Zhang, X.L. Jia, Mater. Chem. Phys. 233 (2019) 155–162.
S.Y. Liu, Z.J. Wang, B. Peng, C.S. Yue, M. Guo, M. Zhang, Chin. J. Eng. 40 (2018) 557–564.
X.D. Xing, Z.G. Pang, C. Mo, S. Wang, J.T. Ju, J. Non-Cryst. Solids 530 (2020) 119801.
W.W. She, Z.J. Liu, X.M. Chen, J.L. Yang, China Metall. 29 (2019) No. 7, 13–16.
J. Li, W.X. Liu, Y.Z. Zhang, A.M. Yang, K. Zhao, Mater. Manuf. Process. 30 (2015) 374–380.
X. Yin, C.M. Zhang, G.C. Wang, J. Yang, Y.H. Cai, C.M. Zhao, Ironmak. Steelmak. 45 (2018) 969–977.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Hebei Province (Grant Number 19273806D) and the Project of Hebei Provincial Department of Education (Grant Number JQN2020042).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Liu, C., Xing, Hw. et al. High-temperature modification and air-quenching granulation of steel slag. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 29, 783–792 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00641-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00641-y