Abstract
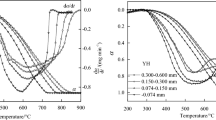
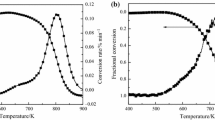
Combustion behavior of single pulverized coals (PCs) and co-combustion characteristics of anthracite (AT) and bituminite (BT) blends with 20 wt.% volatile were studied by thermogravimetric experiments. The results indicated that reaction characteristics of PCs were closely related to their functional group structure and consequently, the pyrolysis of PCs with highly active functional groups initiated at lower temperatures. It was also noticed that the discrepancy of functional group structures between AT and BT might impair their interaction during combustion. The early exhaust of BT at low temperatures would possibly lead to an independent combustion of volatile and residual carbon and eventually the inefficient combustion of their blend. However, the mixing of AT and BT with similar functional group structures was more likely to achieve blends with superior combustion property. Simultaneously, non-isothermal kinetic analysis manifested that the combustion of blends followed random pore model (RPM), and therefore, the parameters calculated by RPM were more accurate to describe their combustion behavior. The kinetic calculation results showed that the activation energy required for decomposition of blends in early combustion stage was much lower owing to the excellent activity of volatile, while residual carbon with stable aromatic hydrocarbon demanded more energy to initiate its combustion.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
X.L. Wang, Induction of ironmaking and steelmaking, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2006.
L.Z. Jin, J. Duan, S.N. Ou, L.Q. Jia, Journal of Safety Science and Technology 8 (2012) No. 4, 40–43.
X. Xue, Energy Sources, Part A: Recovery, Utilization and Environmental Effects 38 (2016) 69–74.
Y.J. Wang, H.B. Zuo, J. Zhao, G.W. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00463-4.
M.Y. Kou, H.B. Zuo, X.J. Ning, G.W. Wang, Z.B. Hong, H.F. Xu, S.L. Wu, Energy 188 (2019) 116030.
S.F. Zhang, C.G. Bai, L.Y. Wen, G.B. Qiu, X.W. Lü, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17 (2010) No. 10, 8–12.
I. Naruse, K. Nakayama, A. Higuchi, Khairil, ISIJ Int. 40 (2000) 744–748.
Z.Q. Gu, L.J. Jia, X.Z. Shi, Industrial Furnace 38 (2016) No. 3, 1–4.
J. Li, C.Y. Song, X.J. Li, X.W. Qin, X.K. Du, Anhui Metallurgy (2017) No. 1, 33–36.
B.L. Ma, Y.Z. Zhang, Y.Q. Cai, Y. Xu, Mining and Metallurgy 26 (2017) No. 3, 50–55.
G.W. Wang, J.L. Zhang, G.H. Zhang, X.J. Ning, X.Y. Li, Z.J. Liu, J. Guo, Energy 131 (2017) 27–40.
L.Y. Wen, C.G. Bai, S.F. Zhang, G.B. Qiu, D.F. Chen, ISIJ Int. 47 (2007) 1239–1244.
Y. Wu, S.F. Zhang, S.S. Cai, X. Xiao, C. Yin, J. Xu, S.X. Qiu, W.Z. Yu, M.L. Hu, L.Y. Wen, J. Comput. Chem. 40 (2019) 2749–2760.
C.B. Wang, H. Shao, M. Lei, Y.H. Wu, L.F. Jia, Appl. Therm. Eng. 93(2016) 438–445.
Q.V. Bach, W.H. Chen, C.F. Eng, C.W. Wang, K.C. Liang, J.Y. Kuo, Fuel 251 (2019) 118–125.
Y.F. Wu, Q.H. Pang, Z.J. He, T.F. Song, W.L. Zhan, J.H. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 26 (2019) 818–828.
X.Z. Zhuang, Y.P. Song, H. Zhan, X.L. Yin, C.Z. Wu, Renew. Energy 140 (2019) 380–389.
J.J. He, P.H. Qiu, S.H. Wu, Energy Conservation Technology 25 (2007) No. 4, 321–325.
P. Sharma, O.P. Pandey, P.K. Diwan, Fuel 253 (2019) 1149–1161.
L.C. Yang, Q.H. Pang, Z.J. He, T.X. Xu, S.J. Yang, Y. Wang, Energy Fuels 33 (2019) 12527–12537.
S. Ren, F.Q. Guo, J. Yang, L. Yao, Q. Zhao, M. Kong, Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 126 (2017) 278–285.
G.W. Wang, J.L. Zhang, W.W. Chang, R.P. Li, Y.J. Li, C. Wang, Energy 147 (2018) 25–35.
J. Liu, W.S. Chen, Q.J. Qi, Journal of Liaoning Technical University (Natural Science) 25 (2006) No. 2, 161–163.
H.E. Kissinger, Anal. Chem. 29 (1957) 1702–1706.
Q.H. Pang, in: Energy Technology 2014: Carbon Dioxide Management and Other Technologies, TMS, San Diego, USA, 2014, pp. 233–239.
G.W. Wang, J.L. Zhang, X.M. Hou, J.G. Shao, W.W. Geng, Bioresour. Technol. 177 (2015) 66–73.
H.B. Bi, C.X. Wang, Q.Z. Lin, X.D. Jiang, C.L. Jiang, L. Bao, Sci. Total Environ. 751 (2021) 142293.
X.Q. He, X.F. Liu, B.S. Nie, D.Z. Song, Fuel 206 (2017) 555–563.
X.G. Li, Y. Lv, B.G. Ma, S.W. Jian, H.B. Tan, Bioresour. Technol. 102 (2011) 9783–9787.
H. Haykiri-Acma, S. Yaman, Waste Manag. 28 (2008) 2077–2084.
Q.H. Pang, J.L. Zhang, R. Mao, Z. Jiang, T. Liu, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 21 (2014) 312–320.
J.S. Yu, Coal chemistry, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, China, 2006.
K.L. Pang, W.G. Xiang, C.S. Zhao, J. Anal. Appl. Pyrol. 80 (2007) 77–84.
J.L. Zhang, J. Guo, G.W. Wang, T. Xu, Y.F. Chai, C.L. Zheng, R.S. Xu, Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 23 (2016) 1001–1010.
Y.Y. Zhang, Z.Z. Zhang, M.M. Zhu, F.Q. Cheng, D.K. Zhang, Bioresour. Technol. 214 (2016) 396–403.
J. Ding, Q.C. Liu, L.J. Jiang, G.Q. Liu, S. Ren, J. Yang, L. Yao, F. Meng, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 23 (2016) 917–923.
Z.G. Liu, R. Balasubramanian, Bioresour. Technol. 146 (2013) 371–378.
K.M. Lu, W.J. Lee, W.H. Chen, T.C. Lin, Appl. Energy 105 (2013) 57–65.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the team partners from the Research Institute of Mass Energy Optimization and New Technology of Metallurgy for their valuable contribution to this work and preparation of this paper. This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51874171, 51604148, 51974154 and 52074150) and Liaoning Provincial Natural Science Foundation Guiding Program of China (2019-ZD-0273).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Lc., Pang, Qh., He, Zj. et al. Kinetic study on co-combustion of pulverized anthracite and bituminite for blast furnace injection. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 949–964 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00564-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-021-00564-8