Abstract
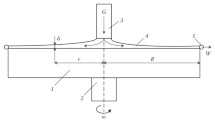
Dry centrifugal granulation (DCG) experiments for blast furnace slag (BFS) were performed by means of a rotary disk atomizer since water quenching method can create a series of problems. The results showed that the DCG method can granulate the BFS, but the results are easily affected by the slag flow rate, disk rotating speed, disk radius, disk material and slag falling height. The granulating parameters with an excessive flow rate, low rotating speed, SiN–SiC disk, stainless steel disk and low slag falling height are detrimental to the granulation process. The most suitable parameters for granulation are a slag flow rate of 5.1 × 10−5 m3/s, a disk rotating speed of 1500–2300 r/min, a slag falling height of 0.8 m and a smooth graphitic disk with the radius of 0.1 m. In the absence of an off-center flow, the overall best granulating effect produces round particles with mean diameter of 3.43 mm without creating slag fiber. The vitreous content of the BFS particles granulated by graphite disks is 92%, which meets the requirements of cement raw materials. The Bond work index of dry granulated BFS is 18.4 kWh/t, and the grindability of dry granulated slag and water-quenched slag is similar.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Mizuochi, T. Akiyama, T. Shimada, E. Kasai, J.I. Yaji, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 1423–1428.
Y.Q. Sun, Z.T. Zhang, L.L. Liu, X.D. Wang, Energies 7 (2014) 1673–1684.
H. Wang, J.J. Wu, X. Zhu, Q. Liao, L. Zhao, Appl. Energy 171 (2016) 314–324.
T. Akiyama, T. Mizuochi, J.I. Yagi, H. Nogami, Steel Res. Int. 75 (2004) 122–127.
H. Purwanto, T. Akiyama, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 31 (2006) 491–495.
J. Ding, Y.R. Wang, R. Gu, W.L. Wang, J.F. Lu, Appl. Energy 250 (2019) 1270–1279.
H. Purwanto, E. Kasai, T. Akiyama, ISIJ Int. 50 (2010) 1319–1325.
M. Cooksey, A. Guiraud, B. Kuan, Y.H. Pan, J. Sustain. Metall. 5 (2019) 181–194
Y.Q. Sun, Z.T. Zhang, Metall. Mater. Trans. E 3 (2016) 114–122.
Y.Q. Sun, Z.T. Zhang, L.L. Liu, X.D. Wang, Energies 8 (2015) 1917–1935.
T. Shimada,V. Kochura, T. Akiyama, E. Kasai, J.I. Yagi, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 111–115.
T.D. Hadley, Y.H. Pan, K.S. Lim, J. Orellana, Int. J. Miner. Process. 142 (2015) 91–100.
N. Wang, H. Peng, X. Ling, J.Q. Kang, M.H. Xu, Energy Procedia 105 (2017) 622–627.
X. Zhu, H. Zhang, Y. Tan, H. Wang, Q. Liao, Appl. Therm. Eng. 88 (2015) 157–164.
J.J. Wu, H. Wang, X. Zhu, Q. Liao, B. Ding, Appl. Therm. Eng. 89 (2015) 494–504.
J.X. Liu, Q.B. Yu, P. Li, W.Y. Du, Appl. Therm. Eng. 40 (2012) 351–357.
J.X. Liu, Q.B. Yu, W.J. Duan, Q. Qin, Appl. Therm. Eng. 73 (2014) 888–893.
J.X. Liu, Q.B. Yu, Z.L. Zuo, W.J. Duan, Z.C. Han, Q. Qin, F. Yang, Appl. Therm. Eng. 103 (2016) 1112–1118.
Y.H. Pan, P. Witt, D.S. Xie, in: 7th Int. Conference on CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries, CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia, 2009, pp. 1–6.
Q.M. Chang, X.W. Li, H.W. Ni, W.Y. Zhu, C.G. Pan, S.D. Hu, ISIJ Int. 55 (2015) 1361–1366.
H. Purwanto, T. Mizuochi, T. Akiyama, Mater. Trans. 46 (2005) 1324–1330.
D.X. Wang, X. Ling, H. Peng, Appl. Therm. Eng. 63 (2014) 387–395.
H. Purwanto, T. Mizuochi, H. Tobo, M. Takagi, T. Akiyama, Mater. Trans. 45 (2004) 3286–3290.
Y. Tan, X. Zhu, X.Y. He, B. Ding, H. Wang, Q. Liao, H. Li, Powder Technol. 323 (2018) 176–185.
B. Lin, H. Wang, X. Zhu, Q. Liao, B. Ding, Appl. Therm. Eng. 96 (2016) 432–440.
Y.Q. Sun, H.W. Shen, H. Wang, X.D. Wang, Z.T. Zhang, Energy 76 (2014) 761–767.
B. Ding, X. Zhu, H. Wang, X.Y. He, Y. Tan, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 118 (2018) 471–479.
X. Zhu, B. Ding, H. Wang, X.Y. He, Y. Tan, Q. Liao, Appl. Therm. Eng. 130 (2018) 1033–1043.
J. Gao, Y.H. Feng, D.L. Feng, Z. Zhang, X.X. Zhang, Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 146 (2020) 118888.
J.J. Wu, H. Wang, X. Zhu, Q. Liao, K. Li, Appl. Therm. Eng. 111 (2017) 1557–1564.
C. Czisch, U. Fritsching, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 477 (2008) 21–25.
T. Mizuochi, T. Akiyama, ISIJ Int. 43 (2003) 1469–1471.
H. Peng, X.K. Shan, X. Ling, D.X. Wang, J. Li, Appl. Therm. Eng. 128 (2018) 1565–1578.
H. Peng, X.K. Shan, X. Ling, D.X. Wang, J. Li, Results Phys. 11 (2018) 385–393.
Y. Tan, H. Wang, X. Zhu, Y.W. Lv, X.Y. He, Q. Liao, Appl. Therm. Eng. 159 (2019) 113977.
Y. Tan, X. Zhu, H. Wang, X.Y. He, B. Ding, Q. Liao, Appl. Therm. Eng. 142 (2018) 683–694.
J.X. Liu, Q.B. Yu, Z.L. Zuo, F. Yang, W.J. Duan, Q. Qin, Constr. Build. Mater. 131 (2017) 381–387.
J.X. Liu, Q.B. Yu, Z.L. Zuo, F. Yang, Z.C. Han, Q. Qin, Cement Concr. Compos. 95 (2019) 19–24.
J.J. Wu, H. Wang, X. Zhu, Q. Liao, J. Li, L. Lin, CIESC Journal 66 (2015) 2474–2480.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2018YFC1900602) and the Open Youth Fund of the State key Laboratory of Refractories and Metallurgy, Wuhan University of Science and Technology (2018QN03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, Rj., Zhang, H., Li, Y. et al. Effect of process parameters on dry centrifugal granulation of molten slag by a rotary disk atomizer. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 28, 263–271 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00523-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00523-9