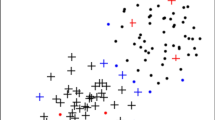
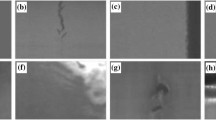
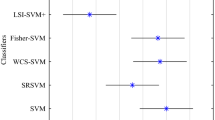
Abstract
Least squares support vector machine (LS-SVM) plays an important role in steel surface defects classification because of its high speed. However, the defect samples obtained from the real production line may be noise. LS-SVM suffers from the poor classification performance in the classification stage when there are noise samples. Thus, in the classification stage, it is necessary to design an effective algorithm to process the defects dataset obtained from the real production line. To this end, an adaptive weight function was employed to reduce the adverse effect of noise samples. Moreover, although LS-SVM offers fast speed, it still suffers from a high computational complexity if the number of training samples is large. The time for steel surface defects classification should be as short as possible. Therefore, a sparse strategy was adopted to prune the training samples. Finally, since the steel surface defects classification belongs to unbalanced data classification, LS-SVM algorithm is not applicable. Hence, the unbalanced data information was introduced to improve the classification performance. Comprehensively considering above-mentioned factors, an improved LS-SVM classification model was proposed, termed as ILS-SVM. Experimental results show that the new algorithm has the advantages of high speed and great anti-noise ability.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Pernkopf, Pattern Anal. Appl. 7 (2004) 333–342.
L.A.O. Martins, F.L.C. Pádua, P.E.A. Almeida, in: IECON 2010-36th Annual Conference on IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, IEEE, Glendale, USA, 2010, pp. 1081–1086.
A. Borselli, V. Colla, M. Vannucci, M. Veroli, in: International Conference on Fuzzy Systems, IEEE, Barcelona, Spain, 2010, pp. 1–6.
Y.H. Yan, K.C. Song, Z.T. Xing, X.H. Feng, in: 2011 Third International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, IEEE, Shanghai, China, 2011, pp. 958–961.
S.Y. Tian, K. Xu, Metals 7 (2017) 311.
L. Yi, G.Y. Li, M.M. Jiang, Steel Res. Int. 88 (2017) 1600068.
S.Y. Zhou, Y.P. Chen, D.L. Zhang, J.M. Xie, Y.F. Zhou, Mater. Technol. 51 (2017) 123–131.
M.X. Chu, X.P. Liu, R.F. Gong, L.M. Liu, Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 176 (2018) 108–118.
R.F. Gong, M.X. Chu, Y.H. Yang, Y. Feng, Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 188 (2019) 70–78.
D. He, K. Xu, P. Zhou, Comput. Ind. Eng. 128 (2019) 290–297.
X.W. Zhang, Y.Q. Ding, Y.Y. Lv, A.Y. Shi, R.Y. Liang, Expert Systems with Applications 38 (2011) 5930–5939.
H.J. Hu, Y.X. Li, M.F. Liu, W.H. Liang, Multimed. Tools Appl. 69 (2014) 199–216.
D.Y. Cui, K.W. Xia, Mathematical Problems in Engineering 2017 (2017) Article ID 4257273. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4257273.
J.A.K. Suykens, I. Vandewalle, Neural Process. Lett. 9 (1999) 293–300.
X.J. Peng, D. Xu, Neurocomputing 99 (2013) 134–143.
R.F. Gong, C.D. Wu, M.X. Chu, Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 172 (2018) 109–117.
Y.F. Ma, X. Liang, X.P. Zhou, Acta Autom. Sin. 43 (2017) 132–141.
Z.X. Xue, S.Y. Liu, W.L. Liu, J. Syst. Simul. 21 (2009) 4324–4327.
K.N. Plataniotis, D. Androutsos, A.N. Venetsanopoulos, Proceedings of the IEEE 87 (1999) 1601–1622.
M.X. Chu, A.N. Wang, R.F. Gong, Acta Electronica Sinica 42 (2013) 998–1003.
P. Karsmakers, K. Pelckmans, K. De Branbanter, H.V. Hamme, J.A.K. Suykens, Mach. Learn. 85 (2011) 109–148.
L.X. Yang, S.Y. Yang, R. Zhang, H.H. Jin, Neurocomputing 131 (2014) 77–86.
K.C. Song, Y.H. Yan, Appl. Surf. Sci. 285 (2013) 858–864.
Y. He, K.C. Song, H.W. Dong, Y.H. Yan, Opt. Lasers Eng. 122 (2019) 294–302.
J. Demšar, J. Mach. Learn. Res. 7 (2006) 1–30.
C.E. Douglas, F.A. Michael, Commun. Statist. Theor. Meth. 20 (1991) 127–139.
Acknowledgements
This paper is sponsored by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (20180550067), Liaoning Province Ministry of Education Scientific Study Project (2020LNZD06 and 2017LNQN11) and University of Science and Technology Liaoning Talent Project Grants (601011507-20 and 601013360-17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Lm., Chu, Mx., Gong, Rf. et al. Unbalanced classification method using least squares support vector machine with sparse strategy for steel surface defects with label noise. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 1407–1419 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00499-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-020-00499-6