Abstract
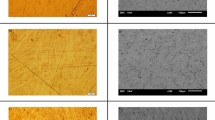
La0.8Pr0.2MgNi3.6Co0.4 alloys were prepared by induction melting, annealing and melt spinning techniques. The influences of annealing treatment and melt spinning on phase structure and hydrogen storage properties were systematically investigated. The results of X-ray diffraction determine that the as-cast and as-spun La0.8Pr0.2MgNi3.6Co0.4 alloys consist of LaMgNi4 and LaNi5 phases, while only LaMgNi4 phase is present in the as-annealed alloy. The scanning electron microscope images illustrate that the grain of the alloy is significantly refined by melt spinning technology. The gaseous hydrogen storage kinetic and thermodynamic properties were measured by using a Sievert’s apparatus at different temperatures. The maximum hydrogen storage capacity of the as-cast, as-spun and as-annealed La0.8Pr0.2MgNi3.6Co0.4 alloy is 1.699, 1.637 and 1.535 wt.% at 373 K and 3 MPa, respectively. The annealed alloy has flatter and wider pressure plateaus compared with the as-cast and as-spun alloys, which correspond to the hydrogen absorption and desorption process of LaMgNi4 and corresponding hydride. Furthermore, the enthalpy and entropy changes of LaMgNi4 during hydrogenation at different temperatures were calculated using Van’t Hoff methods.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Y.H. Zhang, Z.C. Jia, Z.M. Yuan, T. Yang, Y. Qi, D.L. Zhao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 22 (2015) 757–770
T.S. Veras, T.S. Mozer, D.C.R.M. Santos, A.S. Cesar, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42 (2017) 2018–2033.
J.L. Gao, Y. Qi, Y.Q. Li, H.W. Shang, D.L. Zhao, Y.H. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24 (2017) 198–205.
Y. Li, D. Han, S.M. Han, X.L. Zhu, L. Hu, Z. Zhang, Y.W. Liu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 34 (2009) 1399–1404.
X.J. Zhao, Q. Li, K.C. Chou, H. Liu, G.W. Lin, J. Alloy. Compd. 473 (2009) 428–432.
L. Jiang, G.X. Li, L.Q. Xu, W.Q. Jiang, Z.Q. Lan, J. Guo, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 35 (2010) 204–209.
Y.F. Liu, Y.H. Cao, L. Huang, M.X. Gao, H.G. Pan, J. Alloy. Compd. 509 (2011) 675–686.
Y.H. Zhang, K.F. Zhang, Z.M. Yuan, Y.Q. Li, H.W. Shang, Y. Qi, X.P. Dong, D.L. Zhao, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25 (2018) 1255–1264.
D.C. Feng, H. Sun, X.T. Wang, Y.H. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25 (2018) 746–754.
Y. Yin, B. Li, Z.M. Yuan, Y. Qi, Y.H. Zhang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25 (2018) 1172–1178.
L.Z. Ouyang, Z.J. Cao, L.L. Li, H. Wang, J.W. Liu, D. Min, Y.W. Chen, F.M. Xiao, R.H. Tang, M. Zhu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39 (2014) 12765–12772.
Z.J. Cao, L.Z. Ouyang, L.L. Li, Y.S. Lu, H. Wang, J.W. Liu, D. Min, Y.W. Chen, F.M. Xiao, T. Sun, R.H. Tang, M. Zhu, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 40 (2015) 451–455.
L.Z. Ouyang, T.H. Yang, M. Zhu, D. Min, T.Z. Luo, H. Wang, F.M. Xiao, R.H. Tang, J. Alloy. Compd. 735 (2018) 98–103.
T. Kohno, H. Yoshida, F. Kawashima, T. Inaba, I. Sakai, M. Yamamoto, M. Kanda, J. Alloy. Compd. 311 (2000) L5–L7.
K. Kadir, D. Noreus, I. Yamashita, J. Alloy. Compd. 345 (2002) 140–143.
L. Guénée, V. Favre-Nicolin, K. Yvon, J. Alloy. Compd. 348 (2003) 129–137.
Z.M. Wang, H.Y. Zhou, Z.F. Gu, G. Cheng, A.B. Yu, J. Alloy. Compd. 377 (2004) L7–L9.
T. Yang, Z.M. Yuan, W.G. Bu, Z.C. Jia, Y. Qi, Y.H. Zhang, Mater. Des. 93 (2016) 46–52.
X. Tian, G.H. Yun, H.Y. Wang, T. Shang, Z.Q. Yao, W. Wei, X.X. Liang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39 (2014) 8474–8481.
P. Li, J. Zang, F.Q. Zhai, G. Ma, L. Xu, X.H. Qu, J. Rare Earth 33 (2015) 417–424.
Y.H. Zhang, W. Zhang, Z.M. Yuan, H.W. Shang, Y.Q. Li, S.H. Guo, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 42 (2017) 14227–14245.
L.Z. Ouyang, Z.J. Cao, H. Wang, R.Z. Hu, M. Zhu, J. Alloy. Compd. 691 (2017) 422–435.
L.Z. Ouyang, J.L. Huang, H. Wang, J.W. Liu, M. Zhu, Mater. Chem. Phys. 200 (2017) 164–178.
T. Yang, T.T. Zhai, Z.M. Yuan, W.G. Bu, S. Xu, Y.H. Zhang, J. Alloy. Compd. 617 (2014) 29–33.
T.T. Zhai, T. Yang, Z.M. Yuan, Y.H. Zhang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 39 (2014) 14282–14287.
Y.H. Zhang, F. Hu, Z.G. Li, K. Lv, S.H. Guo, X.L. Wang, J. Alloy. Compd. 509 (2011) 294–300.
Y.H. Zhang, Y. Cai, C. Zhao, T.T. Zhai, G.F. Zhang, D.L. Zhao, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 37 (2012) 14590–14597.
H.G. Pan, Y.F. Liu, M.X. Gao, Y.F. Zhu, Y.Q. Lei, Q.D. Wang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 28 (2003) 113–117.
H.G. Pan, N. Chen, M.X. Gao, R. Li, Y.Q. Lei, Q.D. Wang, J. Alloy. Compd. 397 (2005) 306–312.
Y.H. Zhang, Y. Cai, B.W. Li, H.P. Ren, Z.H. Hou, D.L. Zhao, Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 42 (2013) 1981–1987.
Y.V. Verbovytskyy, V.V. Shtender, A. Hackemer, H. Drulis, I.Y. Zavaliy, P.Y. Lyutyy, J. Alloy. Compd. 741 (2018) 307–314.
Y.H. Zhang, S.S. Cui, Y.Q. Li, H.W. Shang, Y. Qi, D.L. Zhao, J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 34 (2018) 370–378.
L. Zhang, S.M. Han, Y. Li, J.J. Liu, J.L. Zhang, J.D. Wang, S.Q. Yang, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 38 (2013) 10431–10437.
Y.H. Zhang, Y.Q. Li, H.W. Shang, Z.H. Hou, Y. Qi, D.L. Zhao, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 28 (2018) 711–721.
T.Z. Huang, J.T. Han, Y.H. Zhang, J.M. Yu, G.X. Sun, H. Ren, X.X. Yuan, J. Power Sources 196 (2011) 9585–9589.
M.B. Baysal, G. Surucu, E. Deligoz, H. Ozisik, Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43 (2018) 23397–23408.
L.F. Cheng, J.X. Zou, X.Q. Zeng, W.J. Ding, Intermetallics 38 (2013) 30–35.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51901105, 51871125 and 51761032), Inner Mongolia Natural Science Foundation (2017BS0507 and 2019BS05005), and Inner Mongolia University of Science and Technology Innovation Fund (2016QDL-B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhai, Tt., Yuan, Zm., Hu, F. et al. Influence of melt spinning and annealing treatment on structures and hydrogen storage thermodynamic properties of La0.8Pr0.2MgNi3.6Co0.4 alloy. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 27, 114–120 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00340-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-019-00340-9