Abstract
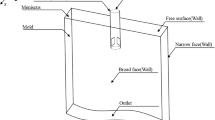
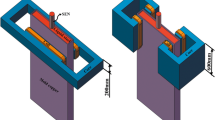
A three-dimensional mathematical model was established to investigate the behavior of molten steel flow and steel/slag interface with different processes and electromagnetic parameters under two different static magnetic field configurations [ruler-type electromagnetic brake (EMBr ruler) and vertical electromagnetic brake (V-EMBr)] in a continuous casting mold. The results showed that the brake effect of EMBr ruler is significantly influenced by its configuration parameters, the distance between the pole and bottom of the submerged entry nozzle (SEN), and the port angle of the SEN outlet; therefore, it is not helpful to depress the diffusion of jet flow along the thickness direction of mold. For a constant SEN depth and port angle, there is a reasonable pole position (P = 0 mm) where the pole simultaneously covers three key zones, i.e., the jet flow impact zone and the upward and downward backflow zones. For V-EMBr, the magnetic field can simultaneously cover the three key zones and depress the diffusion of jet flow along the casting and thickness directions of the mold. Both the meniscus height and the impact intensity of the jet flow can be obviously depressed by V-EMBr even if the SEN depth and port angle have changed in the continuous casting process.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Takatani, K. Nakai, N. Kasai, T. Watanabe, H. Nakajima, ISIJ Int. 29 (1989) 1063–1068.
H. Shen, B. Liu, L. Wang, Int. J. Cast Metal. Res. 18 (2005) No. 4, 209–213.
Y.S. Hwang, P.R. Cha, H.S. Nam, K.H. Moon, J.K. Yoon, ISIJ Int. 37 (1997) 659–667.
H.Q. Yu, B.F. Wang, H.Q. Li, J.C. Li, J. Mater. Process. Technol. 202 (2008) 179–187.
S. Garcia-Hernandez, R.D. Morales, E. Torres-Alonso, Ironmak. Steelmak. 37 (2010) 360–368.
H. Yamamura, T. Toh, H. Harada, E. Takeuchi, T. Ishii, ISIJ Int. 41 (2001) 1229–1235.
M.M. Yavuz, Steel Res. Int. 82 (2011) 809–818.
R. Singh, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 44 (2013) 1201–1221.
K.H. Moon, H.K. Shin, B.J. Kim, J.Y. Chung, Y.S. Hwang, J.K. Yoon, ISIJ Int. 36 (1996) S201–S203.
S. Garcia-Hernandez, R.D. Morales, E. Torres-Alonso, A. Najera-Bastida, Steel Res. Int. 80 (2009) 816–823.
K. Cukierski, B.G. Thomas, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 39 (2008) 94–107.
R. Singh, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 1098–1115.
B.K. Li, T. Okane, T. Umeda, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 31 (2000) 1491–1503.
H. Jia, Z.Q. Zhang, Z. Yu, K. Deng, Z.S. Lei, Z.M. Ren, Acta Metall. Sin. 48 (2012) 1049–1056.
A. Idogawa, M. Sugizawa, S. Takeuchi, K. Sorimachi, T. Fujii, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 173 (1993) 293–297.
E.G. Wang, L. Kang, F. Li, in: The Scientific Committee of EMP, Proceeding of the 6th Int. Conference on Electromagnetic Processing of Materials, Forschungszentrum Dresden-Rossendorf, Dresden, Germany, 2009, pp. 583–586.
L.S. Zhang, X.F. Zhang, B. Wang, Q. Liu, Z.G. Hu, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 45 (2014) 295–306.
Y.F. Wang, A.P. Dong, L.F. Zhang, Steel Res. Int. 82 (2011) 428–439.
B.E. Launder, Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 3 (1974) 269–289.
H.Q. Yu, M.Y. Zhu, Acta Metall. Sin. 44 (2008) 1141–1148.
H.Q. Yu, M.Y. Zhu, J. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 17 (2010) No. 4, 5–11.
J.J. Zhao, S.S. Cheng, in: Steelmaking Committee, Proceeding of the 15th National Conference on Steelmaking, The Chinese Society for Metals, Xiamen, China, 2008, pp. 425–430.
R. Chaudhary, B.G. Thomas, S.P. Vanka, Metall. Mater. Trans. B 43 (2012) 532–553.
Z.D. Qian, Y.L. Wu, ISIJ Int. 44 (2004) 100–107.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51574083) and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (The 111 Project of China, No. B07015). The authors would also like to thank the referees for their work which has contributed to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Z., Wang, Eg. & Xu, Y. Behavior of molten steel flow in continuous casting mold with different static magnetic field configurations. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25, 366–377 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0051-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0051-1