Abstract
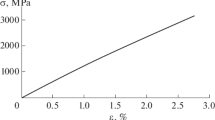
Gd50Al30Co20 wires show excellent magnetocaloric properties and high heat exchange rate due to the microsize. The Weibull and lognormal methods were used for systematically analyzing its mechanical properties for matching the design requirements in cooling system. The wire exhibits average fracture strength of ~ 969.5 MPa and typical fracture behavior of amorphous character. Moreover, the distributions of stresses for tensile strains at 10 values are estimated by probability plot and Chi-square goodness-of-fit test. The random stresses were best fitted by lognormal probability distribution for most studied cases; however, fracture strength was best fitted by Weibull probability distribution. It is interesting to note that the mean and standard deviation of the stresses (to reach specific tensile strain) increase as the tensile strain grows, accompanied by the coefficients of variation of stresses which decrease smoothly. It is concluded that the inhomogeneity of material does cause the scatter of stresses growth, and the scatter could be considerably large.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.H. Wang, Adv. Mater. 21 (2009) 4524–4544.
B.Z. Tang, P. Yu, D. Ding, C. Wu, L. Xia, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 424 (2017) 275–278.
M.D. Kuz’min, Appl. Phys. Lett. 90 (2007) 251916.
D. Vuarnoz, T. Kawanami, Appl. Therm. Eng. 37 (2012) 388–395.
B. Schwarz, B. Podmilsak, N. Mattern, J. Eckert, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322 (2010) 2298–2303.
J. Du, Q. Zheng, Y.B. Li, Q. Zhang, J. Appl. Phys. 103 (2008) 023918.
Y. Bao, D.Y. Yang, N. Liu, G.Q. Zhang, Z. Li, F.Y. Cao, J.F. Sun, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24 (2017) 435–441.
J.F. Zhao, S.G.X.G. Yuan, J.F. Sun, H.J. Huang, F.Y. Cao, H.X. Shen, Y.L. Wang, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24 (2017) 469–474.
Y.J. Huang, P. Xue, X. Cheng, Y.M. Wang, F.Y. Cao, Z.L. Ning, J.F. Sun, J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 24 (2017) 416–420.
H. Shen, H. Wang, L. Jingshun, F. Cao, F. Qin, D. Xing, D. Chen, Y. Liu, J. Sun, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 372 (2014) 23–26.
H. Wang, D. Xing, X. Wang, J. Sun, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 42 (2010) 1103–1108.
J. Liu, F. Qin, D. Chen, H. Shen, H. Wang, D. Xing, M.H. Phan, J. Sun, J. Appl. Phys. 115 (2014) 17A326.
D. Xing, H. Shen, S. Jiang, J. Liu, M.H. Phan, H. Wang, F. Qin, D. Chen, Y. Liu, J. Sun, Phys Status Solidi A 212 (2015) 1905–1910.
H. Shen, H. Wang, J. Liu, D. Xing, F. Qin, F. Cao, D. Chen, Y. Liu, J. Sun, J. Alloy. Compd. 603 (2014) 167–171.
H.X. Shen, D.W. Xing, H. Wang, J.S. Liu, D.M. Chen, Y.F. Liu, J.F. Sun, Mater. Res. 18 (2015) 66–71.
H.X. Shen, D.W. Xing, J.L. Sánchez Llamazares, C.F. Sánchez-Valdés, H. Belliveau, H. Wang, F.X. Qin, Y.F. Liu, J.F. Sun, H. Srikanth, M.H. Phan, Appl. Phys. Lett. 108 (2016) 092403.
W.N. Sharpe, J. Pulskamp, D.S. Gianola, C. Eberl, R.G. Polcawich, R.J. Thompson, Exp. Mech. 47 (2007) 649–658.
W. Weibull, J. Appl. Mech. 18 (1951) 293–297.
Z. Han, L.C. Tang, J. Xu, Y. Li, Scripta Mater 61 (2009) 923–926.
J. Schijve, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 17 (1994) 381–396.
J. Dominguez, J. Zapatero, J. Pascual, Eng. Fract. Mech. 56 (1997) 65–76.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful for the supports from the Key National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1533202), the Shandong Independent Innovation and Achievements Transformation Fund (No. 2014CGZH1101), the Civil Aviation Administration of China (No. MHRD20150104), National Science-technology Support Plan Project “the application paradigm of full lifecycle information closed-loop management for construction machinery” (No. 2015BAF32B01-4) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51775132, 51671071 and 51371067).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, B., Shen, Hx., Lin, L. et al. Mechanical property statistical analysis of Gd50Al30Co20 amorphous wires for providing reference to design requirements of cooling system. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 25, 261–267 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0028-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42243-018-0028-0