Abstract
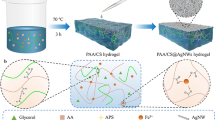
In this work, a facile strategy is proposed to construct stretchable electronics based on agarose hydrogels. The hot agarose solution is casted onto a template with patterned Ag nanowires, endowing agarose hydrogel with patterned conductive surface. After further heating treatment, Ag nanowires can be embedded into the agarose hydrogel, which improves the stability of Ag pattern and has no obvious effect on the conductivity of hydrogels. The agarose hydrogel with patterned Ag nanowires is certified to be an effective stretchable electrode to record the motion of joints, which has great potential applications in the field of wearable devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang Y, Gao W (2019) Wearable and flexible electronics for continuous molecular monitoring. Chem Soc Rev 48(6):1465–1491. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7cs00730b
Toh WY, Tan YK, Koh WS, Siek L (2014) Autonomous wearable sensor nodes with flexible energy harvesting. IEEE Sens J 14(7):2299–2306. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2014.2309900
Teng X-F, Zhang Y-T, Poon CCY, Bonato P (2008) Wearable medical systems for p-Health. IEEE Rev Biomed Eng 1:62–74. https://doi.org/10.1109/rbme.2008.2008248
Sanni A, Vilches A, Toumazou C (2012) Inductive and ultrasonic multi-tier interface for low-power, deeply implantable medical devices. IEEE Trans Biomed Circuits Syst 6(4):297–308. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbcas.2011.2175390
Yuk H, Lu B, Zhao X (2019) Hydrogel bioelectronics. Chem Soc Rev 48(6):1642–1667. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8cs00595h
Guo Y, Zhong M, Fang Z, Wan P, Yu G (2019) A wearable transient pressure sensor made with MXene nanosheets for sensitive broad-range human-machine interfacing. Nano Lett 19(2):1143–1150. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04514
Liao M, Wan P, Wen J, Gong M, Wu X, Wang Y, Shi R, Zhang L (2017) Wearable, healable, and adhesive epidermal sensors assembled from mussel-inspired conductive hybrid hydrogel framework. Adv Funct Mater 27(48):1703852. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201703852
Zhang M, Zhao M, Jian M, Wang C, Yu A, Yin Z, Liang X, Wang H, Xia K, Liang X, Zhai J, Zhang Y (2019) Printable smart pattern for multifunctional energy-management e-textile. Matter. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2019.02.003
Trivedi TJ, Rao KS, Kumar A (2014) Facile preparation of agarose–chitosan hybrid materials and nanocomposite ionogels using an ionic liquid via dissolution, regeneration and sol–gel transition. Green Chem 16(1):320–330. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3gc41317a
Hur J, Im K, Kim SW, Kim J, Chung D-Y, Kim T-H, Jo KH, Hahn JH, Bao Z, Hwang S, Park N (2014) Polypyrrole/agarose-based electronically conductive and reversibly restorable hydrogel. ACS Nano 8(10):10066–10076. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn502704g
Zheng WJ, An N, Yang JH, Zhou J, Chen YM (2015) Tough Al-alginate/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) hydrogel with tunable LCST for soft robotics. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(3):1758–1764. https://doi.org/10.1021/am507339r
Nordqvist D, Vilgis TA (2011) Rheological study of the gelation process of agarose-based solutions. Food Biophys 6(4):450–460. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11483-011-9225-0
Kusukawa N, Ostrovsky MV, Garner MM (1999) Effect of gelation conditions on the gel structure and resolving power of agarose-based DNA sequencing gels. Electrophoresis 20(7):1455–1461. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1522-2683(19990601)20:7%3c1455:aid-elps1455%3e3.3.co;2-c
Lin T, Shi M, Huang F, Peng J, Bai Q, Li J, Zhai M (2018) One-pot synthesis of a double-network hydrogel electrolyte with extraordinarily excellent mechanical properties for a highly compressible and bendable flexible supercapacitor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10(35):29684–29693. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b11377
Vardar E, Vert M, Coudane J, Hasirci V, Hasirci N (2012) Porous agarose-based semi-IPN hydrogels: characterization and cell affinity studies. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed 23(18):2273–2286. https://doi.org/10.1163/156856211X614770
Chen Q, Zhu L, Zhao C, Wang Q, Zheng J (2013) A robust, one-pot synthesis of highly mechanical and recoverable double network hydrogels using thermoreversible sol-gel polysaccharide. Adv Mater 25(30):4171–4176. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201300817
Wang S, Zhang R, Yang Y, Wu S, Cao Y, Lu A, Zhang L (2018) Strength enhanced hydrogels constructed from agarose in alkali/urea aqueous solution and their application. Chem Eng J 331:177–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.118
Jian H, Wang M, Wang S, Wang A, Bai S (2018) 3D bioprinting for cell culture and tissue fabrication. Biodes Manuf 1(1):45–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-018-0006-1
Sun S, Xiao Q-R, Zhou X, Wei Y-Y, Shi L, Jiang Y (2018) A bio-based environment-friendly membrane with facile preparation process for oil–water separation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 559:18–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2018.09.038
Deng J, Liang W, Rhodes S, Fang J (2019) Influence of polymer networks on the sensor properties of hydrogel dispersed liquid crystal droplets. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 570:438–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2019.03.066
Bai S, Nguyen TL, Mulvaney P, Wang D (2010) Using hydrogels to accommodate hydrophobic nanoparticles in aqueous media via solvent exchange. Adv Mater 22(30):3247–3250. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201000336
Wang J, Zhang X, Huang X, Wang S, Qian Q, Du W, Wang Y (2013) Forced assembly of water-dispersible carbon nanotubes trapped in paper for cheap gas sensors. Small 9(22):3759–3764. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201300655
Yamada T, Hayamizu Y, Yamamoto Y, Yomogida Y, Izadi-Najafabadi A, Futaba DN, Hata K (2011) A stretchable carbon nanotube strain sensor for human-motion detection. Nat Nanotechnol 6(5):296–301. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.36
Yang Y, Ding S, Araki T, Jiu J, Sugahara T, Wang J, Vanfleteren J, Sekitani T, Suganuma K (2016) Facile fabrication of stretchable Ag nanowire/polyurethane electrodes using high intensity pulsed light. Nano Res 9(2):401–414. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-015-0921-9
McAlpine MC, Ahmad H, Wang D, Heath JR (2007) Highly ordered nanowire arrays on plastic substrates for ultrasensitive flexible chemical sensors. Nat Mater 6(5):379–384. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1891
Qian F, Lan PC, Freyman MC, Chen W, Kou T, Olson TY, Zhu C, Worsley MA, Duoss EB, Spadaccini CM, Baumann T, Han TY (2017) Ultralight conductive silver nanowire aerogels. Nano Lett 17(12):7171–7176. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.7b02790
Chen R, Das SR, Jeong C, Khan MR, Janes DB, Alam MA (2013) Co-percolating graphene-wrapped silver nanowire network for high performance, highly stable, transparent conducting electrodes. Adv Funct Mater 23(41):5150–5158. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201300124
Wu C, Fang L, Huang X, Jiang P (2014) Three-dimensional highly conductive graphene-silver nanowire hybrid foams for flexible and stretchable conductors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(23):21026–21034. https://doi.org/10.1021/am505908d
Amjadi M, Pichitpajongkit A, Lee S, Ryu S, Park I (2014) Highly stretchable and sensitive strain sensor based on silver nanowire-elastomer nanocomposite. ACS Nano 8(5):5154–5163. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn501204t
Park M, Im J, Shin M, Min Y, Park J, Cho H, Park S, Shim MB, Jeon S, Chung DY, Bae J, Park J, Jeong U, Kim K (2012) Highly stretchable electric circuits from a composite material of silver nanoparticles and elastomeric fibres. Nat Nanotechnol 7(12):803–809. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2012.206
Song P, Qin H, Gao HL, Cong HP, Yu SH (2018) Self-healing and superstretchable conductors from hierarchical nanowire assemblies. Nat Commun 9(1):2786. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05238-w
Jiu J, Araki T, Wang J, Nogi M, Sugahara T, Nagao S, Koga H, Suganuma K, Nakazawa E, Hara M, Uchida H, Shinozaki K (2014) Facile synthesis of very-long silver nanowires for transparent electrodes. J Mater Chem A 2(18):6326–6330. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ta00502c
Xu F, Zhu Y (2012) Highly conductive and stretchable silver nanowire conductors. Adv Mater 24(37):5117–5122. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201201886
Jiu J, Murai K, Kim D, Kim K, Suganuma K (2009) Preparation of Ag nanorods with high yield by polyol process. Mater Chem Phys 114(1):333–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.09.028
Jiu J, Tokuno T, Nogi M, Suganuma K (2012) Synthesis and application of Ag nanowires via a trace salt assisted hydrothermal process. J Nanopart Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-0975-5
Sun YG, Yin YD, Mayers BT, Herricks T, Xia YN (2002) Uniform silver nanowires synthesis by reducing AgNO3 with ethylene glycol in the presence of seeds and poly(vinyl pyrrolidone). Chem Mater 14(11):4736–4745. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm020587b
Fatin-Rouge N, Milon A, Buffle J, Goulet RR, Tessier A (2003) Diffusion and partitioning of solutes in agarose hydrogels: the relative influence of electrostatic and specific interactions. J Phys Chem B 107(44):12126–12137. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0303164
Rees DA (1969) Structure, conformation, and mechanism in the formation of polysaccharide gels and networks. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 24:267–332
Wang H, Tang H, Liang J, Chen Y (2018) Dynamic agitation-induced centrifugal purification of nanowires enabling transparent electrodes with 99.2% transmittance. Adv Funct Mater 28(45):1804479. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201804479
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 21774132, 21703253, 21877052, 31700706), Natural Science Foundation for Distinguished Young Scholars of Jiangsu Province (BK20180030), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (JUSRP51712B) and Open Funding Project of the State Key Laboratory of Biochemical Engineering (No. 2019KF-02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 2 (AVI 5044 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, Q., Chen, Y., Song, W. et al. Fabrication of agarose hydrogel with patterned silver nanowires for motion sensor. Bio-des. Manuf. 2, 269–277 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-019-00051-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42242-019-00051-w