Abstract
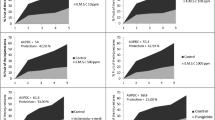
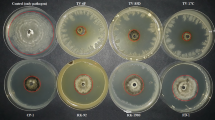
Monilinia laxa is one of the most destructive fungal pathogens causing brown rot, blossom blight and spur infection on stone fruits such as peach, nectarine, apricot, cherry and plum. In 2019–2020 surveys, 30 orchards in the apricot and almond production areas of Malatya and Elazıg provinces of Turkey exhibited blossom and twig blight symptoms. The objective of this study was to evaluate the in vitro and in vivo efficacy of boron products, pyroligneous acid and some fungicides on Monilinia laxa. Boron derivatives and boscalid were tested at different concentrations (0.01, 0.03, 0.05, 0.07, 0.09, 0.1,0.2, 0.4, 0.6%; w/v, μg.ml−1) for their inhibitory effect on mycelial growth of M. laxa. Mycelial growth of M. laxa was completely inhibited by boric acid (0.1%), borax (0.09%), Etidot (0.09%), pyroligneous acid (0.8%) and boscalid (0.6 µgml−1). Boric acid (0.12%), borax (0.1%), Etidot-67 (0.15%), PA (1.2%) and boscalid (0.8 µg ml−1) significantly inhibited germination of conidia of M. laxa isolates. EC50 values for 4 isolates of M. laxa ranged from 0.028 to 0.569% (MIC values ranged from 0.09 to 0.8 µgml−1) for mycelial growth and from 0.052 to 0.750% (MIC values ranged from 0.1 to 0.12) for conidial germination. In field trials conducted in the two subsequent years, boscalid + pyraclostrobin showed the highest efficacy (82.4% and 85.2%), followed by PA + borax (64.2% and 65.6%), PA + boric acid (48.2% and 54.6%), and boric acid + borax (18.2% and 21.9%, respectively).



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analysed in this study.
References
Arslan U (2016) Efficacy of boric acid, monopotassium phosphate and sodium metabisulfite on the control of apple scab. J Phytopathol 164: 678–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12491
Arslan U, Ilhan K, Vardar C, Karabulut OA (2009) Evaluation of antifungal activity of food additives against soilborne phytopathogenic fungi. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 25:537–543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9921-1
Avenot HF, Michailides TJ (2007) Resistance to boscalid fungicide in Alternaria alternata isolates from pistachio in California. Plant Dis 91:1345–1350. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-91-10-1345
Baharom NA, Rahman MHA, Mohammad Shahid Shahrun MS, Suherman FHS, Siti Nur Hafizah Masdar SNM (2020) Chemical composition and antimicrobial activities of wood vinegars from carambola, coconut shells and mango against selected plant pathogenic microorganisms. Malays J Microbiol 16(6):438–445. https://doi.org/10.21161/mjm.190652
Baimark Y, Niamsa N (2009) Study on wood vinegars for use as coagulating and antifungal agents on the production of natural rubber sheets. Biomass Bioenergy 33:994–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2009.04.001
Bedmutha R, Booker CJ, Ferrante L, Briens C, Berruti F, Yeung KKC, Scott I, Conn K (2011) Insecticidal and bactericidal characteristics of the bio-oil from the fast pyrolysis of coffee grounds. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 90:224–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2010.12.011
Boratyn GM, Camacho C, Cooper PS, Coulouris G, Fong A, Ma N, Madden TL, Matten WT, McGinnis SD, Merezhuk Y, Raytselis Y, Sayers EW, Tao T, Ye J, Zaretskaya I (2013) BLAST: a more efficient report with usability improvements. Nucleic Acids Res 41:29–33. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt282
Bouket AC, Narmani A, Tavasolee A, Elyasi G, Abdi A, Naeimi S, Sharifi K, Oszako T, Alenezi FN, Belbahri L (2022) In vitro evaluation of wood vinegar (Pyroligneous Acid) VOCs inhibitory effect against a fungus-like microorganism Ovatisporangium (Phytopythium) isolate recovered from tomato fields in Iran. Agronomy 12:1609. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy12071609
Burnett AL, Lalancette N, McFarland KA (2010) Effect of QoI fungicides on colonization and sporulation of Monilinia fructicola on peach fruit and blossom blight cankers. Plant Dis 94:8. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-94-8-1000
Byrde RJW, Willetts HJ (1977) The brown rot fungi of fruit: their biology and control. Pergamon Press, New York, pp 15–22. https://www.elsevier.com/books/the-brown-rot-fungi-of-fruit/byrde/978-0-08-019740-1
Casals C, Segarra J, Torres R, Teixidó N, De Cal A, Usall J (2023) Validation of a warning system to control brown rot in peach and nectarine. Agron 13:254. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy13010254
Chalermsan Y, Peerapan S (2009) Wood vinegar: by-product from rural charcoal kiln and its role in plant protection. Asian J Food Agro-Ind Special Issue 189–195. http://www.pyroligneousacid.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2015/04/Wood-vinegar-a-by-product-from-rural-charcoal-kilns-and-its-role-in-plant-protection.pdf
Chen YH, Li YF, Wei H, Li XX, Zheng HT, Dong XY, Xu TF, Meng JF (2020) Inhibition efficiency of wood vinegar on grey mould of table grapes. Food Biosci 38:100–755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbio.2020.100755
Conway WS, Leverentz B, Janisiewicz WJ, Saftner RA, Camp MJ (2005) Improving biocontrol using antagonist mixtures with heat and/or sodium bicarbonate to control postharvest decay of apple fruit. Postharvest Biol Technol 36:235–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2005.01.006
Crepier J, Le Masle A, Charon N, Albrieux F, Duchene P, Heinisch S (2018) Ultra-high performance supercritical fluid chromatography hyphenated to atmospheric pressure chemical ionization high resolution mass spectrometry for the characterization of fast pyrolysis bio-oils. J Chromatogr A 1086:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2018.04.005
de Souza Araújo E, Pimenta AS, Feijo FMC, Castro RVO, Fasciotti M, Monteiro TVC, de Lima KMG (2017) Antibacterial and antifungal activities of Pyroligneous acid from wood of Eucalyptus urograndis and Mimosa tenuiflora. J Appl Microbiol 124:85–96. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13626
Durak MR, Arslan K, Silan E, Yildiz G, Ozkilinc H (2021) A novel approach for in vitro fungicide screening and the sensitivity of Monilinia populations from peach orchards in Turkey to respiratory inhibitor fungicides. Crop Prot 147:105688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2021.105688
Erper I, Kalkan C, Kaçar G, Türkkan M (2019) Antifungal effect of some boron salts against Penicillium expansum, which causes blue mold on apples. Anadolu J Agr Sci 34:250–258. https://doi.org/10.7161/omuanajas.515031
Erper I, Türkkan M, Karaca GH, Kılıç G (2011) Evaluation of in vitro antifungal activity of potassium bicarbonate against Rhizoctonia solani AG 4 HG-I, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum and Trichoderma sp. Afr J Biotechnol 10(43):8605–8612. https://doi.org/10.5897/AJB11.411
Eti Maden (2021) Activity Reports. Eti Maden, Ankara https://www.etimaden.gov.tr/storage/uploads/sunumlar/2022en/EtiMadenEN/dergi.html
Firouzbehi F, Efhamisisi D, Hamzeh Y, Tarmian A, Oladi R (2021) Pyrolysis acid as sustainable wood preservative against rot fungi. Biofuels Bioprod Biorefin 15:74–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/bbb.2149
Hossain MM, Scott IM, McGarvey BD, Conn K, Ferrante L, Berruti F, Briens C (2015) Insecticidal and anti-microbial activity of bio-oil derived from fast pyrolysis of lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose. J Pestic Sci 88:171–179. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-014-0568-4
Hrustić J, Mihajlović M, Grahovac M, Delibašić G, Tanović B (2018) Fungicide sensitivity, growth rate, aggressiveness and frost hardiness of Monilinia fructicola and Monilinia laxa isolates. Eur J Plant Pathol 151:389–400. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1380-9
Kadota M, Hirano T, Imizu K (2002) Pyroligneous acid improves in vitro rooting of Japanese Pear cultivars. Hortic Sci 37:194–195. https://doi.org/10.21273/HORTSCI.37.1.194
Kadota M, Niimi Y (2004) Effects of cytokinin types and their concentrations on shoot proliferation and hyperhydrocity in vitro pear cultivar shoots. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult (PCTOC) 72:261–265. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022378511659
Kara M, Soylu S, Kurt S, Soylu EM, Uysal A (2020) Determination of antagonistic traits of bacterial isolates obtained from apricot against green fruit rot disease agent Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. Acta Hortic 1290. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2020.1290.25
Koç İ, Yardım EN (2019) Investigation of the effects of pesticides and wood vinegar on some microbial and physico-chemical soil parameters. KSU J Agric Nat 22(6):896–904. https://doi.org/10.18016/ksutarimdoga.vi.550376
Kurt Ş, Emir B (2004) Effect of soil solarization, chicken litter and viscera on populations of soilborne fungal pathogens and pepper growth. Plant Pathol J 3(2):118–124. https://doi.org/10.3923/ppj.2004.118.124
Lebleu F, Cueto JD, Stefani P, Christen D (2019) Organic substances against Monilinia laxa on apricot – in-vitro and on-farm experiments. Agroscope. https://orgprints.org/id/eprint/37386/1/lebleu-etal-2019-Organic-products-test-Agroscope-FiBL_Poster.pdf
Lieten P (2002) Boron deficiency of strawberries grown in substrate culture. Acta Hortic 567:451–454. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2002.567.94
Martini C, Mari M (2014) Monilinia fructicola, Monilinia laxa (Monilinia Rot, Brown Rot). Postharvest Decay Control Strategies, Chapter 7:233–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-411552-1.00007-7
McLaren GF, Fraser JA, Lynch DG (1996) An evaluation of sulphur for brown rot control in Central Otago stone fruit. Proceedings of the New Zealand. Plant Protect Conf 49:32–36. https://doi.org/10.30843/nzpp.1996.49.11406
Mills AAS, Platt HW, Hurta RAR (2004) Effect of salt compounds on mycelial growth, sporulation and spore germination of various potato pathogens. Postharvest Biol Technol 34:341–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2004.05.022
Mu J, Uehara T, Furuno T (2003) Effect of bamboo vinegar on regulation of germination and radicle growth of seed plants. J Wood Sci 49:262–270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-002-0472-z
Numata K, Ogawa T, Tanaka K (1994) Effect of pyroligneous acid (Wood Vinegar) on several soilborne diseases. Proceedings of the Kanto-Tosan Plant Protection Society, 107–110. https://eurekamag.com/research/002/816/002816567.php
Obi VI, Barriuso JJ, Moreno MA, Giménez R, Gogorcena Y (2017) Optimizing protocols to evaluate brown rot (Monilinia laxa) susceptibility in peach and nectarine fruits. Australas Plant Pathol 46:183–189. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-017-0475-2
Obi VI, Barriuso JJ, Gogorcena Y (2018) Effects of pH and titratable acidity on the growth and development of Monilinia laxa (Aderh. & Ruhl.) in-vitro and in-vivo. Eur J Plant Pathol 145:815–827. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-017-1413-4
Ons L, Dany Bylemans DB, Thevissen K, Cammue BPA (2020) Combining Biocontrol Agents with Chemical Fungicides for Integrated Plant Fungal Disease Control. Microorganisms 8:1930. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8121930
Orak F, Nazik H, Yalcinkaya KT, Gundes A, Doganer A, Nazik S, Mulayim MK, Ozturk P. (2022) Antifungal efficacy of pure boron on yeast and mold isolates causing superficial mycosis. J Pak Med Assoc 72(7): 1330–1334. https://doi.org/10.47391/JPMA.2219
Oramahi HA, Yoshimura T (2013) Antifungal and antitermitic activities of wood vinegar from Vitex pubescens Vahl. J Wood Sci 59:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10086-013-1340-8
Psota V, Bagar M, Ackermann P, Veselovský M (2013) Control of brown rot blossom blight (Monilinia laxa) on apricot in organic agriculture. Integrated protection of fruit crops IOBC-WPRS Bulletin 91:357–360. https://www.ecofruit.net/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/56-psota-360-363-1.pdf
Rolshausen PE, Gubler WD (2005) Use of boron for the control of eutypa dieback of grapevines. Plant Dis 89(7):734–738. https://doi.org/10.1094/PD-89-0734
Rungjindamai N, Jeffries P, Xu XM (2014) Epidemiology and management of brown rot on stone fruit caused by Monilinia laxa. Eur J Plant Pathol 140:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-014-0452-3
Rungjindamai N, Xu XM, Jeffries P (2013) Identification and characterisation of new microbial strains of biocontrol of Monilinia laxa, the causal agent of brown rot on stone fruit. Agron 3:685–703. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy3040685
Scannavini M, Donati G, Pradolesi G, Cavazza F, Franceschelli F (2006) Efficacy of boscalid + pyraclostrobin (Signum) against peach brown rot in Emilia Romagna. Phytopathological Meeting 2006, Riccione (RN), 27–29 March 2006. Proceedings, pp 125–130 ref 3
Schnabel G, Bryson PK, Bridges WC, Brannen PM (2004) Reduced sensitivity in Monilinia fructicola to propiconazole in Georgia and implications for disease management. Plant Dis 88:1000–1004. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2004.88.9.1000
Shi XQ, Li BQ, Qin GZ, Tian SP (2011) Antifungal activity and possible mode of action of borate against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides on mango. Plant Dis 95:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS-06-10-0437
Souza JBG, Re-poppi N, Raposo JL (2012) Characterization of pyroligneous acid used in agriculture by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Braz Chem Soc 4:610–617. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0103-50532012000400005
Soylu EM, Kurt Ş, Soylu S (2010) In vitro and in vivo antifungal activities of the essential oils of various plants against tomato grey mould disease agent Botrytis cinerea. Int J Food Microbio 143(3):183–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2010.08.015
Spiegel J, Stammler G (2006) Baseline sensitivity of Monilinia laxa and M. fructigena to pyraclostrobin and boscalid. J Plant Dis Prot 113(5):199–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356181
Thomidis T, Exadaktylou E (2010) Effect of boron on the development of brown rot (Monilinia laxa) on peaches. Crop Prot 6:572–576. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2009.12.023
Thomidis T, Karagiannidis N, Stefanou S et al. (2015) Influence of boron applications on preharvest and postharvest nectarine fruit rot caused by brown rot. Australasian Plant Pathol 46:177–181. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-017-0474-3
Tiilikkala K, Fagernäs L, Tiilikkala J (2010) History and use of wood pyrolysis liquids as biocide and plant protection product. Open Agric 4:111–118. https://doi.org/10.2174/1874331501004010111
TUIK (2021) Crop Production Statistics. https://biruni.tuik.gov.tr/medas/?kn=92&locale=tr. (Date of Access 04 Jan 2022)
Türkkan M (2019) Effect of various salts on the growth and development of Geotrichum candidum, the causal agent of carrot sour rot. J Phytopathol 167:230–239. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12790
Türkkan M, Erper I (2015) Inhibitory influence of organic and inorganic sodium salts and synthetic fungicides against bean root rot pathogens. Gesunde Pflanzen 67:83–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10343-015-0339-z
Türkmen M, Kara M, Maral H, Soylu S (2022) Determination of chemical component of essential oil of Origanum dubium plants grown at different altitutes and antifungal activity against Sclerotinia sclerotiorum. J Food Process Preserv 46:15787. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfpp.15787
van Leeuwen GCM, Holb I, Jeger MJ (2002) Factors affecting mummification and sporulation of pome fruit in-fected by Monilinia fructigena in Dutch orchards. Plant Pathol J 51:787–793. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-3059.2002.00789.x
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In PCR protocols a guide to methods and applications, Academic Press, San Diego. 315–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-372180-8.50042-1
Acknowledgements
The author thank Şener Kurt (Professor) and Soner Soylu (Professor) for technical advice and support, Mahmut Keskin (Professor) for helping statistical analysis. In addition, all phases of this study were carried out in the laboratories of the Plant Health Clinic (BISAK) of Hatay Mustafa Kemal University.
Funding
This research has not received external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This study does not contain any studies with human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Uysal, A. Control of Monilinia blossom and twig blight (Monilinia laxa) by boron, pyroligneous acid and boscalid. J Plant Pathol 106, 211–223 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-023-01546-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-023-01546-3