Abstract
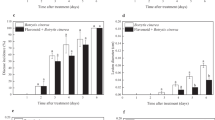
Gray mold, caused by Botrytis cinerea, is a major disease affecting postharvest apples, where it significantly reduces their commercial value. In this study, we conducted in vitro tests at a laboratory scale that showed that two monomeric phenols, caffeic acid and epicatechin, can directly inhibit the growth of B. cinerea in a dose-dependent manner. In in vivo experiments, caffeic acid or epicatechin treatment significantly reduced the incidence of ‘Fuji’ “Fuji” apple gray mold and inhibited lesion development. Relative to the control group, caffeic acid-treated apples inoculated with B. cinerea showed greater accumulation of disease-related proteins, lower H2O2 synthesis, less residual malondialdehyde (MDA), and reduced damage to cell membrane lipids. However, caffeic acid had no significant effect on the accumulation of superoxide anions (O2.−), ascorbic acid (AsA), or glutathione (GSH). In contrast, epicatechin treatment not only induced the accumulation of reactive oxygen species and disease-related proteins in apples, but also activated AsA and GSH biosynthesis. Caffeic acid and epicatechin treatments both inhibited the invasion and expansion of pathogens but did so by regulating different disease-related proteins. Caffeic acid mainly promoted the accumulation of chitinase (CHI), while epicatechin mainly induced the synthesis of β-1,3-glucanase (GLU).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeles FB, Forrence LE (1970) Temporal and hormonal control of beta-1,3-glucanase in Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Physiol 45:395–400. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.45.4.3953
Berrie AM, Xu X-M, Johnson D (2011) Lower temperatures more effective than atmosphere modification in controlling Botrytis and Nectria rots in stored apples. J Phytopathol 159:73–79
Boller T, Gehri A, Mauch F, Vogeli U (1983) Chitinase in bean leaves: induction by ethylene, purification, properties, and possible function. Planta 157:22–31. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00394536
Cao J, Jiang W, Zhao Y (2007) Physiological and biochemical experiment guidance for fruits and vegetables after harvest (1nd Ed ed.): China Light Industry Press
Chamnongpol S, Willekens H, Moeder W, Langebartels C, Sandermann H, Van Montagu A, Inze D, Van Camp W (1998) Defense activation and enhanced pathogen tolerance induced by H2O2 in transgenic tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5818–5823. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.10.5818
Chen ZX, Ricigliano JW, Klessig DF (1993) purification and characterization of a soluble salicylic acid-binding protein from tobacco. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:9533–9537. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.90.20.9533
Coleysmith JR, Verhoeff K, Jarvis WR (1980) The Biology of Botrytis. Academic Press
Davey M W, Van Montagu M, Inze D, Sanmartin M, Kanellis A, Smirnoff N, Benzie I J, Strain J, Favell D, Fletcher J (2000) Plant L-ascorbic acid: chemistry, function, metabolism, bioavailability and effects of processing. J Sci Food Agric 80:825–860
Dean R, Van Kan JAL, Pretorius ZA, Hammond-Kosack KE, Di Pietro A, Spanu PD, Rudd J, Dickman M, Kahmann R, Ellis J, Foster GD (2012) The Top 10 fungal pathogens in molecular plant pathology. Mol Plant Pathol 13:414–430. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1364-3703.2011.00783.x
Dietz KJ, Mittler R, Noctor G (2016) Recent progress in understanding the role of reactive oxygen species in plant cell signaling. Plant Physiol 171:1535–1539. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.16.00938
Fan JB, Cai XT, Feng XQ, Hou Y, Xiao-Feng YU, Jiang M (2014) The comparison of five natural phenolic compounds on antioxidant activity in vitro. Food Ferment Ind 40:77–83. https://doi.org/10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2014.07.002
Fraga CG, Oteiza PI, Galleano M (2018) Plant bioactives and redox signaling: (-)-Epicatechin as a paradigm. Mol Aspects Med 61:31–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2018.01.007
He JH, Ma LJ, Wang DJ, Zhang MY, Zhou HL (2019) Ferulic acid treatment reinforces the resistance of postharvest apple fruit during gray mold infection. J Plant Pathol 101:503–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-018-00223-0
Huang R, Yi F, He H, Wu S, Fang J, Yang m, (2014) Antioxidant activity of (-)-epicatechin from the root Tubers of Fagopyrum dibotrys. Food Sci 35:118–121. https://doi.org/10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201415024
Jacobo-Velazquez DA, Gonzalez-Aguero M, Cisneros-Zevallos L (2015) Cross-talk between signaling pathways: the link between plant secondary metabolite production and wounding stress response. Scie Rep 5:10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep08608
Kalinowska M, Bielawska A, Lewandowska-Siwkiewicz H, Priebe W, Lewandowski W (2014) Apples: content of phenolic compounds vs. variety, part of apple and cultivation model, extraction of phenolic compounds, biological properties. Plant Physiol Biochem 84:169–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2014.09.006
Lachhab N, Sanzani SM, F Fallanaj, Youssef K, F Nigro, Boselli M, Ippolito A (2015) Protein hydrolysates as resistance inducers for controlling green mould of citrus fruit. Acta Hortic 1065:1593–1598. https://doi.org/10.17660/ActaHortic.2015.1065.203
Lima VN, Oliveira-Tintino CDM, Santos ES, Morais LP, Tintino SR, Freitas TS, Geraldo Yuri S, Pereira Raimundo LS, Cruz Rafael P, Menezes Irwin RA, Coutinho HDM (2016) Antimicrobial and enhancement of the antibiotic activity by phenolic compounds: gallic acid, caffeic acid and pyrogallol. Microb Pathog 99:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2016.08.004
Ma LJ, He JH, Liu H, Zhou HL (2018) The phenylpropanoid pathway affects apple fruit resistance to Botrytis cinerea. J Phytopathol 166:206–215. https://doi.org/10.1111/jph.12677
Macarisin D, Cohen L, Eick A, Rafael G, Belausov E, Wisniewski M, Droby S (2007) Penicillium digitatum suppresses production of hydrogen peroxide in host tissue during infection of citrus fruit. Phytopathology 97:1491–1500. https://doi.org/10.1094/phyto-97-11-1491
Meyer AJ (2008) The integration of glutathione homeostasis and redox signaling. J Plant Physiol 165:1390–1403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jplph.2007.10.015
Prakash M, Basavaraj BV, Murthy KNC (2019) Biological functions of epicatechin: Plant cell to human cell health. J Funct Food 52:14–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2018.10.021
Roberto SR, Youssef K, Hashim AF, Ippolito A (2019) Nanomaterials as alternative control means against postharvest diseases in fruit crops. Nanomaterials 9:20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9121752
Romanazzi G, Smilanick JL, Feliziani E, Droby S (2016) Integrated management of postharvest gray mold on fruit crops. Postharvest Biol Technol 113:69–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.11.003
Spotts RA, Serdani M (2006) Inoculum sources of Botrytis cinerea important to pear orchards in Oregon. Plant Dis 90:750–754. https://doi.org/10.1094/pd-90-0750
Suarez B, Alvarez AL, Garcia YD, del Barrio G, Lobo AP, Parra F (2010) Phenolic profiles, antioxidant activity and in vitro antiviral properties of apple pomace. Food Chem 120:339–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.09.073
Takshak S, Agrawal SB (2015) Defence strategies adopted by the medicinal plant Coleus forskohlii against supplemental ultraviolet-B radiation: augmentation of secondary metabolites and antioxidants. Plant Physiol Biochem 97:124–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.09.018
Wood M (2006) Nuts’–new aflatoxin fighter: caffeic acid? Agricul Res 54:9
Wu GS, Shortt BJ, Lawrence EB, Leon J, Fitzsimmons KC, Levine EB, Raskin I, Shah DM (1997) Activation of host defense mechanisms by elevated production of H2O2 in transgenic plants. Plant Physiol 115:427–435. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.115.2.427
Youssef K, Roberto SR (2021) Chitosan/silica nanocomposite-based formulation alleviated gray mold through stimulation of the antioxidant system in table grapes. Int J Biol Macromol 168:242–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.12.047
Youssef K, Roberto SR, Oliveira A (2019) Ultra-structural alterations in Botrytis cinerea-the causal agent of gray mold-treated with salt solutions. Biomolecules 9:17. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9100582
Zhu Z, Tian SP (2012) Resistant responses of tomato fruit treated with exogenous methyl jasmonate to Botrytis cinerea infection. Sci Hortic 142:38–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2012.05.002
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Modern Agricultural Industry Technology System of Apple (China), Grant/Award Number nycytx-08-05-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships with people or organizations that can inappropriately influence this work. There is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service, and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, M., Liu, H., Yue, Z. et al. The effects of caffeic acid and epicatechin treatment on gray mold resistance and antioxidant metabolism in apples. J Plant Pathol 104, 661–670 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-022-01054-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42161-022-01054-w