Abstract
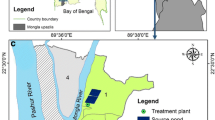
Waterborne infections have long posed a significant challenge in the slums of emerging cities, including Dodoma, the administrative capital of Tanzania. Access to safe drinking water is challenged in Dodoma, Tanzania where shallow wells are common sources. This study assessed microbiological quality and health risks of shallow well water in Chang’ombe ward, one of Dodoma’s largest informal settlements housing over 12,000 residents per km2. Water samples from 13 wells were collected during rains and analyzed for bacteria and protozoa using standard methods. Questionnaires provided data on sanitation and reported illnesses. Analysis revealed widespread bacterial contamination above WHO guidelines, with 96% of samples containing fecal indicator bacteria Escherichia coli at mean counts of 40 CFU/100 ml. Pathogenic protozoa Giardia lamblia were detected in 23% of samples at 3–4 CFU/100 ml. Field observations implicated improper human and solid waste disposal allowing fecal contamination of wells. Over 60% of households reported cases of diarrhea and 35% typhoid in the past year, correlating to detected pathogens. As Dodoma’s population doubles, health risks from contaminated groundwater sources escalate without improved sanitation and hygiene. Urgent interventions such as upgrading infrastructure, promotion of low-cost treatment and safe hygiene practices are needed to protect this vulnerable community from waterborne disease burden.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Balkhair, K. S. (2016). Microbial contamination of vegetable crop and soil profile in arid regions under controlled application of domestic wastewater. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences, 23(1), S83–S92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2015.10.029
Baltag, V. (2023). Progress on drinking water, sanitation and hygiene in schools: Global overview on the WASH programme. European Journal of Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurpub/ckad160.190
Brugger, S. D., Baumberger, C., Jost, M., Jenni, W., Brugger, U., & Mühlemann, K. (2012). Automated counting of bacterial colony forming units on agar plates. PLoS One, 7(3), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033695
Cairo, S. B., Pu, Q., Malemo Kalisya, L., Fadhili Bake, J., Zaidi, R., Poenaru, D., & Rothstein, D. H. (2020). Geospatial mapping of pediatric surgical capacity in North Kivu, democratic republic of congo. World Journal of Surgery. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-020-05680-2
Costa, D., & Iraola, G. (2019). Pathogenomics of emerging Campylobacter species. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 32(4), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00072-18
D’Enfert, C., Kaune, A. K., Alaban, L. R., Chakraborty, S., Cole, N., Delavy, M., Kosmala, D., Marsaux, B., Frois-Martins, R., Morelli, M., & Rosati, D. (2021). The impact of the fungus-host-microbiota interplay upon Candida albicans infections: Current knowledge and new perspectives. FEMS Microbiology Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsre/fuaa060
Drzewiecka, D. (2016). Significance and Roles of Proteus spp. Bacteria in Natural Environments. Microbial Ecology, 72(4), 741–758. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-015-0720-6
Espelage, W., der an Heiden, M., Stark, K., & Alpers, K. (2010). Characteristics and risk factors for symptomatic Giardia lamblia infections in Germany. BMC Public Health. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2458-10-41
Hamilton, A. L., Kamm, M. A., & Ng, S. C. (2018). Proteus spp. as putative gastrointestinal pathogens. Clinical Microbiology Reviews, 31(3), 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00085-17
Hofmann, P. (2022). Toward equitable urban water supply and sanitation in Dar es Salaam: The dialectic relationship between policy-driven and everyday practices. Utilities Policy, 78(June), 101395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jup.2022.101395
Ishii, S., & Sadowsky, M. J. (2008). Escherichia coli in the environment: Implications for water quality and human health. Microbes and Environments, 23(2), 101–108. https://doi.org/10.1264/jsme2.23.101
Jalolitdin, N., & Erkinovich, S. (2022). Bacteria of the genus proteus as sanitary indica ive microorganisms of water bodies. 4(1), 4–6. https://doi.org/10.37532/puljem.22.4(1).1
Jang, J., Hur, H. G., Sadowsky, M. J., Byappanahalli, M. N., Yan, T., & Ishii, S. (2017). Environmental Escherichia coli: Ecology and public health implications—a review. Journal of Applied Microbiology, 123(3), 570–581. https://doi.org/10.1111/jam.13468
Kaper, J. B., Nataro, J. P., & Mobley, H. L. T. (2004). Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 2(2), 123–140. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro818
Laluraj, C. M., Gopinath, G., Dinesh Kumar, P. K., & Seralathan, P. (2006). Seasonal variations in groundwater chemistry of a phreatic coastal and crystalline terrain of central Kerala, India. Environmental Forensics, 7(4), 335–344. https://doi.org/10.1080/1527592060099630
Li, P., Karunanidhi, D., Subramani, T., & Srinivasamoorthy, K. (2021). Sources and consequences of groundwater contamination. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 80(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-020-00805-z
Liu, F., Ma, R., Wang, Y., & Zhang, L. (2018). The clinical importance of campylobacter concisus and other human hosted Campylobacter species. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology, 8, 243. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2018.00243
Liu, Y. R., van der Heijden, M. G., Riedo, J., Sanz-Lazaro, C., Eldridge, D. J., Bastida, F., Moreno-Jiménez, E., Zhou, X. Q., Hu, H. W., He, J. Z., & Moreno, J. L. (2023). Soil contamination in nearby natural areas mirrors that in urban greenspaces worldwide. Nature Communications, 14(1), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37428-6
Lopes, J. P., & Lionakis, M. S. (2022). Pathogenesis and virulence of Candida albicans. Virulence, 13(1), 89–121. https://doi.org/10.1080/21505594.2021.2019950
Mwesongo, C. S., & Mwakipesile, A. E. (2023). Trends for sanitation practices in Tanzania: The history from colonial to current times. Journal of Water Sanitation and Hygiene for Development, 13(4), 265–275. https://doi.org/10.2166/washdev.2023.158
Nkrumah, B., & Nguah, S. (2011). Giardia lamblia: A major parasitic cause of childhood diarrhoea in patients attending a district hospital in Ghana. Parasites and Vectors, 4(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-3305-4-163
Oluyege, J. O., Olowomofe, T., & Abiodun, O. (2014). Microbial Contamination of Packaged Drinking Water in Ado-Ekiti Metropolis, South Western Nigeria. American Journal of Research Communication, 2(10), 231–246.
Rafiei, A., Rahdar, M., & Valipour Nourozi, R. (2014). Isolation and Identification of Parasitic Protozoa in Sampled Water From the Southwest of Iran. Jundishapur Journal of Health Sciences, 6(4), 10–13. https://doi.org/10.5812/jjhs.23462
Ringo, J. (2016). Status of Sewage Disposal in Dodoma Municipality, Tanzania., International Journal of Marine, Atmospheric & Earth Sciences Int. J. Mar. Atmos. & Earth Sci, 4(1), pp. 24–34. Available at: www.ModernScientificPress.com/Journals/IJMaes.aspx.
Ruheka, A., Luthi, C., & Kessy, F. (2008). Chang’ombe Status Assessment Report, Dodoma, February 2008. Maji na Maendeleo (NGO) Dodoma, Tanzania; Sandec/Eawag, Dübendorf, Switzerland; and Ifakara Health Research & Development Centre, Dodoma, Tanzania
Terefe, Y., Deblais, L., Ghanem, M., Helmy, Y. A., Mummed, B., Chen, D., Singh, N., Ahyong, V., Kalantar, K., Yimer, G., & Yousuf Hassen, J. (2020). Co-occurrence of campylobacter species in children from eastern ethiopia, and their association with environmental enteric dysfunction diarrhea, and host microbiome. Frontiers in Public Health, 8(April), 1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2020.00099
Thomas, J., Holbro, N., & Young, D. (2013). A Review of Sanitation and Hygiene in Tanzania. Dar es Salaam. https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/media/57a08a2fed915d3cfd000628/tanzania-sanitationreview.pdf.
United Nations Department of Social Affairs (UNDESA) (2020) ‘Towards Sustainable Development For All’, https://www.unwater.org/sites/default/files/app/uploads/2021/11/Annual-Report-2020.pdf.
URT, Tanzania. Ministry of Water. (2016). Impact Evaluation of the Rural Water Supply and Sanitation Programme, United Republic of Tanzania: Volume I. Dar es Salaam: African Development Bank. https://idev.afdb.org/sites/default/files/Evaluations/2020-03/Tanzania%20-%20Impact%20Evaluation%20of%20the%20Rural%20Water%20Supply%20and%20Sanitation%20Programme.pdf.
United Republic of Tanzania [URT]. (2021). the United Republic of Tanzania Prime Minister’s Office Regional Administration and Local Government Dodoma Municipal Council Strategic’. Available at: https://dodomacc.go.tz/storage/app/uploads/public/61c/54d/fa4/61c54dfa48781312582168.pdf.
URT. (2022). Administrative Units Population Distribution Report. National Population and House Census of Tanzania. National Bureau of Statistics, Dar es Salaam, Tanzania. https://www.nbs.go.tz/nbs/takwimu/Census2022/Administrative_units_Population_Distribution_Report_Tanzania_volume1a.pdf.
Van Elsas, J. D., Semenov, A. V., Costa, R., & Trevors, J. T. (2011). Survival of Escherichia coli in the environment: Fundamental and public health aspects. ISME Journal, 5(2), 173–183. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2010.80
WBG. (2017). Reaching for the SDGs: the untapped potential of tanzania’s water supply, sanitation, and hygiene sector. WASH poverty diagnostic, pp. 16–23. Available at: http://documents.worldbank.org/curated/en/143241507014979219/Reaching-for-the-SDGs-the-untapped-potential-of-Tanzania-s-water-supply-sanitation-and-hygiene-sector-executive-summary.
Zaongo, S. D., Ouyang, J., Isnard, S., Zhou, X., Harypursat, V., Cui, H., Routy, J. P., & Chen, Y. (2023). Candida albicans can foster gut dysbiosis and systemic inflammation during HIV infection. Gut Microbes, 15(1), 1–24. https://doi.org/10.1080/19490976.2023.2167171
Acknowledgements
The acknowledgment of Ms. Flora S. Paul, who was actively involved in data collection during her pursuit of a BSc in Environmental Sciences at the University of Dodoma, is hereby recognized by the author.
Funding
This work was funded by the University of Dodoma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MMK was responsible for developing the study concept, designing the methodology, conducting formal analysis, visualization, data collection, and performing the laboratory experiment. MMK contributed to the study by reviewing and editing the work, providing critical revision, and supervising the research process. The final version of the manuscript, ready for publication, has been reviewed, approved, and signed by both authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal ties that would have influenced the work presented in this study.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kwikima, M.M. Analyzing the presence of microbial contaminants in water sourced from shallow wells within Dodoma city, Tanzania. Int J Energ Water Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-024-00278-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-024-00278-z