Abstract
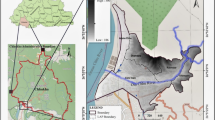
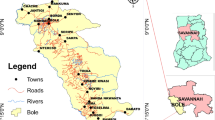
This study explores possible groundwater areas in the Ogun drainage basin in Ogun State, Nigeria, using the Vertical Electrical Sounding VES system for remote sensing and GIS. Thematic maps are built as geodatabase or GIS layers of lineament density, lithology, land use and land cover, drainage and slopes. Each layer is given weights based on a pair comparison of considerable factors in the retention, storage and transmission of groundwater. Potentials are created through the analysis process hierarchy (AHP) in a GIS environment that includes five thematic maps with factors that result in groundwater occurrence and movement using weighted overlay. We assigned weightages of factors influencing groundwater prospects such that lithology had the highest (43%) followed by lineament density (33%). Slope weighed (13%) and drainage density (7%). The least groundwater contributor in the study area, {is the} land use/land cover was assigned 4%. The AHP consistency ratio CR was calculated to be 0.04 for this analysis which is less than the threshold consistency value of 0.10. The result of the study showed that high groundwater potential occupies 3818.57km2 (21%) and low potential areas constitute 1022.50 km2 (6%) of the study area including. The moderate and very low potentials occupy the highest coverage constitute about 5530.63 km2 (31%) and 7725.37 km2 (42%) respectively. Validation of the aquifers from the VES shows that the GIS analysis map for groundwater potential corresponds to field results. However, it is suggested to add more detailed VES data, well data/pumping tests into the GPZ map for accurate validation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdulrazzaq, Z. T., Agbasi, O. E., Aziz, N. A., & Etuk, S. E. (2020). Identification of potential groundwater locations using geophysical data and fuzzy gamma operator model in Imo, Southeastern Nigeria. Applied Water Science, 10, 188.
Adegoke, O. S., Ogbe, F. G. A., & Jan Du Chene, R. E. (1976). Excursion to the Ewekoro quarry(Paleocene-Eocene). Geology Guide Nigerian Cretaceous-Recent Loc, 1, 1–17.
Adiat, K. A. N., Nawawi, M. N. M., & Abdullah, K. (2012). Assessing the accuracy Of GIS- based elementary multi-criteria decision analysis as spatial prediction tool: a case of predicting potential zones of sustainable groundwater resources. Journal of Hydrology, 440–441, 75–89.
Agbasi, O. E., Aziz, N. A., Abdulrazzaq, Z. T., & Etuk, S. E. (2019). Integrated geophysical data and GIS technique to forecast the potential groundwater locations in part of South Eastern Nigeria. Iraqi Journal of Science, 60(5), 1013–1022.
Al-Hadithi, M., Singhal, D. C., & Israel, M. (2003). Evaluation ofgroundwater resources potentialinRatman-PathriRao Watershed Haridwar District,Uttaranchal,India,using geoelectrical,remotesensing and GIStechniques. In V. P. Singh & R. N. Yadava (Eds.), Groundwater pollution. New Delhi: Allied Publishers.
Anayah, F., & Kaluarachi, J. J. (2009). Groundwater resources of NorthernGhana:initial assessment ofdataavailability. Logan: Utah State University College of Engineering.
Ayazi, M. H., Pirasteh, S., Arvin, A. K. P., Pradhan, B., Nikouravan, B., & Mansor, S. (2010). Disasters and risk reduction in groundwater: Zagros Mountain Southwest Iran using geo-informatics techniques. Disaster Advances, 3(1), 51–57.
Chowdhary, V. M., Roan, N. H., & Sarma, P. B. S. (2003). GIS based decision support system for groundwater assessment in large irrigation project areas. Agricultural Water Management, 62, 229–252.
Chowdhury, M. K. J., & Chowdary, V. M. (2010). Delineation ofgroundwaterrecharge zones andidentification of artificial rechargesitesin West MedinipurDistrict, West Bengal usingRS, GISand MCDM techniques. Journal of Environmental Earth Sciences, 59(6), 1209–1222.
Coker, J. O., Makinde, V., Adesodun, J. K., & Mustapha, A. O. (2013). Integration of Geophysical and Geotechnical Investigation for a proposed New Lecture Theatre at Federal University of Agriculture, Abeokuta, South Western Nigeria. International Journal of Emerging Trends in Engineering and Development, 5, 338–348.
Ejepu, S. J., Olasehinde, P. I., Omar, D. M., Abdullahi, D. S., Adebowale, T. A., & Ochimana, A. (2005). Integration of geology, remote sensing and geographic information system in assessing groundwater potential of Piako Sheet 185 North-Central Nigeria. Journal of Information Education Science and Technology (JIEST), 2(1), 145–155.
Fashae, N., Moshood, A. O. T., & Adedeji, O. I. (2014). Delineation ofgroundwater potential zones in the crystallinebasement terrain of southwest Nigeria: anintegrated GISand RemoteSensing approach. Applied Water Science, 14, 19–38.
Hiscock, M. (2006). Application of resistivity survey and geographical information system (GIS) analysis for hydrogeological zoning of a piedmont area, Himalayan foothill region, India. Hydrogeology Journal, 14, 753–759.
Jain, P. K. (1998). Remote sensing techniques to locate ground water potential zones in upper Urmil River basin, district Chatarpur-central India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing., 26(3), 135–147.
Jones, H. A., & Hockey, R. D. (1964). The geology of parts of south western Nigeria. Bulletin Geological Survey Nigeria, 31, 101.
Khalek, A.A., Ahmed, O. (2008). Integration of remote sensing, geophysics and GIS to evaluate groundwater potentiality—a case study in Sohag Region, Egypt. The 3rd international conference on water resources and arid environments, 1st Arab Water Forum, 2008
Kilicoglu, C., Cetin, M., Aricak, B., & Sevik, H. (2020a). Site selection by using the multi-criteria technique-a case study of Bafra, Turkey. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 192(9), 608.
Kilicoglu, C., Cetin, M., Aricak, B., & Sevik, H. (2020b). Integrating multicriteria decision-making analysis for a GIS-based settlement area in the district of Atakum, Samsun, Turkey. Theoretical and Applied Climatology, 143(1), 379–388.
Krishnamurthy, J., Venkataesa, K. N., Jayarama, V., & Manivel, M. (1996). An approach to demarcate groundwater potential zones through Remote Sensing and GIS. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 17(10), 1867–1884.
Magesh, N. S., Chandrasekar, N., & Soundranayagam, J. P. (2012). Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosciences Frontiers, 3(2), 189–196.
Mogaji, K. A., Aboyeji, O. S., & Omosuyi, G. O. (2011). Mappingof lineaments for groundwatertargetinginthe basement complexregion of Ondo State,Nigeria, using RemoteSensingand GeographicInformation System (GIS) techniques. International Journal of Water Resources and Environmental Engineering, 3(7), 150–160.
Muheeb, M.A., Mohammed, M. (2001). Integrated GIS and Remote Sensing for mapping groundwater potential zones in Tulul al Ashaqif highlands, NE Jordan. Unpublished doctoral dissertation Jordan University
Murthy, K. S. R. (2000). Groundwater potential in a semi-arid region of Andhara Pradesh, a geographical information system approach. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 21(9), 1867–1884.
Nag, S. K. (2005). Application of lineament density and hydrogeomorphology to delineate groundwater potential zones of Baghmundi block in Purulia district, West Bengal. Journal of Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 33(4), 513–521.
Obaje, N. G. (2009). Geology and mineral resources of Nigeria. Berlin: Springer.
Obi-Reddy, G. P., Chandra, M. K., Srivastav, S. K., Srinivas, C. V., & Maji, A. K. (2000). Evaluation of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing data- a case study of Gaimukh watershed, Bhandara district, Maharashtra. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 28, 19–32.
Prasad, R. K., Mondal, N. C., Banerjee, P., Nandakumar, M. V., & Singh, V. S. (2008). Deciphering potential groundwater zone in hard rock through the application of GIS. Environmental Geology, 55(3), 467–475.
Rahaman, M. A. (1976). A reviewof thebasement geologyof South Western Nigeria. In C. A. Kogbe (Ed.), GeologyofNigeria (pp. 41–58). Surulere: Elizabethan Publishing.
Saaty, T. L. (1980). The analytic hierarchy process: planning, priority setting, resource allocation. New York: McGraw-Hill.
Saaty, T. L. (1992). Decision making for leaders. Pittsburgh: RWS Publications.
Saraf, A. K., & Choudhary, P. R. (1998). Integrated remote sensing and GIS for groundwater exploration and identification of artificial recharge sites. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 19(10), 1825–1841.
Sarkar, B. C., Deota, B. S., Raju, P. L. N., & Jugran, D. K. (2001). A geographic information system approach to evaluation of groundwater potentiality of Shamri micro-watershed in the Shimla taluk, Himachal Pradesh. Journal Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 29(3), 151–164.
Sener, E., Davraz, A., & Ozcelik, M. (2005). An Integration of GIS and remote sensing in groundwater investigations: a case study in Burdur, Turkey. Hydrogeology Journal, 13, 826–834.
Singh, A.K., Prakash, S.R. (2002). An integrated approach of remote sensing, geophysics and GIS to evaluation of groundwater potentiality of Ojhala sub-watershed, Mirjapur district, UP, India. In: Asian Conference on GIS, GPS, aerial photography and remote sensing, Bangkok-Thailand.
Subba, R. N., Chakradhar, G. K. J., & Srinivas, V. (2001). Identification of groundwater potential zones using remote sensing techniques in and Around Guntur Town, Andhra Pradesh, India. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 29, 69–78.
Subramanya, G. J., Ritsema, I. L., & De Jong, S. J. (2008). Electromagneticprospecting for groundwaterin Precambrian Terrains in the Republicof Upper Volta. Geophysical Prospecting, 29, 932–955.
Surrette, M., Allen, D., & Journeay, M. (2008). Regional evaluation of hydraulic properties in variably fractured rock using a hydro-structural domain approach. Hydrogeology Journal, 16(1), 11–30.
Teeuw, R. (1995). Ground water exploration using remote sensing and a low-cost geographic information system. Hydrogeology Journal, 3, 21–30.
Yeh, H. F., Lee, C. H., Hsu, K. C., & Chang, P. H. (2009). GIS for the assessment of the groundwater recharge potential zone. Environmental Geology, 58, 185–195.
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict ofinterest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aladeboyeje, A.I., Coker, J.O., Agbasi, O.E. et al. Integrated hydrogeophysical assessment of groundwater potential in the Ogun drainage basin, Nigeria. Int J Energ Water Res 5, 461–475 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-021-00121-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42108-021-00121-9