Abstract
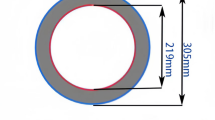
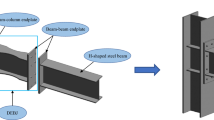
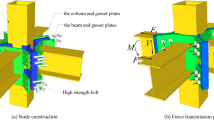
Since the last decade, Castellated steel sections are being used in steel constructions for their valuable characteristics, such as being lightweight, having superior aesthetics, a higher strength-to-weight ratio, and comfort to handlement. A steel I-section that has been modified to have two portions split longitudinally along its web in a particular arrangement is kNown as a castellated steel column. The two cut portions are reconnected after moving to produce a perforated column with a larger width and strength. Castellated steel columns (CSC) are divided into groups according to the many types of job openings that are available in the component i.e. hexagonal, circular, diamond, sinusoidal, octagonal, etc. are a few of the most popular opening shapes. According to studies, the introduction of differently shaped web openings affects the structural behaviour of CSC. In this experimental investigation, the behaviour of CSCs with circular and diamond-shaped openings has been studied under axial loading and validated the results by using the ANSYS software. According to the results, the load-carrying capacity of the CSC with circular-shaped openings (with MS stiffener) is on average 17.3% higher than that of the CSC with circular-shaped openings (without stiffener). The load- carrying capacity of the CSC with diamond-shaped openings (with MS stiffener) is on average 6% higher than the load-carrying capacity of the diamond-shaped openings (without stiffener). The study concludes that the CSC with circular openings performs better than the CSC with diamond openings.


























Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
7. References
Dhede, M., & Shirsat, M. (2020). Geometrical optimization and buckling analysis of castellated steel column. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 7, 1304–1307.
El-Sawy, K. M., Sweedan, A. M. I., & Martini, M. I. (2009). Major-axis elastic buckling of axially loaded castellated steel columns. Thin-Walled Structures, 47, 1295–1304.
El-Tobgy, H. H., Abu-Sena, A. B. B., & Fares, M. W. (2021). Experimental and parametric investigation of castellated steel beam column in various expansion ratios, lengths and loading conditions. Structures, 33, 484–507.
Gorakshanath, S., & Autade, P. B. (2017). Experimental Investigation on buckling analysis of castellated column with software. International Journal of Advance Research and Innovative Ideas in Education, 3, 694–710.
Huddar, R. R., & Sagade, A. V. (2019). Comparative study and Buckling Analysis of hollow castellated column by experimentation and software Analysis. International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology, 6, 3512–3515.
Junus, M., Herman, P., Jonie, T., & Rudy, D. (2014). Behaviour of castellated beam column due to cyclic loads. International Journal of Technology Enhancements and Emerging Engineering Research, 2, 36–39.
Kaveh, A., & Fakoor, A. (2021). Cost optimization of steel-concrete composite floor systems with castellated steel beams. Periodica Polytechnica Civil Engineering, 65(2), 353–375.
Kaveh, A., & Ghafari, M. H. (2016). Optimum design of steel floor system: Effect of floor division number, deck thickNess and castellated beams. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 59(5), 933–950.
Kaveh, A., & Shokohi, F. (2016). Application of grey wolf optimizer in the design of castellated beams. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering (BHRC), 17(5), 683–700.
Kaveh, A., Kaveh, A., & Shokohi, F. (2016). A hybrid optimization algorithm for the optimal design of laterally-supported castellated beams. Scientia Iranica, 23(2), 508–519.
Kaveh, A., Almasi, P., & Khodagholi, A. (2023). Optimum design of castellated beams using four recently developed meta-heuristic algorithms. Iranian Journal of Science and Technology, Transactions of Civil Engineering, 47(2), 713–725.
Kaveh, A., & Ghafari, M. H. (2017). Optimum design of castellated beams: Effect of composite action and semi-rigid connections. Scientia Iranica, 25, 162–173.
Morkhade, S. G., Lokhande, R. S., Gund, U. D., Divate, A. B., Deosarkar, S. S., & Chavan, M. U. (2020). Structural behaviour of castellated steel beams with reinforced web openings. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 21, 1–13.
Sonck, D., & Belis, J. (2016). Weak-axis flexural buckling of cellular and castellated columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 124, 91–100.
Thomas, A. C., & Baskar, K. (2018). Strengthening of thin-webbed castellated column using CFRP. International Journal for Computational Methods in Engineering Science and Mechanics, 19, 1–9.
Yuan, W., & BoksunKimb, L.-y. (2014). Buckling of axially loaded castellated steel columns. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 92, 40–45.
Funding
No any funding is available for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by RAP and PBS. The first draft of the manuscript was written by RAP and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Patil, R.A., Salgar, P.B. Experimental investigation on structural behaviour of castellated column under axial load. Asian J Civ Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-024-01070-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-024-01070-4