Abstract
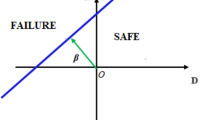
Large deflection of a simply supported beam (SSB) carrying central point load is a well-known area in mechanics that has been researched extensively by numerous scholars. Various techniques, including the finite element approach and analytical exact solutions, have been implemented. Few researchers also used machine learning (ML) technique to predict deflection of SSB. This study offers ML based prediction method for deflection of SSB carrying point load and compares the applicability and adaptability of ridge regression model, artificial neural network and Gaussian process regression (GPR) in the reliability investigation of SSB. The central point load (W), beam length (L), beam width (B), beam depth (D), and concrete’s modulus of elasticity (E) are the five key input parameters that these three machine learning models take into consideration when applying them to 200 datasets in order to predict the beam deflection (∆) at the centre of the beam. The effectiveness of the well-established ML models is evaluated using a variety of performance metrics, such as coefficient of determination (R2), variance account factor, A-10 index, root mean square error (RMSE), mean absolute error and mean absolute deviation. Based on performance parameters, the findings indicate that, out of the three suggested machine learning models, GPR had the best predictive performance. This was attributed to its maximum R2 = 1.000 and the lowest RMSE = 1.157E-06 during the training phase, as well as R2 = 0.999 and RMSE = 0.006 during the testing phase. Rank analysis, reliability analysis, regression plot, William’s plot, and error matrix plot are further tools used to assess the performance of the model. First-order second moment (FOSM) approach is used to determine the reliability index (β) of the model and compared with the actual value. A sensitivity analysis is also carried out to determine the impact of each input parameter on the result.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data presented in the paper are available with authors.
References
Bardhan, A., Kardani, N., GuhaRay, A., Burman, A., Samui, P., & Zhang, Y. (2021). Hybrid ensemble soft computing approach for predicting penetration rate of tunnel boring machine in a rock environment. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering, 13(6), 1398–1412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.06.015
Batbooti, R., Mohammed, B., Jabbar, T., & Faisal, S. H. (2023). Bayesian regression based approach for beam deflection estimation. Advances in Science and Technology. https://doi.org/10.12913/22998624/166313
Cortes, J. C., Lopez-Navarro, E., Romero, J.-V., & Rosello, M. D. (2023). Probabilistic analysis of a cantilever beam subjected to random loads via probability density functions. Computational and Applied Mathematics, 42(1), 42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40314-023-02194-0
Dan, W., Yue, X., Yu, M., Li, T., & Zhang, J. (2023). Prediction and global sensitivity analysis of long-term deflections in reinforced concrete flexural structures using surrogate models. Materials, 16, 4671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16134671
Eamon, C., & Jensen, E. (2012). Reliability analysis of prestressed concrete beams exposed to fire. Engineering Structures, 43(4), 69–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.engstruct.2012.05.016
Eidgahee, D. R., Soleymani, A., Hasani, H., Kontoni, D. N., & Jahangir, H. (2023). Flexural capacity estimation of FRP reinforced T-shaped concrete beams via soft computing techniques. Computers and Concrete, 32(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.12989/cac.2023.32.1.001
Ghani, S., Kumari, S., & Bardhan, A. (2021). A novel liquefaction study for fine-grained soil using PCA-based hybrid soft computing models. Sadhna, 46(3), 113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-021-01640-1
Hoerl, A. E., & Kennard, R. W. (1970). Ridge regression: Biased estimation for non-orthogonal problems. Technometrics, 12(1), 55–67. https://doi.org/10.1080/00401706.1970.10488634
Kaveh, A. (2017). Applications of metaheuristic optimization algorithms in civil engineering. Switzerland: Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48012-1_1
Kaveh, A., & Ghaffarian, R. (2015). Shape optimization of arch dams with frequency constraints by enhanced charged system search algorithm and neural network. International Journal of Civil Engineering, 13(1), 102–111. https://doi.org/10.22068/IJCE.13.1.102
Kaveh, A., Eskandari, A., & Movasat, M. (2023a). Buckling resistance prediction of high-strength steel columns using Metaheuristic-trained artificial neural networks. Structures, 56(C), 104853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.istruc.2023.07.043
Kaveh, A., Seddighian, M. R., & Farsi, N. (2023b). A metaheuristic-based artificial neural network for plastic limit analysis of frames. International Journal of Optimization in Civil Engineering, 13(2), 143–154.
Kulkarni, A., & Datta, D. (2019). Probabilistic analysis of RC beams according to IS456:2000 in limit state of collapse. Structural Engineering and Mechanics, 71(2), 165–173. https://doi.org/10.12989/sem.2019.71.2.165
Kumar, A., Rai, B., & Samui, P. (2024). Soft computing-based reliability analysis of simply supported beam: A comparative study of hybrid ANN models. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00969-8
Le, M. V., Prakash, I., & Nguyen, D. D. (2023a). Predicting load-deflection of composite concrete bridges using machine learning models. Journal of Science and Transport Technology. https://doi.org/10.58845/jstt.utt.2023.en.3.4.44-52
Le, M. V., Nguyen, D. D., Ha, H., Prakash, I., & Pham, B. T. (2023b). Ensemble soft computing models for prediction of deflection of steel concrete composite bridges. Arabian Journal of Science and Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-023-08474-5
Liu, K., Liu, B., & Xu, C. (2009). Intelligent analysis model of slope nonlinear displacement time series based on genetic-Gaussian process regression algorithm of combined kernel function. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 10, 2128–2134.
Liu, J., Wu, H., & Sun, Q. (2023). Research on the prediction of rigid frame continuous girder bridge deflection using BP and RBF neural networks. Stavební Obzor - Civil Engineering Journal, 32(2), 257–270. https://doi.org/10.14311/CEJ.2023.02.0020
Mathew, D. B., Girija, K., Nazeer, M., et al. (2024). Experimental and numerical analysis of lateral–torsional buckling behaviour of monosymmetric simply supported beam. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00920-x
Meyghani, B., Awang, M., & Wu, C. S. (2020). Probabilistic finite element analysis of the deflection on a beam. IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, 863(1), 012002. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/863/1/012002
Mottaghi, L., Kaveh, A., & Izadifard, R. A. (2022). Optimal design of a non-prismatic reinforced concrete box girder bridge with three meta-heuristic algorithms. Scientia Iranica, 29(3), 1154–1167.
Mustafa, R., Samui, P., Kumari, S., et al. (2023a). Probabilistic analysis of gravity retaining wall against bearing failure. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering, 24, 3099–3119. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00697-z
Mustafa, R., Samui, P., & Kumari, S. (2023b). Seismic performance of gravity retaining walls under quasi-static approach using probabilistic analysis. Transportation Infrastructure Geotechnology. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40515-023-00298-y
Nagaraju, V., Sireesha, M., Sunil, B.M., & Sk, A. (2023). A review on application of soft computing techniques in geotechnical engineering. In book: Proceedings of The 5th International Conference on Advances in Civil and Ecological Engineering Research. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-5716-3_26
Nguyen, T. (2022). Effect of span to depth ratio on strength and deflection reliability of reinforced concrete beams. In book: Recent Advances in Structural Health Monitoring and Engineering Structures. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-4835-0_28
Rofooei, F. R., Kaveh, A., & Farahani, F. M. (2011). Estimating the vulnerability of the concrete moment resisting frame structures using artificial neural networks. International Journal of Optimization in Civil Engineering, 1(3), 433–448.
Sharma, N., Lallipeli, A. K., Hirwani, C. K., Das, A., Panda, S., Topal, U., & Dede, T. (2021). Optimal deflection and stacking sequence prediction of curved composite structure using hybrid (FEM and Soft Computing) technique. Engineering with Computers, 37, 477–487. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00366-019-00836-8
Shreyas, S. K., & Dey, A. (2019). Application of soft computing techniques in tunnelling and underground excavations: State of the art and future prospects. Innovative Infrastructure Solutions, 4, 46. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-019-0234-z
Singhal, D., & Narayanamurthy, V. (2019). Large and small deflection analysis of a cantilever beam. Journal of the Institution of Engineers (india): Series A, 100(1), 83–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-018-0342-3
Tabrizikahou, A., Pavic, G., Shahsavani, Y., & Hadzima-Nyarko, M. (2023). Prediction of reinforced concrete walls shear strength based on soft computing based techniques. Soft Computing. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00500-023-08974-4
Thapa, I., Kumar, N., Ghani, S., et al. (2024). Applications of bentonite in plastic concrete: A comprehensive study on enhancing workability and predicting compressive strength using hybridized AI models. Asian Journal of Civil Engineering. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-023-00966-x
Toratti, T., Schnabl, S., & Turk, G. (2007). Reliability analysis of a glulam beam. Structural Safety, 29(4), 279–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.strusafe.2006.07.011
Zhang, H., Zhou, J., Armaghani, D. J., Tahir, M., Pham, B. T., & Huynh, V. V. (2020). A combination of feature selection and random forest techniques to solve a problem related to blast induced ground vibration. Applied Sciences, 10(3), 869. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10030869
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
RM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing—original draft, Writing—review & editing; TA: Software.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mustafa, R., Ahmad, M.T. Probabilistic analysis of simply supported concrete beam using machine learning techniques: a comparative study. Asian J Civ Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-024-01020-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42107-024-01020-0