Abstract
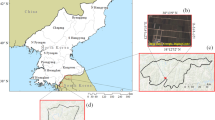
Paddy rice is an important grain production in the world. Southern China experienced substantial losses in paddy rice area over the last three decades in traditionally cropping area. As gross primary production (GPP) is a proxy of land productivity, study on its spatial–temporal dynamics is helpful to understand effect of cropping practices on variation of rice grain production. In our study, Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) data and meteorological data were combined to drive Vegetation Photosynthesis Model (VPM) for estimating GPP in paddy rice fields of southern China (Hubei province) during 2000–2015 at 1 km spatial resolution. Paddy fields area was varied by the influence of industrialization and urbanization of the region as well as changes in aquaculture area during the 16 years. Annual GPP showed significant increasing trends during 2000–2004 and 2009–2015, and sharply decreasing trend from 2004 to 2009. The assessment of relationship between annual GPP and grain production of paddy rice at municipal-scale and provincial-scale during 2000–2015 demonstrated the potential of annual GPP derived from satellite-based GPP model as a tool to estimate annual rice grain production in the region. The analysis of spatial–temporal pattern of rice GPP demonstrated a high correlation between cropping frequency of paddy rice and mean annual GPP of paddy rice along the main rivers of Hubei province, which provided positive suggestions for promote the production of paddy rice cultivation in sustainable development.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are included in this published article. The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Allen, R., Pereira, L., Raes, D., Smith, M., Allen, R. G., Pereira, L. S., & Martin, S. (1998). Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements, FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 56. FAO, 56.
Angstrom, A. (1924). Solar and terrestrial radiation. Report to the international commission for solar research on actinometric investigations of solar and atmospheric radiation. Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, 50(210), 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.49705021008
Baldocchi, D., Falge, E., Gu, L. H., Olson, R., Hollinger, D., Running, S., & Wofsy, S. (2001). FLUXNET: A new tool to study the temporal and spatial variability of ecosystem-scale carbon dioxide, water vapor, and energy flux densities. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, 82(11), 2415–2434. https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(2001)082%3c2415:fantts%3e2.3.co;2
Baldocchi, D., Sturtevant, C., & Fluxnet, C. (2015). Does day and night sampling reduce spurious correlation between canopy photosynthesis and ecosystem respiration? Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 207, 117–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.03.010
Cai, X. B., Feng, L., Hou, X. J., & Chen, X. L. (2016). Remote Sensing of the Water Storage Dynamics of Large Lakes and Reservoirs in the Yangtze River Basin from 2000 to 2014. Scientific Reports, 6. doi:ARTN 36405 https://doi.org/10.1038/srep36405
Cao, J. J., Cai, X. L., Tan, J. W., Cui, Y. L., Xie, H. W., Liu, F. P., & Luo, Y. F. (2021). Mapping paddy rice using Landsat time series data in the Ganfu Plain irrigation system, Southern China, from 1988–2017. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 42(4), 1556–1576.
Chen, Z., Ren, Y., & Wang, K. (2010). The assessment on the extreme high-temperature event and its influences in the summer of2009in Hubei province. Journal of Central China Normal University (natural Sciences), 44(02), 319–324. https://doi.org/10.19603/j.cnki.1000-1190.2010.02.034
Donat, M. G., Alexander, L. V., Yang, H., Durre, I., Vose, R., Dunn, R. J. H., & Kitching, S. (2013). Updated analyses of temperature and precipitation extreme indices since the beginning of the twentieth century: The HadEX2 dataset. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 118(5), 2098–2118. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgrd.50150
Dong, J. W., Xiao, X. M., Menarguez, M. A., Zhang, G. L., Qin, Y. W., Thau, D., & Moore, B. (2016). Mapping paddy rice planting area in northeastern Asia with Landsat 8 images, phenology-based algorithm and Google Earth Engine. Remote Sensing of Environment, 185, 142–154.
Elert, E. (2014). A good grain. Nature, 514(7524), S50–S51.
Falge, E., Baldocchi, D., Olson, R., Anthoni, P., Aubinet, M., Bernhofer, C., & Wofsy, S. (2001). Gap filling strategies for defensible annual sums of net ecosystem exchange. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 107(1), 43–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1923(00)00225-2
FAOSTAT. (2020). Statistical Database of the Food and Agricultural Organization of the United Nations.
He, M., Kimball, J. S., Maneta, M. P., Maxwell, B. D., Moreno, A., Begueria, S., & Wu, X. (2018). Regional Crop Gross Primary Productivity and Yield Estimation Using Fused Landsat-MODIS Data. Remote Sensing, 10(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10030372
He, Y. L., Dong, J. W., Liao, X. Y., Sun, L., Wang, Z. P., You, N. S., . . . Fu, P. (2021). Examining rice distribution and cropping intensity in a mixed single- and double-cropping region in South China using all available Sentinel 1/ 2 images. International Journal of Applied Earth Observation and Geoinformation, 101. doi:ARTN 102351 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jag.2021.102351
Huang, D., Chi, H., Xin, F. F., Miyata, A., Kang, M., Liu, K. W., . . . Xiao, X. M. (2021). Improved estimation of gross primary production of paddy rice cropland with changing model parameters over phenological transitions. Ecological Modelling, 445. doi:ARTN 109492 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2021.109492
Huang, M. T., Piao, S. L., Ciais, P., Penuelas, J., Wang, X. H., Keenan, T. F., & Janssens, I. A. (2019). Air temperature optima of vegetation productivity across global biomes. Nature Ecology & Evolution, 3(5), 772–779. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41559-019-0838-x
Huete, A., Didan, K., Miura, T., Rodriguez, E. P., Gao, X., & Ferreira, L. G. (2002). Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sensing of Environment, 83(1–2), 195–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(02)00096-2
Huete, A. R., Liu, H. Q., Batchily, K., & vanLeeuwen, W. (1997). A comparison of vegetation indices global set of TM images for EOS-MODIS. Remote Sensing of Environment, 59(3), 440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(96)00112-5
Hutchinson, M. F. (2002). Anusplin Version 4.2 User Guide. Retrieved from
Jiang, H., Hu, H., Zhong, R. H., Xu, J. F., Xu, J. L., Huang, J. F., & Lin, T. (2020). A deep learning approach to conflating heterogeneous geospatial data for corn yield estimation: A case study of the US Corn Belt at the county level. Global Change Biology, 26(3), 1754–1766. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14885
Jiang, L., Deng, X. Z., & Seto, K. C. (2012). Multi-level modeling of urban expansion and cultivated land conversion for urban hotspot counties in China. Landscape and Urban Planning, 108(2–4), 131–139.
Justice, C. O., Townshend, J. R. G., Vermote, E. F., Masuoka, E., Wolfe, R. E., Saleous, N., & Morisette, J. T. (2002). An overview of MODIS Land data processing and product status. Remote Sensing of Environment, 83(1–2), 3–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(02)00084-6
Kalfas, J. L., Xiao, X., Vanegas, D. X., Verma, S. B., & Suyker, A. E. (2011). Modeling gross primary production of irrigated and rain-fed maize using MODIS imagery and CO2 flux tower data. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 151(12), 1514–1528. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2011.06.007
Li, Y. Y., Zhu, Y. X., Chen, L., & Shen, Z. Y. (2018). The Time Delay of Flow and Sediment in the Middle and Lower Yangtze River and Its Response to the Three Gorges Dam. Journal of Hydrometeorology, 19(3), 625–638. https://doi.org/10.1175/Jhm-D-17-0119.1
Liang, S. L., Zhao, X., Liu, S. H., Yuan, W. P., Cheng, X., Xiao, Z. Q., & Townshend, J. (2013). A long-term Global LAnd Surface Satellite (GLASS) data-set for environmental studies. International Journal of Digital Earth, 6, 5–33.
Liu, J., Kuang, W., Zhang, Z., Xu, X., Qin, Y., Ning, J., & Chi, W. (2014). Spatiotemporal characteristics, patterns, and causes of land-use changes in China since the late 1980s. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 24(2), 195–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-014-1082-6
Lobell, D. B., Asner, G. P., Ortiz-Monasterio, J. I., & Benning, T. L. (2003). Remote sensing of regional crop production in the Yaqui Valley, Mexico: estimates and uncertainties. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 94(2), 205–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-8809(02)00021-x
Lobell, D. B., Hicke, J. A., Asner, G. P., Field, C. B., Tucker, C. J., & Los, S. O. (2002). Satellite estimates of productivity and light use efficiency in United States agriculture, 1982–98. Global Change Biology, 8(8), 722–735. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2486.2002.00503.x
Luo, Y., Zhang, Z., Chen, Y., Li, Z., & Tao, F. (2020). ChinaCropPhen1km: A high-resolution crop phenological dataset for three staple crops in China during 2000–2015 based on leaf area index (LAI) products. Earth System Science Data, 12(1), 197–214. https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-12-197-2020
Mc Carthy, U., Uysal, I., Badia-Melis, R., Mercier, S., O’Donnell, C., & Ktenioudaki, A. (2018). Global food security—Issues, challenges and technological solutions. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 77, 11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2018.05.002
Meek, D. W., Hatfield, J. L., Howell, T. A., Idso, S. B., & Reginato, R. J. (1984). A generalized relationship between photosynthetically active radiation and solar-radiation. Agronomy Journal, 76(6), 939–945. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj1984.00021962007600060018x
Monteith, J. L. (1972). Solar-radiation and productivity in tropical ecosystems. Journal of Applied Ecology, 9(3), 747–766. https://doi.org/10.2307/2401901
Monteith, J. L. (1977). Climate and efficiency of crop production in britain. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London Series B-Biological Sciences, 281(980), 277–294. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.1977.0140
Nichol, C. J., Huemmrich, K. F., Black, T. A., Jarvis, P. G., Walthall, C. L., Grace, J., & Hall, F. G. (2000). Remote sensing of photosynthetic-light-use efficiency of boreal forest. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 101(2–3), 131–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1923(99)00167-7
Potter, C. S., Randerson, J. T., Field, C. B., Matson, P. A., Vitousek, P. M., Mooney, H. A., & Klooster, S. A. (1993). Terrestrial ecosystem production—a process model-based on global satellite and surface data. Global Biogeochemical Cycles, 7(4), 811–841. https://doi.org/10.1029/93gb02725
Prince, S. D., & Goward, S. N. (1995). Global primary production: a remote sensing approach. Journal of BIogeography, 22(4–5), 815–835. https://doi.org/10.2307/2845983
Raich, J. W., Rastetter, E. B., Melillo, J. M., Kicklighter, D. W., Steudler, P. A., Peterson, B. J., & Vorosmarty, C. J. (1991). Potential net primary productivity in south america: application of a global model. Ecological Applications, 1(4), 399–429. https://doi.org/10.2307/1941899
Running, S. W., Baldocchi, D. D., Turner, D. P., Gower, S. T., Bakwin, P. S., & Hibbard, K. A. (1999). A global terrestrial monitoring network integrating tower fluxes, flask sampling, ecosystem modeling and EOS satellite data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 70(1), 108–127. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0034-4257(99)00061-9
Sanchez, M. L., Pardo, N., Perez, I. A., & Garcia, M. A. (2015). GPP and maximum light use efficiency estimates using different approaches over a rotating biodiesel crop. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 214, 444–455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2015.09.012
Savitzky, A., & Golay, M. J. E. (1964). Smoothing + differentiation of data by simplified least squares procedures. Analytical Chemistry, 36(8), 1627–2000. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60214a047
Sellers, P. J., Berry, J. A., Collatz, G. J., Field, C. B., & Hall, F. G. (1992). Canopy reflectance, photosynthesis, and transpiration. III. A reanalysis using improved leaf models and a new canopy integration scheme. Remote Sensing of Environment, 42(3), 187–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/0034-4257(92)90102-P
Sims, D. A., Rahman, A. F., Cordova, V. D., El-Masri, B. Z., Baldocchi, D. D., Flanagan, L. B., . . . Xu, L. (2006). On the use of MODIS EVI to assess gross primary productivity of North American ecosystems. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 111(G4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2006jg000162
Spielmann, F. M., Wohlfahrt, G., Hammerle, A., Kitz, F., Migliavacca, M., Alberti, G., & Delle Vedove, G. (2019). Gross primary productivity of four european ecosystems constrained by joint CO2 and COS flux measurements. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(10), 5284–5293. https://doi.org/10.1029/2019gl082006
Wagle, P., Xiao, X., & Suyker, A. E. (2015). Estimation and analysis of gross primary production of soybean under various management practices and drought conditions. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 99, 70–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2014.10.009
Wu, C. Y., Niu, Z., & Gao, S. A. (2010). Gross primary production estimation from MODIS data with vegetation index and photosynthetically active radiation in maize. Journal of Geophysical Research-Atmospheres, 115. doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2009jd013023
Wu, C., Peng, D., Soudani, K., Siebicke, L., Gough, C. M., Arain, M. A., & Ge, Q. (2017). Land surface phenology derived from normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI) at global FLUXNET sites. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 233, 171–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2016.11.193
Wu, X. C., Xiao, X. M., Zhang, Y., He, W., Wolf, S., Chen, J. Q., & Blanken, P. D. (2018). Spatiotemporal consistency of four gross primary production products and solar-induced chlorophyll fluorescence in response to climate extremes across CONUS in 2012. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 123(10), 3140–3161. https://doi.org/10.1029/2018jg004484
Xia, J. Q., Deng, S. S., Lu, J. Y., Xu, Q. X., Zong, Q. L., & Tan, G. M. (2016). Dynamic channel adjustments in the Jingjiang Reach of the Middle Yangtze River. Scientific Reports, 6. doi:ARTN 22802 https://doi.org/10.1038/srep22802
Xiao, J., Davis, K. J., Urban, N. M., Keller, K., & Saliendra, N. Z. (2011). Upscaling carbon fluxes from towers to the regional scale: Influence of parameter variability and land cover representation on regional flux estimates. Journal of Geophysical Research-Biogeosciences, 116. doi:https://doi.org/10.1029/2010jg001568
Xiao, X., Boles, S., Frolking, S., Salas, W., Moore, B., Li, C., & Zhao, R. (2002). Observation of flooding and rice transplanting of paddy rice fields at the site to landscape scales in China using VEGETATION sensor data. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 23(15), 3009–3022. https://doi.org/10.1080/01431160110107734
Xiao, X. M., Hollinger, D., Aber, J., Goltz, M., Davidson, E. A., Zhang, Q. Y., & Moore, B. (2004a). Satellite-based modeling of gross primary production in an evergreen needleleaf forest. Remote Sensing of Environment, 89(4), 519–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2003.11.008
Xiao, X. M., Zhang, Q. Y., Braswell, B., Urbanski, S., Boles, S., Wofsy, S., & Ojima, D. (2004b). Modeling gross primary production of temperate deciduous broadleaf forest using satellite images and climate data. Remote Sensing of Environment, 91(2), 256–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.03.010
Xie, W. Q., Wang, H. N., Chi, H., Dang, H. S., Huang, D., Li, H., & Xiao, X. M. (2020). Spatial-temporal variation of satellite-based gross primary production estimation in wheat-maize rotation area during 2000–2015. Geocarto International. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2020.1822928
Xin, F., Xiao, X., Dong, J., Zhang, G., Zhang, Y., Wu, X., . . . Li, B. (2020). Large increases of paddy rice area, gross primary production, and grain production in Northeast China during 2000-2017. Science of the Total Environment, 711. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135183
Xin, F. F., Xiao, X. M., Zhao, B., Miyata, A., Baldocchi, D., Knox, S., & Biradar, C. (2017). Modeling gross primary production of paddy rice cropland through analyses of data from CO2 eddy flux tower sites and MODIS images. Remote Sensing of Environment, 190, 42–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2016.11.025
Xu, X. L., Wang, L., Cai, H. Y., Wang, L. Y., Liu, L., & Wang, H. Z. (2017). The influences of spatiotemporal change of cultivated land on food crop production potential in China. Food Security, 9(3), 485–495.
Xue, W., Lindner, S., Dubbert, M., Otieno, D., Ko, J., Muraoka, H., & Tenhunen, J. (2017). Supplement understanding of the relative importance of biophysical factors in determination of photosynthetic capacity and photosynthetic productivity in rice ecosystems. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 232, 550–565.
Yan, H. M., Liu, F., Qin, Y. W., Niu, Z. E., Doughty, R., & Xiao, X. M. (2019). Tracking the spatio-temporal change of cropping intensity in China during 2000–2015. Environmental Research Letters, 14(3).
Yan, H., Fu, Y., Xiao, X., Huang, H. Q., He, H., & Ediger, L. (2009). Modeling gross primary productivity for winter wheat-maize double cropping System using MODIS time series and CO2 eddy flux tower data. Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment, 129(4), 391–400. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agee.2008.10.017
Yang, Q., Shi, L. S., Han, J. Y., Yu, J., & Huang, K. (2020a). A near real-time deep learning approach for detecting rice phenology based on UAV images. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 287. ARTN 107938 https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2020a.107938
Yang, Y. J., Ren, W., Tao, B., Ji, L., Liang, L., Ruane, A. C., & Tian, Q. J. (2020b). Characterizing spatiotemporal patterns of crop phenology across North America during 2000–2016 using satellite imagery and agricultural survey data. Isprs Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 170, 156–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2020.10.005
Yuan, W., Cai, W., Xia, J., Chen, J., Liu, S., Dong, W., & Wohlfahrt, G. (2014). Global comparison of light use efficiency models for simulating terrestrial vegetation gross primary production based on the La Thuile database. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 192, 108–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2014.03.007
Yuan, W., Liu, S., Zhou, G., Zhou, G., Tieszen, L. L., Baldocchi, D., & AmeriFlux, C. (2007). Deriving a light use efficiency model from eddy covariance flux data for predicting daily gross primary production across biomes. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 143(3–4), 189–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2006.12.001
Zhang, Y., Xiao, X., Wu, X., Zhou, S., Zhang, G., Qin, Y., & Dong, J. (2017b). Data Descriptor: A global moderate resolution dataset of gross primary production of vegetation for 2000-2016. Scientific Data, 4. https://doi.org/10.1038/sdata.2017b.165
Zhang, X., Wu, B. F., Ponce-Campos, G. E., Zhang, M., Chang, S., & Tian, F. Y. (2018). Mapping up-to-Date Paddy Rice Extent at 10 M Resolution in China through the Integration of Optical and Synthetic Aperture Radar Images. Remote Sensing, 10(8).
Zhang, G. L., Xiao, X. M., Biradar, C. M., Dong, J. W., Qin, Y. W., Menarguez, M. A., & Moore, B. (2017a). Spatiotemporal patterns of paddy rice croplands in China and India from 2000 to 2015. Science of the Total Environment, 579, 82–92.
Zhang, Q., Middleton, E. M., Margolis, H. A., Drolet, G. G., Barr, A. A., & Black, T. A. (2009). Can a satellite-derived estimate of the fraction of PAR absorbed by chlorophyll (FAPAR(chl)) improve predictions of light-use efficiency and ecosystem photosynthesis for a boreal aspen forest? Remote Sensing of Environment, 113(4), 880–888. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2009.01.002
Zhao, M. S., Heinsch, F. A., Nemani, R. R., & Running, S. W. (2005). Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sensing of Environment, 95(2), 164–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2004.12.011
Zuo, D., Wang, Y., & Chen, J. (1963). Characteristics of the distribution of total radiation in China. Acta Meteorologica, Sinica(01), 78–96.
Funding
This work was supported by the CRSRI Open Research Program (Program SN: CKWV2016402/KY), the Department of Natural Resources of Hubei Province, Natural resources Research Program under Grant [No. ZRZY2021KJ06] and [No. ZRZY2022KJ09]; a grant from the State Key Laboratory of Resources and Environmental Information System.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H., Zhang, J., He, L. et al. Monitoring and Assessing Gross Primary Productivity of Paddy Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Cropland in Southern China Between 2000 and 2015. Int. J. Plant Prod. 16, 579–593 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-022-00215-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-022-00215-2