Abstract
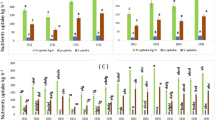
Sugar beet is an important economic crop in Northwest China. In this area, efficient use of nitrogen (N) fertilizer has become crucial due to decreased profits associated with both under- and oversupply relative to sugar beet requirements. Thus, fast and non-destruction diagnostic tools for estimating plant N status have an important role in reducing N inputs while maintaining sugar beet yield and qualify. The objective of our study was to quantify leaf color characterization of sugar beet with an inexpensive scanner and establish the relationship with yield, leaf nitrogen content (LNC), plant total nitrogen content (PTNC), chlorophyll content (CC), soil nitrate nitrogen content (SNNC) and soil plant analysis development (SPAD) readings in sugar beet. In 2017 and 2018, field experiments were conducted with five N treatments ranging from 0 to 180 kg N ha−1. The main results showed the following: The SPAD readings (SPR) and CC exhibited a significant or highly significant correlation (maximum = 0.70, P < 0.01), both of which reflected well the N nutrient status of the entire plant. Furtherly, a detailed association analysis revealed that there was a close relationship (maximum = − 0.63, P < 0.01) of LNC, SPR, PTNC, CC and yield with leaf color parameter Red/Blue (R/B), which was recommended as leaf color parameters for N diagnosis in sugar beet. In addition, based on the distribution of R/B value under different N rate, the yield was low with greater R/B value than 1.36 indicating an insufficient N supply, and with the R/B value was lower than 1.36, the theoretical yield reached its peak indicating an adequate supply of N fertilizer. To summarize, compared to the complicated and expensive of hyperspectral and other remote sensing technologies, scanned leaf image (SLI) processing technique was a simple, inexpensive and reliable method of determining sugar beet N status that has potential as a diagnostic tool for determining crop N requirement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bu, H., Lakesh, K., Sharma, A. D., & David, W. F. (2016). Sugar beet yield and quality prediction at multiple harvest dates using active-optical sensors. Agronomy Journal, 108, 273–328. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2015.0268.
Cai, H. C., Cui, H. X., Song, W. T., & Gao, L. H. (2006). Preliminary study on photosynthetic pigments content and color characteristics of cucumber leaves during early flowering. Journal of Agricultural Engineering, 09, 34–38. https://doi.org/10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2006.09.007.
Carlos, C., Lianne, M. D., & Pierre, D. (2001). Inter relationships of applied nitrogen, SPAD, and yield of leafy and non-leafy maize genotypes. Journal of Plant Nutrition, 24, 1173–1194. https://doi.org/10.1081/PLN-100106974.
Casa, R., Pelosi, F., Pascucci, S., Fontana, F., Castaldi, F., Pignatti, S., et al. (2017). Early stage variable rate nitrogen fertilization of silage maize driven by multi-temporal clustering of archive satellite data. Advances in Animal Biosciences, 8, 288–292. https://doi.org/10.1017/S2040470017000103.
Chatterjee, A., Subedi, K., Franzen, D. W., Mickelson, H., & Cattanach, N. (2018). Nitrogen fertilizer optimization for sugar beet in the red river valley of North Dakota and Minnesota. Agronomy Journal, 110, 1554. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2017.12.0694.
Clémence, R., Quemada, M., & Marie-Hélène, J. (2017). Use of a chlorophyll meter to assess nitrogen nutrition index during the growth cycle in winter wheat. Field Crops Research, 214, 73–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2017.08.023.
Confalonieri, R., Paleari, L., Movedi, E., Pagani, V., Orlando, F., Foi, M., et al. (2015). Improving in vivo plant nitrogen content estimates from digital images: Trueness and precision of a new approach as compared to other methods and commercial devices. Biosystems Engineering, 135, 21–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2015.04.013.
Gehl, R. J., & Boring, T. J. (2011). In-season prediction of sugar beet yield, quality, and nitrogen status using an active sensor. Agronomy Journal, 103, 1012–1018. https://doi.org/10.2134/agronj2011.0040.
Huang, S., Miao, Y., Zhao, G., Yuan, F., Ma, X., Tan, C., et al. (2015). Satellite remote sensing-based in-season diagnosis of rice nitrogen status in Northeast China. Remote Sensing, 2015(7), 10646–10667. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs70810646.
Jia, L., Buerkert, A., Chen, X., Roemheld, V., & Zhang, F. (2004). Low-altitude aerial photography for optimum N fertilization of winter wheat on the North China Plain. Field Crops Research, 89, 389–395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2004.02.014.
Jia, L., Chen, X., Zhang, F., Buerkert, A., & Roemheld, V. (2007). Optimum nitrogen fertilization of winter wheat based on color digital camera images. Communications in Soil Science and Plant Analysis, 38, 1385–1394. https://doi.org/10.1080/00103620701375991.
Jonckheere, I., Fleck, S., Nackaerts, K., Muys, B., Coppin, P., Weiss, M., et al. (2004). Review of methods for in situ leaf area index determination. Part I. Theories, sensors and hemispherical photography. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology, 121, 19–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2003.08.027.
Karcher, D. E., & Richardson, M. D. (2003). Quantifying turf grass color using digital image analysis. Crop Science, 43, 943–951. https://doi.org/10.2135/cropsci2003.9430.
Lamb, J. A., Bredehoeft, M. W., & Dunsmore, C. (2013). Nitrogen management strategies for increasing sugar beet root quality. Sugar beet Research and Extension Reports, 43, 91–99.
Lebourgeois, V., Bégué, A., Labbé, S., Houlès, M., & Martiné, J. F. (2012). A light-weight multi-spectral aerial imaging system for nitrogen crop monitoring. Precision Agriculture, 13, 525–541. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-012-9262-9.
Lee, K. J., & Lee, B. W. (2013). Estimation of rice growth and nitrogen nutrition status using color digital camera image analysis. European Journal of Agronomy, 48, 57–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2013.02.011.
Li, Y., Chen, D., Walker, C. N., & Angus, J. F. (2010). Estimating the nitrogen status of crops using a digital camera. Field Crops Research, 118, 221–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2010.05.011.
Li, F., Mistele, B., Hu, Y., Chen, X., & Schmidhalter, U. (2014a). Reflectance estimation of canopy nitrogen content in winter wheat using optimised hyperspectral spectral indices and partial least squares regression. European Journal of Agronomy, 52, 198–209. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eja.2013.09.006.
Li, L., Zhang, Q., & Huang, D. F. (2014b). A review of imaging techniques for plant phenotyping. Sensors, 14, 20078–20111. https://doi.org/10.3390/s141120078.
Li, H., Zhang, Y., Lei, Y., Antoniuk, V., & Hu, C. (2019). Evaluating different non-destructive estimation methods for winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) nitrogen status based on canopy spectrum. Remote Sensing, 12, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12010095.
Lichtenthale, H. K. (1987). Chlorophyll and carotenoids. The pigments of photosynthetic biomembranes. Methods in Enzymology, 148, 350–382.
Miao, Y., Mulla, D. J., Randall, G. W., Vetsch, J. A., & Vintila, R. (2009). Combining chlorophyll meter readings and high spatial resolution remote sensing images for in-season site-specific nitrogen management of corn. Precision Agriculture, 10, 45–62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-008-9091-z.
Mulla, D. J. (2013). Twenty-five years of remote sensing in Precis. Agric. Key advances and remaining knowledge gaps. Biosystems Engineering, 114, 358–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2012.08.009.
Muñoz-Huerta, R. F., Guevara-Gonzalez, R. G., Contreras-Medina, L. M., Torres-Pacheco, I., Prado-Olivarez, J., & Ocampo-Velazquez, R. V. (2013). A review of methods for sensing the nitrogen status in plants: Advantages, disadvantages and recent advances. Sensors, 13, 10823–10843. https://doi.org/10.3390/s130810823.
Paleari, L., Movedi, E., Vesely, F. M., Thoelke, W., Tartarini, S., Foi, M., et al. (2019). Estimating crop nutritional status using smart apps to support nitrogen fertilization. A case study on paddy rice. Sensors, 19, 981. https://doi.org/10.3390/s19040981.
Peng, S., Garcia, F. V., Laza, R. C., Sanico, A. L., Visperas, R. M., & Cassman, K. G. (1996). Increased N-use efficiency using a chlorophyll meter on high-yielding irrigated rice. Field Crop Research, 47, 243–252.
Putra, B., & Peeyush, S. (2019). Improving nitrogen assessment with an RGB camera across uncertain natural light from above-canopy measurements. Precision Agriculture. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11119-019-09656-8.
Shao, J. W., Cai, B., & Zhang, J. H. (1991). Sugar beet physiology. In J. W. Shao (Ed.), Nitrogen nutrition and division of development period (pp. 210–222). Beijing: Agricultural Press.
Shaw, B., Thomas, T. H., & Cooke, D. T. (2002). Responses of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) to drought and nutrient deficiency stress. Plant Growth Regulation, 37, 77–83. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020381513976.
Tian, H., Shi, S., Wang, H., Li, F., Li, Z., Alva, A., et al. (2016). Estimation of sugar beet aboveground biomass by band depth optimization of hyperspectral canopy reflectance. Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing, 45, 795–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-016-0632-z.
Treder, W., Klamkowski, K., Kowalczyk, W., Sas, D., & Wójcik, K. (2016). Possibilities of using image analysis to estimate the nitrogen nutrition status of apple trees. Zemdirbyste-Agriculture, 103, 319–326. https://doi.org/10.13080/z-a.2016.103.041.
Vanden Berg, A. K., & Perkins, T. D. (2004). Evaluation of a portable chlorophyll meter to estimate chlorophylls and nitrogen contents in sugar maple leaves. Forest Ecology Management, 200, 113–117.
Wang, Y., Wang, D., Zhang, G., & Wang, J. (2013). Estimating nitrogen status of rice using the image segmentation of G-R thresholding method. Field Crops Research, 149, 33–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fcr.2013.04.007.
Wang, Y., Wang, D. J., Shi, P. H., & Omasa, K. (2014). Estimating rice chlorophyll content and leaf nitrogen concentration with a digital still color camera under natural light. Plant Methods, 10, 36. https://doi.org/10.1186/1746-4811-10-36.
Wang, Q. H., Zhou, J. C., & Wang, X. C. (2015). Study on the diagnostic technology of sugar beet nitrogen nutrition by SPAD Instrument. China Agricultural Bulletin, 31, 92–98.
Yue, X., Hu, Y., Zhang, H., Zhang, H. Z., & Schmidhalter, U. (2019). Evaluation of both SPAD reading and SPAD index on estimating the plant nitrogen status of winter wheat. International Journal of Plant Production, 9, 1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-019-00068-2.
Zhao, S. M. (2014). Breeding of new sugar beet monogerm male sterile hybrid variety Nei2499. Inner Mongolia Agricultural Science and Technology, 1, 100–101.
Zhang, J., Tian, H. Q., & Li, Z. (2018). Near-earth remote sensing monitoring model of sugar beet nitrogen based on digital image. Journal of China Agricultural University, 23, 130–139.
Zheng, H., Cheng, T., Li, D., Zhou, X., Yao, X., Tian, Y., et al. (2018). Evaluation of RGB, color-infrared and multispectral images acquired from unmanned aerial systems for the estimation of nitrogen accumulation in rice. Remote Sensing., 2018(10), 824–841. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10060824.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Modern Agriculture Industry Technology System Construction Project (CARS-170702). National Natural Science Foundation of China (31560084).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest with respect to authorship or publication of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Liang, X., Qi, B. et al. Diagnosis of Nitrogen Nutrition in Sugar Beet Based on the Characteristics of Scanned Leaf Images. Int. J. Plant Prod. 14, 663–677 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-020-00109-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42106-020-00109-1