Abstract
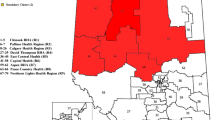
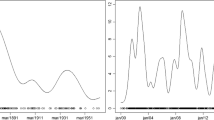
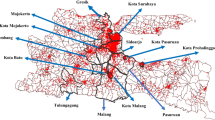
We discuss computation of the conditional expectation in a multinomial distribution. The problem is motivated by the evaluation of the multiplicity-adjusted p-value of scan statistics in spatial epidemiology. We propose a recursive summation/integration technique using the Markov property, which is extracted from a chordal graph defined by temporal and spatial structures. This methodology can be applied to a class of distributions, including the Poisson distribution (that is, the conditional distribution is the multinomial). To illustrate the approach, we present the real data analyses for detecting temporal and spatial clustering.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badsberg, J. H., & Malvestuto, F. M. (2001). An implementation of the iterative proportional fitting procedure by propagation trees. Computational Statistics and Data Analysis, 37(3), 297–322.
Blair, J. R. S., & Peyton, B. W. (1993). An introduction to chordal graphs and clique trees. In A. George, J. R. Gilbert, & J. W. H. Liu (Eds.), Graph theory and sparse matrix computation (pp. 1–29). New York: Springer.
Buneman, P. (1974). A characterization on rigid circuit graphs. Discrete Mathematics, 9(3), 205–212.
Cowell, R. G., Dawid, P., Lauritzen, S. L., & Spiegelhalter, D. J. (1999). Probabilistic networks and expert systems: Exact computational methods for Bayesian networks. New York: Springer.
Fukuda, M., Kojima, M., Murota, K., & Nakata, K. (2000). Exploiting sparsity in semidefinite programming via matrix completion I: General framework. SIAM Journal on Optimizations, 11(3), 647–674.
Hara, H., & Takemura, A. (2006). Boundary cliques, clique trees and perfect sequences of maximal cliques of a chordal graph. (arXiv:cs/0607055).
Hara, H., & Takemura, A. (2010). A localization approach to improve iterative proportional scaling in Gaussian graphical models. Communications in Statistics: Theory and Methods, 39(8–9), 1643–1654.
Hirotsu, C., & Marumo, K. (2002). Changepoint analysis as a method for isotonic inference. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 29(1), 125–138.
Kjærulff, U. (1992). Optimal decomposition of probabilistic networks by simulated annealing. Statistics and Computing, 2(1), 7–17.
Koyama, T., Nakayama, H., Nishiyama, K., & Takayama, N. (2014). Holonomic gradient descent for the Fisher-Bingham distribution on the \(d\)-dimensional sphere. Computational Statistics, 29(3–4), 661–683.
Kulldorff, M. (1997). A spatial scan statistic. Communications in Statistics: Theory and Methods, 26(6), 1481–1496.
Kulldorff, M. (2006). Tests of spatial randomness adjusted for an inhomogeneity: A general framework. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 101(475), 1289–1305.
Kuriki, S., Shimodaira, H., & Hayter, A. J. (2002). The isotonic range statistic for testing against an ordered alternative. Journal of Statistical Planning and Inference, 105(2), 347–362.
Lauritzen, S. L. (1996). Graphical models. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Neff, N. D., & Naus, J. I. (1980). Selected tables in mathematical statistics: The distribution of the size of the maximum cluster of points on a line (Vol. VI). Providence: American Mathematical Society.
Parter, S. (1961). The use of linear graphs in Gauss elimination. SIAM Review, 3(2), 119–130.
Redfern, D., & Campbell, C. (1998). The MATLAB 5 handbook. New York: Springer.
Rose, J. D. (1971). A graph theoretic study of the numerical solution of sparse positive definite. In R. C. Read (Ed.), Graph theory and computing (pp. 183–217). New York: Academic Press.
Tango, T. (1984). The detection of disease clustering in time. Biometrics, 40(1), 15–26.
Tango, T. (2010). Statistical methods for disease clustering. New York: Springer.
Tango, T., Yokoyama, T., & Takahashi, K. (2012). Introduction to spatial epidemiology: Disease mapping and disease clustering (in Japanese). Tokyo: Asakura.
Takahashi K., Yokoyama T., & Tango T. (2013). FleXScan: software for the flexible scan statistic. https://sites.google.com/site/flexscansoftware/. Accessed 1 May 2018.
Wallenstein, S. (1980). A test for detection of clustering over time. American Journal of Epidemiology, 111(3), 367–372.
Wallenstein, S., & Naus, J. I. (1973). Probabilities for a \(k\)th nearest neighbor problem on the line. The Annals of Probability, 1(1), 188–190.
Worsley, K. J. (1986). Confidence regions and tests for a change-point in a sequence of exponential family random variables. Biometrika, 73(1), 91–104.
Xu, P. F., Guo, J. H., & He, X. (2011). An improved iterative proportional scaling procedure for Gaussian graphical models. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 20(2), 417–431.
Xu, P. F., Guo, J. H., & Tang, M. L. (2012). An improved Hara-Takamura procedure by sharing computations on junction tree in Gaussian graphical models. Statistics and Computing, 22(5), 1125–1133.
Xu, P. F., Guo, J. H., & Tang, M. L. (2014). A localized implementation of the iterative proportional scaling procedure for Gaussian graphical models. Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 24(1), 205–229.
Yamashita, N. (2008). Sparse quasi-Newton updates with positive definite matrix completion. Mathematical Programming, 115(1), 1–30.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Takashi Tsuchiya, Anthony J. Hayter, Nobuki Takayama, and Yi-Ching Yao for their helpful comments. They also thank the Editor and the two referees for their constructive and insightful comments. This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant nos. 21500288 and 24500356.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuriki, S., Takahashi, K. & Hara, H. Multiplicity adjustment for temporal and spatial scan statistics using Markov property. Jpn J Stat Data Sci 1, 191–213 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42081-018-0007-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42081-018-0007-5