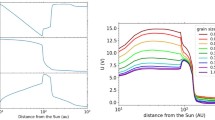
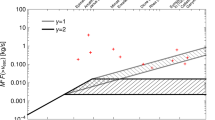
Abstract
Jupiter is one of the major targets for planetary exploration, and dust in the Jovian system is of great interest to researchers in the field of planetary science. In this paper, we review the five dust populations outside the ring system: grains in the region of the Galilean moons, potential dust from plumes on Europa, Jovian stream particles, particles in the outer region of the Jovian system ejected from the irregular satellites, and dust in the region of the Trojan asteroids. The physical environment for the dust dynamics is described, including the gravity, the magnetic field and the plasma environment. For each population, the dust sources are described, and the relevant perturbation forces are discussed. Observations and results from modeling are reviewed, and the distributions of the individual dust populations are shown. The understanding of the Jovian dust environment allows to assess the dust hazard to spacecraft, and to characterize the material exchange between the Jovian moons, their surface properties and distribution of non-icy constituents.
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
11 February 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42064-022-0136-2
References
Humes, D. H., Alvarez, J. M., O’Neal, R. L., Kinard, W. H. The interplanetary and near-Jupiter meteoroid environments. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1974, 79(25): 3677–3684.
Humes, D. H., Alvarez, J. M., Kinard, W. H., O’Neal, R. L. Pioneer 11 meteoroid detection experiment: preliminary results. Science, 1975, 188(4187): 473–474.
Smith, B. A., Soderblom, L. A., Johnson, T. V., Ingersoll, A. P., Collins, S. A., Shoemaker, E. M., Hunt, G. E., Masursky, H., Carr, M. H., Davies, M. E. et al. The Jupiter system through the eyes of Voyager 1. Science, 1979, 204(4396): 951–792.
Owen, T., Danielson, G. E., Cook, A. F., Hansen, C., Hall, V. L., Duxbury, T. C. Jupiter’s rings. Nature, 1979, 281(5731): 442–446.
Zeehandelaar, D. B., Hamilton, D. P. A local source for the Pioneer 10 and 11 circumjovian dust detections. In: Proceedings of Dust in Planetary Systems. Kauai, Hawaii, USA, 2007, 103–106.
Showalter, M. R., Burns, J. A., Cuzzi, J. N., Pollack, J. B. Discovery of Jupiter’s ‘gossamer’ ring. Nature, 1985, 316(6028): 526–528.
Showalter, M. R., Burns, J. A., Cuzzi, J. N., Pollack, J. B. Jupiter’s ring system: new results on structure and particle properties. Icarus, 1987, 69(3): 458–498.
Throop, H. B., Porco, C. C., West, R. A., Burns, J. A., Showalter, M. R., Nicholson, P. D. The Jovian rings: new results derived from Cassini, Galileo, Voyager, and Earth-based observations. Icarus, 2004, 172(1): 59–77.
Showalter, M. R., de Pater, I., Verbanac, G., Hamilton, D. P., Burns, J. A. Properties and dynamics of Jupiter’s gossamer rings from Galileo, Voyager, Hubble and Keck images. Icarus, 2008, 195(1): 361–377.
Ockert-Bell, M. E., Burns, J. A., Daubar, I. J., Thomas, P. C., Veverka, J., Belton, M. J. S., Klaasen, K. P. The structure of Jupiter’s ring system as revealed by the Galileo imaging experiment. Icarus, 1999, 138(2): 188–213.
Burns, J. A., Showalter, M. R., Hamilton, D. P., Nicholson, P. D., de Pater, I., Ockert-Bell, M. E., Thomas, P. C. The formation of Jupiter’s faint rings. Science, 1999, 284(5417): 1146–1150.
McMuldroch, S., Pilorz, S. H., Danielson, G. E., the NIMS Science Team. Galileo NIMS Near-infrared observations of Jupiter’s ring system. Icarus, 2000, 146(1): 1–11.
Brooks, S. M., Esposito, L. W., Showalter, M. R., Throop, H. B. The size distribution of Jupiter’s main ring from Galileo imaging and spectroscopy. Icarus, 2004, 170(1): 35–57.
Krüger, H., Grn, E., Hamilton, D. P., Baguhl, M., Dermott, S., Fechtig, H., Gustafson, B. A., Hanner, M. S., Horányi, M., Kissel, J. et al. Three years of Galileo dust data: II. 1993–1995. Planetary and Space Science, 1998, 47(1–2): 85–106.
Krüger, H., Grün, E., Graps, A., Bindschadler, D., Dermott, S., Fechtig, H., Gustafson, B. A., Hamilton, D. P., Hanner, M. S., Horányi, M. et al. One year of Galileo dust data from the Jovian system: 1996. Planetary and Space Science, 2001, 49(3): 1285–1301.
Krüger, H., Krivov, A. V., Sremčević, M., Grün, E. Impact-generated dust clouds surrounding the Galilean moons. Icarus, 2003, 164(1): 170–187.
Krüger, H., Bindschadler, D., Dermott, S. F., Graps, A. L., Grün, E., Gustafson, B. A., Hamilton, D. P., Hanner, M. S., Horányi, M., Kissel, J. et al. Galileo dust data from the Jovian system: 1997–1999. Planetary and Space Science, 2006, 54(9–10): 879–910.
Krüger, H., Hamilton, D. P., Moissl, R., Grün, E. Galileo in-situ dust measurements in Jupiter’s gossamer rings. Icarus, 2009, 203(1): 198–213.
Krüger, H., Bindschadler, D., Dermott, S. F., Graps, A. L., Grün, E., Gustafson, B. A., Hamilton, D. P., Hanner, M. S., Horányi, M., Kissel, J. et al. Galileo dust data from the Jovian system: 2000 to 2003. Planetary and Space Science, 2010, 58(7–8): 965–993.
Grün, E., Baguhl, M., Hamilton, D. P., Riemann, R., Zook, H. A., Dermott, S., Fechtig, H., Gustafson, B. A., Hanner, M. S., Horányi, M. et al. Constraints from Galileo observations on the origin of Jovian dust streams. Nature, 1996, 381(6581): 395–398.
Thiessenhusen, K. U., Krüger, H., Spahn, F., Grün, E. Dust grains around Jupiter—the observations of the Galileo dust detector. Icarus, 2000, 144(1): 89–98.
Krivov, A. V., Krüger, H., Grün, E., Thiessenhusen, K. U., Hamilton, D. P. A tenuous dust ring of Jupiter formed by escaping ejecta from the Galilean satellites. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(E1): 5002.
Krivov, A. V., Wardinski, I., Spahn, F., Krüger, H., Grün, E. Dust on the outskirts of the Jovian system. Icarus, 2002, 157(2): 436–455.
Porco, C. C., West, R. A., McEwen, A., del Genio, A. D., Ingersoll, A. P., Thomas, P., Squyres, S., Dones, L., Murray, C. D., Johnson, T. V. et al. Cassini imaging of Jupiter’s atmosphere, satellites, and rings. Science, 2003, 299(5612): 1541–1547.
Brown, R. H., Baines, K. H., Bellucci, G., Bibring, J. P., Buratti, B. J., Capaccioni, F., Cerroni, P., Clark, R. N., Coradini, A., Cruikshank, D. P. et al. Observations with the visual and infrared mapping spectrometer (VIMS) during Cassini’s flyby of Jupiter. Icarus, 2003, 164(2): 461–470.
Showalter, M. R., Cheng, A. F., Weaver, H. A., Stern, S. A., Spencer, J.R., Throop, H.B., Birath, E.M., Rose, D., Moore, J. M. Clump detections and limits on moons in Jupiter’s ring system. Science, 2007, 318(5848): 232–234.
Poppe, A., James, D., Jacobsmeyer, B., Horányi, M. First results from the Venetia Burney student dust counter on the new horizons mission. Geophysical Research Letters, 2010, 37(11): L11101.
Grün, E., Zook, H. A., Baguhl, M., Fechtig, H., Hanner, M. S., Kissel, J., Lindblad, B. A., Linkert, D., Linkert, G., Mann, I. B. et al. Ulysses dust measurements near Jupiter. Science, 1992, 257(5076): 1550–1552.
Grün, E., Zook, H. A., Baguhl, M., Balogh, A., Bame, S. J., Fechtig, H., Forsyth, R., Manner, M. S., Horányi, M., Kissel, J. et al. Discovery of Jovian dust streams and interstellar grains by the Ulysses spacecraft. Nature, 1993, 362(6419): 428–430.
Krüger, H., Graps, A. L., Hamilton, D. P., Flandes, A., Forsyth, R. J., Horányi, M., Grün, E. Ulysses Jovian latitude scan of high-velocity dust streams originating from the Jovian system. Planetary and Space Science, 2006, 54(9–10): 919–931.
Meier, R., Smith, B. A., Owen, T. C., Becklin, E. E., Terrile, R. J. Near infrared photometry of the Jovian ring and Adrastea. Icarus, 1999, 141(2): 253–262.
de Pater, I., Showalter, M. R., Burns, J. A., Nicholson, P. D., Liu, M. C., Hamilton, D. P., Graham, J. R. Keck infrared observations of Jupiter’s ring system near Earth’s 1997 ring plane crossing. Icarus, 1999, 138(2): 214–223.
de Pater, I., Showalter, M. R., Macintosh, B. Keck observations of the 2002–2003 Jovian ring plane crossing. Icarus, 2008, 195(1): 348–360.
Krüger, H., Krivov, A. V., Hamilton, D. P., Grün, E. Detection of an impact-generated dust cloud around Ganymede. Nature, 1999, 399(6736): 558–560.
Colwell, J. E., Horányi, M., Grün, E. Capture of interplanetary and interstellar dust by the Jovian magnetosphere. Science, 1998, 280(5360): 88–91.
Colwell, J. E., Horányi, M., Grün, E. Jupiter’s exogenic dust ring. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103(E9): 20023–20030.
Quick, L. C., Barnouin, O. S., Prockter, L. M., Patterson, G. W. Constraints on the detection of cryovolcanic plumes on Europa. Planetary and Space Science, 2013, 86: 1–9.
Roth, L., Saur, J., Retherford, K. D., Strobel, D. F., Feldman, P. D., McGrath, M. A., Nimmo, F. Transient water vapor at Europa’s south pole. Science, 2014, 343(6167): 171–174.
Roth, L., Retherford, K. D., Saur, J., Strobel, D. F., Feldman, P. D., McGrath, M. A., Nimmo, F. Orbital apocenter is not a sufficient condition for HST/STIS detection of Europa’s water vapor aurora. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2014, 111(48): E5123–E5132.
Southworth, B. S., Kempf, S., Schmidt, J. Modeling Europa’s dust plumes. Geophysical Research Letters, 2015, 42(24): 10541–10548.
Sparks, W. B., Hand, K. P., McGrath, M. A., Bergeron, E., Cracraft, M., Deustua, S. E. Probing for evidence of plumes on Europa with HST/STIS. The Astrophysical Journal, 2016, 829(2): 121.
Graps, A. L., Grün, E., Svedhem, H., Krüger, H., Horányi, M., Heck, A., Lammers, S. Io as a source of the Jovian dust streams. Nature, 2000, 405(6782): 48–50.
Liu, X., Schmidt, J. Dust arcs in the region of Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2018, 609: A57.
Zimmer, A. K., Grogan, K. Orbital evolution of dust particles originating from Jupiter’s Trojan asteroids. Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 2014, 152: 3049–3060.
de Elia, G. C., Brunini, A. Studying the Jovian Trojan dust. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 2010, 512: A65.
de Pater, I., Hamilton, D. P., Showalter, M. R., Throop, H. B., Burns, J. A. The rings of Jupiter. Planetary Ring Systems, 2018: 125–134.
Burns, J. A., Simonelli, D. P., Showalter, M. R., Hamilton, D. P., Porco, C. D., Throop, H., Esposito, L. W. Jupiter’s ring-moon system. Cambridge University Press, 2004, 241–262.
Miner, E. D., Wessen, R. R., Cuzzi, J. N. Planetary ring systems. Praxis Publishing Ltd, 2007.
Krüger, H., Horányi, M., Krivov, A. V., Graps, A. L. Jovian dust: streams, clouds and rings. Jupiter: The Planet, Satellites and Magnetosphere, 2004, 219–240.
Plaut, J. J., Barabash, S., Bruzzone, L., Dougherty, M., Erd, C., Fletcher, L., Gladstone, R., Grasset, O., Gurvits, L., Hartogh, P. et al. Jupiter icy moons explorer (JUICE): science objectives, mission and instruments. In: Proceedings of the 45th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Texas, USA, 2014.
Phillips, C. B., Pappalardo, R. T. Europa clipper mission concept: exploring Jupiter’s ocean moon. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 2014, 95(20): 165–167.
Levison, H. F., Olkin, C., Noll, K. S., Marchi, S., Team, L. Lucy: surveying the diversity of the Trojan asteroids: the fossils of planet formation. In: Proceedings the 48th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, 2017.
Burns, J. A., Lamy, P. L., Soter, S. Radiation forces on small particles in the solar system. Icarus, 1979, 40(1): 1–48.
Liu, X., Sachse, M., Spahn, F., Schmidt, J. Dynamics and distribution of Jovian dust ejected from the Galilean satellites. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2016, 121(7): 1141–1173.
Draine, B. T., Salpeter, E. E. On the physics of dust grains in hot gas. The Astrophysical Journal, 1979, 231: 77–94.
Banaszkiewicz, M., Fahr, H. J., Scherer, K. Evolution of dust particle orbits under the influence of solar wind outflow asymmetries and the formation of the zodiacal dust cloud. Icarus, 1994, 107(2): 358–374.
Morfill, G. E., Grn, E., Johnson, T. V. Dust in Jupiter’s magnetosphere: physical processes. Planetary and Space Science, 1980, 28(12): 1087–1100.
Dikarev, V. V. Dynamics of particles in Saturn’s E ring: effects of charge variations and the plasma drag force. Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1999, 346: 1011–1019.
Northrop, T. G., Birmingham, T. J. Plasma drag on a dust grain due to Coulomb collisions. Planetary and Space Science, 1990, 38(3): 319–326.
Connerney, J. E. P. Magnetic fields of the outer planets. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1993, 98(E10): 18659–18679.
Dougherty, M. K., Balogh, A., Southwood, D. J., Smith, E. J. Ulysses assessment of the Jovian planetary field. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1996, 101(A11): 24929–24941.
Connerney, J. E. P., Acu˜na, M. H., Ness, N. F., Satoh, T. New models of Jupiter’s magnetic field constrained by the Io flux tube footprint. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103(A6): 11929–11939.
Randall, B. A. An improved magnetic field model for Jupiter’s inner magnetosphere using a Microsignature of Amalthea. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103(A8): 17535–17542.
Connerney, J. E. P. Planetary magnetism. Treatise on Geophysics, 2007, 243–280.
Hess, S. L. G., Bonfond, B., Zarka, P., Grodent, D. Model of the Jovian magnetic field topology constrained by the Io auroral emissions. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(A5): A05217.
Schaffer, L., Burns, J. A. The dynamics of weakly charged dust: motion through Jupiter’s gravitational and magnetic fields. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1987, 92(A3): 2264–2280.
Burns, J. A., Schaffer, L. E., Greenberg, R. J., Showalter, M. R. Lorentz resonances and the structure of the Jovian ring. Nature, 1985, 316(6024): 115–119.
Divine, N., Garrett, H. B. Charged particle distributions in Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1983, 88(A9): 6889–6903.
Sittler, E. C. Jr., Strobel, D. F. Io plasma torus electrons: voyager 1. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1987, 92(A6): 5741–5762.
Frank, L. A., Paterson, W. R. Galileo observations of electron beams and thermal ions in Jupiter’s magnetosphere and their relationship to the auroras. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2002, 107(A12): 1478.
Bagenal, F., Delamere, P. A. Flow of mass and energy in the magnetospheres of Jupiter and Saturn. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2011, 116(A5): A05209.
Garrett, H. B., Kim, W., Belland, B., Evans, R. Jovian plasma modeling for mission design. Jet Propulsion Laboratory, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Pasadena, CA. 2015. https://doi.org/hdl.handle.net/2014/45478.
Horányi, M. Charged dust dynamics in the solar system. Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics, 1996, 34: 383–418.
Dzhanoev, A. R., Schmidt, J., Liu, X., Spahn, F. Charging of small grains in a space plasma: application to Jovian stream particles. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2016, 591: A147.
Gustafson, B. Å. S. Physics of zodiacal dust. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 1994, 22: 553–595.
Landgraf, M. Modeling the motion and distribution of interstellar dust inside the heliosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 2000, 105(A5): 10303–10316.
Krüger, H., Grün, E. Dust en-route to Jupiter and the Galilean satellites. COSPAR Colloquia Series, 2002, 15: 144–159.
Krüger, H., Krivov, A. V., Grün, E. A dust cloud of Ganymede maintained by hypervelocity impacts of interplanetary micrometeoroids. Planetary and Space Science, 2000, 48(15): 1457–1471.
Horányi, M., Szalay, J. R., Kempf, S., Schmidt, J., Grün, E., Srama, R., Sternovsky, Z. A permanent, asymmetric dust cloud around the Moon. Nature, 2015, 522(7556): 324–326.
Soja, R. H., Hamilton, D. P., Altobelli, N. A new analysis of Galileo dust data near Jupiter. Planetary and Space Science, 2015, 109–110: 76–91.
Bottke, W. F., Vokrouhlický, D., Nesvorný, D., Moore, J. M. Black rain: the burial of the Galilean satellites in irregular satellite debris. Icarus, 2013, 223(2): 775–795.
Horányi, M. New Jovian ring? Geophysical Research Letters, 1994, 21(11): 1039–1042.
Soja, R. H., Altobelli, N., Krüger, H., Sterken, V. J. Dust environment predictions for the ESA L-class mission JUICE. Planetary and Space Science, 2013, 75: 117–128.
Sachse, M. A planetary dust ring generated by impactejection from the Galilean satellites. Icarus, 2018, 303: 166–180.
Szalay, J. R., Horányi, M. The impact ejecta environment of near earth asteroids. The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 2016, 830(2): L29.
Rhoden, A. R., Hurford, T. A., Roth, L., Retherford, K. Linking Europa’s plume activity to tides, tectonics, and liquid water. Icarus, 2015, 253: 169–178.
Postberg, F., Kempf, S., Schmidt, J., Brilliantov, N., Beinsen, A., Abel, B., Buck, U., Srama, R. Sodium salts in E-ring ice grains from an ocean below the surface of Enceladus. Nature, 2009, 459(7250): 1098–1101.
Postberg, F., Schmidt, J., Hillier, J., Kempf, S., Srama, R. A salt-water reservoir as the source of a compositionally stratified plume on Enceladus. Nature, 2011, 474(7353): 620–622.
Krüger, H., Geissler, P., Horányi, M., Grap, A. L., Kempf, S., Srama, R., Moragas-Klostermeyer, G., Moissl, R., Johnson, T. V., Grün, E. Jovian dust streams: a monitor of Io’s volcanic plume activity. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(21): 2101.
Krüger, H., Linkert, G., Linkert, D., Moissl, R., Grn, E. Galileo long-term dust monitoring in the Jovian magnetosphere. Planetary and Space Science, 2005, 53(11): 1109–1120.
Zook, H. A., Grün, E., Baguhl, M., Hamilton, D. P., Linkert, G., Liou, J. C., Forsyth, R., Phillips, J. L. Solar wind magnetic field bending of Jovian dust trajectories. Science, 1996, 274(5292): 1501–1503.
Krüger, H., Grün, E., Graps, A., Lammers, S. Observations of electromagnetically coupled dust in the Jovian magnetosphere. Astrophysics and Space Science, 1998, 264(1–4): 247–256.
Krger, H., Horányi, M., Grün, E. Jovian dust streams: probes of the Io plasma torus. Geophysical Research Letters, 2003, 30(2): 1058.
Postberg, F., Kempf, S., Srama, R., Green, S. F., Hillier, J. K., McBride, N., Grün, E. Composition of Jovian dust stream particles. Icarus, 2006, 183(1): 122–134.
Horányi, M., Morfill, G., Grün, E. Mechanism for the acceleration and ejection of dust grains from Jupiter’s magnetosphere. Nature, 1993, 363(6425): 144–146.
Horányi, M., Morfill, G., Grn, E. The dusty ballerina skirt of Jupiter. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1993, 98(A12): 21245–21251.
Horányi, M., Grün, E., Heck, A. Modeling the Galileo dust measurements at Jupiter. Geophysical Research Letters, 1997, 24(17): 2175–2178.
Grün, E., Krüger, H., Graps, A. L., Hamilton, D. P., Heck, A., Linkert, G., Zook, H. A., Dermott. S. F., Fechtig, H., Gustafson, B. A. et al. Galileo observes electromagnetically coupled dust in the Jovian magnetosphere. Journal of Geophysical Research, 1998, 103(E9): 20011–20022.
Hamilton, D. P., Burns, J. A. Ejection of dust from Jupiter’s gossamer ring. Nature, 1993, 364(6439): 695–699.
Jontof-Hutter, D., Hamilton, D. P. The fate of submicron circumplanetary dust grains I: aligned dipolar magnetic fields. Icarus, 2012, 218(1): 420–432.
Jontof-Hutter, D., Hamilton, D. P. The fate of submicron circumplanetary dust grains II: multipolar fields. Icarus, 2012, 220(2): 487–502.
Flandes, A. Dust escape from Io. Geophysical Research Letters, 2004, 31(16): L16802.
Flandes, A., Krüger, H., Hamilton, D. P., Valdés-Galicia, J. F., Spilker, L., Caballero, R. Magnetic field modulated dust streams from Jupiter in interplanetary space. Planetary and Space Science, 2011, 59(13): 1455–1471.
Kuchner, M. J., Reach, W. T., Brown, M. E. A search for resonant structures in the zodiacal cloud with COBE DIRBE: the mars wake and Jupiter’s Trojan clouds. Icarus, 2000, 145(1): 44–52.
Jewitt, D. C., Trujillo, C. A., Luu, J. X. Population and size distribution of small Jovian Trojan asteroids. The Astronomical Journal, 2000, 120(2): 1140–1147.
Liu, X., Schmidt, J. Comparison of the orbital properties of Jupiter Trojan asteroids and Trojan dust. Astronomy & Astrophysics, 2018, 614: A97.
Liou, J. C., Zook, H. A., Jackson, A. A. Radiation pressure, Poynting-Robertson drag, and solar wind drag in the restricted three-body problem. Icarus, 1995, 116(1): 186–201.
Liou, J. C., Zook, H. A. An asteroidal dust ring of micron-sized particles trapped in the 1:1 mean motion resonance with Jupiter. Icarus, 1995, 113(2): 403–414.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the European Space Agency under the project “Jovian Micrometeoroid Environment Model” (JMEM) (Contract No. 4000107249/12/NL/AF) at the University of Oulu, and by the Academy of Finland under the project “Earth and Near-Space System and Environmental Change”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Xiaodong Liu was born in Shandong Province in 1985. He received his B.S. degree in engineering mechanics from Shandong University, in 2008, and his Ph.D. degree in aeronautical and astronautical science and technology from Tsinghua University, in 2013. He received the grand prize for graduate students at Tsinghua University, and national excellent doctor thesis in the field of aeronautical and astronautical science and technology. Currently he is a postdoctoral researcher in the Astronomy Research Unit at University of Oulu, Finland. His research interest focuses on circumplanetary and interplanetary dust dynamics, tenuous planetary rings, estimate of dust hazard to spacecraft, and orbital dynamics around non-spherical bodies.
Jürgen Schmidt received his diploma degree in theoretical physics from the University of Saarbrcken in Germany, and his Ph.D. degree in theoretical physics from the University of Potsdam, Germany. He is now a professor in the Astronomy Research Unit of the University of Oulu, in Finland. His research interests in the field of celestial mechanics focus on the dynamics of circumplanetary dust and dense planetary rings. He is the coinvestigator in the science teams of the Cassini Cosmic Dust Analyzer, the Surface Dust Mass Analyzer of the Europa Clipper Mission, and the JANUS camera onboard the Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Schmidt, J. Dust in the Jupiter system outside the rings. Astrodyn 3, 17–29 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42064-018-0031-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42064-018-0031-z