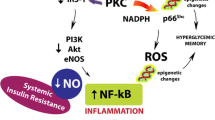
Abstract
Prediabetes has developed into a global pandemic, its prevalence increasing year by year. Although lifestyle changes are advocated as the basis for prediabetes treatment, some patients fail to choose or adhere to appropriate interventions. The basis for selecting an appropriate intervention is determining the stage and cause of the disease. In this review, we aimed to examine the various types and disease processes of prediabetes caused by overnutrition, the present review supporting the hypothesis that overnutrition-induced hyperinsulinemia precedes insulin resistance (IR) and independently causes β-cell dysfunction. Tissue insulin resistance is the main feature of prediabetes with the crosstalk between tissues promoting the formation of systemic insulin resistance. Finally, both β-cell dysfunction induced by hyperinsulinemia or IR and reduced β-cell mass can lead to abnormal insulin secretion and contribute to development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Hence, overnutrition can cause multiple prediabetes phenotypes resulting in development of T2DM through different trajectories. Future diagnosis and treatment should therefore more carefully consider the disease phenotype and stage of development in patients with prediabetes to reduce the incidence of T2DM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Samocha-Bonet D, Debs S, Greenfield JR (2018) Prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes: a pathophysiological-based approach. Trends Endocrinol Metab 29(6):370–379. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2018.03.014
Bansal N (2015) Prediabetes diagnosis and treatment: a review. World J Diabetes 6(2):296–303. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i2.296
American Diabetes A (2021) Prevention or delay of type 2 diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 44(Suppl 1):S34–S39. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc21-S003
Herman WH, Pan Q, Edelstein SL, Mather KJ, Perreault L, Barrett-Connor E, Dabelea DM, Horton E, Kahn SE, Knowler WC, Lorenzo C, Pi-Sunyer X, Venditti E, Ye W, Diabetes Prevention Program Research G (2017) Impact of lifestyle and metformin interventions on the risk of progression to diabetes and regression to normal glucose regulation in overweight or obese people with impaired glucose regulation. Diabetes Care 40(12):1668–1677. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc17-1116
Goodpaster BH, Sparks LM (2017) Metabolic flexibility in health and disease. Cell Metab 25(5):1027–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2017.04.015
Esser N, Utzschneider KM, Kahn SE (2020) Early beta cell dysfunction vs insulin hypersecretion as the primary event in the pathogenesis of dysglycaemia. Diabetologia 63(10):2007–2021. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-020-05245-x
James DE, Stockli J, Birnbaum MJ (2021) The aetiology and molecular landscape of insulin resistance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22:751–771. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-021-00390-6
Vliet SV, Koh H, Patterson BW, Yoshino M, Laforest R, Gropler RJ, Klein S, Mittendorfer B (2020) Obesity is associated with increased basal and postprandial β-cell insulin secretion even in the absence of insulin resistance. Diabetes 69(10):2112–2119. https://doi.org/10.2337/db20-0377
DeFronzo RA, Tripathy D (2009) Skeletal muscle insulin resistance is the primary defect in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(Suppl 2):S157-163. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc09-S302
Czech MP (2017) Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Med 23(7):804–814. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4350
Turner N, Kowalski GM, Leslie SJ, Risis S, Yang C, Lee-Young… R, (2013) Distinct patterns of tissue-specific lipid accumulation during the induction of insulin resistance in mice by high-fat feeding. Diabetologia 56(7):1638–1648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-013-2913-1
Brons C, Jensen CB, Storgaard H, Hiscock NJ, White A, Appel JS, Jacobsen S, Nilsson E, Larsen CM, Astrup A, Quistorff B, Vaag A (2009) Impact of short-term high-fat feeding on glucose and insulin metabolism in young healthy men. J Physiol 587(Pt 10):2387–2397. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.2009.169078
Wadden D, Cahill F, Amini P, Randell E, Vasdev S, Yi Y, Zhang W, Sun G (2012) Serum acylated ghrelin concentrations in response to short-term overfeeding in normal weight, overweight, and obese men. PLoS One 7(9):e45748. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045748
Tschen SI, Dhawan S, Gurlo T, Bhushan A (2009) Age-dependent decline in beta-cell proliferation restricts the capacity of beta-cell regeneration in mice. Diabetes 58(6):1312–1320. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-1651
Prato SD, Leonetti F, Simonson DC, Sheehan P, Matsuda M, Defronzo RA (1994) Effect of sustained physiologic hyperinsulinaemia and hyperglycaemia on insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity in man. Diabetologia 37(10):1025–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00400466
Kolb H, Stumvoll M, Kramer W, Kempf K, Martin S (2018) Insulin translates unfavourable lifestyle into obesity. BMC Med 16(1):232. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-018-1225-1
Kolb H, Kempf K, Rohling M, Martin S (2020) Insulin: too much of a good thing is bad. BMC Med 18(1):224. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-020-01688-6
Kobayashi M, Olefsky JM (1979) Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on insulin binding, glucose transport, and intracellular glucose metabolism in isolated rat adipocytes. Diabetes 28(2):87–95. https://doi.org/10.2337/diab.28.2.87
Catalano KJ, Maddux BA, Szary J, Youngren JF, Goldfine ID, Schaufele F (2014) Insulin resistance induced by hyperinsulinemia coincides with a persistent alteration at the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase domain. PLoS One 9(9):e108693. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0108693
Taegtmeyer H, Beauloye C, Harmancey R, Hue L (2013) Insulin resistance protects the heart from fuel overload in dysregulated metabolic states. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 305(12):H1693-1697. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00854.2012
Pories WJ, Dohm GL (2012) Diabetes: have we got it all wrong? Hyperinsulinism as the culprit: surgery provides the evidence. Diabetes Care 35(12):2438–2442. https://doi.org/10.2337/dc12-0684
Choi CS, Kim YB, Lee FN, Zabolotny JM, Kahn BB, Youn JH (2002) Lactate induces insulin resistance in skeletal muscle by suppressing glycolysis and impairing insulin signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283(2):E233–E240. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00557.2001
Siklova-Vitkova M, Polak J, Klimcakova E, Vrzalova J, Hejnova J, Kovacikova M, Kovacova Z, Bajzova M, Rossmeislova L, Hnevkovska Z, Langin D, Stich V (2009) Effect of hyperinsulinemia and very-low-calorie diet on interstitial cytokine levels in subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 297(5):E1154-1161. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00086.2009
Hall C, Yu H, Choi E (2020) Insulin receptor endocytosis in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Exp Mol Med 52(6):911–920. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-020-0456-3
Smith GI, Mittendorfer B, Klein S (2019) Metabolically healthy obesity: facts and fantasies. J Clin Invest 129(10):3978–3989. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI129186
Stefan N, Häring H-U, Hu FB, Schulze MB (2013) Metabolically healthy obesity: epidemiology, mechanisms, and clinical implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 1(2):152–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(13)70062-7
Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R (2013) Are metabolically healthy overweight and obesity benign conditions?: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 159(11):758–769. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-159-11-201312030-00008
Vogelzangs N, van der Kallen CJH, van Greevenbroek MMJ, van der Kolk BW, Jocken JWE, Goossens GH, Schaper NC, Henry RMA, Eussen S, Valsesia A, Hankemeier T, Astrup A, Saris WHM, Stehouwer CDA, Blaak EE, Arts ICW, Diogenes c (2020) Metabolic profiling of tissue-specific insulin resistance in human obesity: results from the Diogenes study and the Maastricht Study. Int J Obes (Lond) 44(6):1376–1386. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-0565-z
Oosterman JE, Wopereis S, Kalsbeek A (2020) The circadian clock, shift work, and tissue-specific insulin resistance. Endocrinology 161(12):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1210/endocr/bqaa180
Chen DL, Liess C, Poljak A, Xu A, Zhang J, Thoma C, Trenell M, Milner B, Jenkins AB, Chisholm DJ, Samocha-Bonet D, Greenfield JR (2015) Phenotypic characterization of insulin-resistant and insulin-sensitive obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100(11):4082–4091. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2015-2712
Bergman M, Abdul-Ghani M, DeFronzo RA, Manco M, Sesti G, Fiorentino TV, Ceriello A, Rhee M, Phillips LS, Chung S, Cravalho C, Jagannathan R, Monnier L, Colette C, Owens D, Bianchi C, Del Prato S, Monteiro MP, Neves JS, Medina JL, Macedo MP, Ribeiro RT, Filipe Raposo J, Dorcely B, Ibrahim N, Buysschaert M (2020) Review of methods for detecting glycemic disorders. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 165:108233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108233
Riccardi G, Giacco R, Rivellese AA (2004) Dietary fat, insulin sensitivity and the metabolic syndrome. Clin Nutr 23(4):447–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2004.02.006
Buettner R, Parhofer KG, Woenckhaus M, Wrede CE, Kunz-Schughart LA, Schölmerich J, Bollheimer LC (2006) Defining high-fat-diet rat models: metabolic and molecular effects of different fat types. J Mol Endocrinol 36(3):485–501. https://doi.org/10.1677/jme.1.01909
Wilkes JJ, Bonen A, Bell RC (1998) A modified high-fat diet induces insulin resistance in rat skeletal muscle but not adipocytes. Am J Physiol 275(4 Pt 1):679–686. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.1998.275.4.E679
Small L, Brandon AE, Turner N, Cooney GJ (2018) Modeling insulin resistance in rodents by alterations in diet: what have high-fat and high-calorie diets revealed? Am J Physiol-Endocrinology and Metab 314(3):E251–E265. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00337.2017
Sakamoto E, Seino Y, Fukami A, Mizutani N, Tsunekawa S, Ishikawa K, Ogata H, Uenishi E, Kamiya H, Hamada Y, Sato H, Harada N, Toyoda Y, Miwa I, Nakamura J, Inagaki N, Oiso Y, Ozaki N (2012) Ingestion of a moderate high-sucrose diet results in glucose intolerance with reduced liver glucokinase activity and impaired glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion. J Diabetes Investig 3(5):432–440. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2040-1124.2012.00208.x
Pagliassoti MJ, Prach PA (1996) Changes in insulin action, triglycerides, and lipid composition during sucrose feeding in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 271(5 Pt 2):R1319–R1326. https://doi.org/10.0000/PMID8945970
Wefers J, van Moorsel D, Hansen J, Connell NJ, Havekes B, Hoeks J, van Marken Lichtenbelt WD, Duez H, Phielix E, Kalsbeek A, Boekschoten MV, Hooiveld GJ, Hesselink MKC, Kersten S, Staels B, Scheer F, Schrauwen P (2018) Circadian misalignment induces fatty acid metabolism gene profiles and compromises insulin sensitivity in human skeletal muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(30):7789–7794. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1722295115
Jonathan C, Milena S, Orzechowski WJ, Mi J, Alexander C, Sarah V, Megan O, Heike V, Katarina H, Dickson SL (2018) Acute sleep loss results in tissue-specific alterations in genome-wide DNA methylation state and metabolic fuel utilization in humans. Sci Adv 4(8):eaar8590. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aar8590
Meex RCR, Blaak EE, van Loon LJC (2019) Lipotoxicity plays a key role in the development of both insulin resistance and muscle atrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Obes Rev 20(9):1205–1217. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12862
Kurtzhals P, Nishimura E, Haahr H, Hoeg-Jensen T, Johansson E, Madsen P, Sturis J, Kjeldsen T (2021) Commemorating insulin’s centennial: engineering insulin pharmacology towards physiology. Trends Pharmacol Sci 42(8):620–639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2021.05.005
Ferrannini E (2012) Physiology of glucose homeostasis and insulin therapy in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 41(1):25–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2012.01.003
Ahmed B, Sultana R, Greene MW (2021) Adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese. Biomed Pharmacother 137:111315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111315
Batista TM, Jayavelu AK, WewerAlbrechtsen NJ, Iovino S, Lebastchi J, Pan H, Dreyfuss JM, Krook A, Zierath JR, Mann M, Kahn CR (2020) A cell-autonomous signature of dysregulated protein phosphorylation underlies muscle insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab 32(5):844–859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2020.08.007
Zafar U, Khaliq S, Ahmad HU, Manzoor S, Lone KP (2018) Metabolic syndrome: an update on diagnostic criteria, pathogenesis, and genetic links. Hormones (Athens) 17(3):299–313. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-018-0051-3
Perseghin G, Price TB, Petersen KF, Roden M, Shulman GI (1996) Increased glucose transport–phosphorylation and muscle glycogen synthesis after exercise training in insulin-resistant subjects. N Engl J Med 335(18):1357–1362. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199610313351804
Shulman GI (2014) Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. N Engl J Med 371(12):1131. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc1412427#SA2
Roden M, Shulman GI (2019) The integrative biology of type 2 diabetes. Nature 576(7785):51–60. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1797-8
Chaurasia B, Summers SA (2021) Ceramides in metabolism: key lipotoxic players. Ann Rev Physiol 83:303–330. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-031620-093815
Abdul-Ghani MA, Molina-Carrion M, Jani R, Jenkinson C, Defronzo RA (2008) Adipocytes in subjects with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance are resistant to the anti-lipolytic effect of insulin. Acta Diabetol 45(3):147–150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-008-0033-z
Taylor R, Al-Mrabeh A, Zhyzhneuskaya S, Peters C, Barnes AC, Aribisala BS, Hollingsworth KG, Mathers JC, Sattar N, Lean MEJ (2018) Remission of human type 2 diabetes requires decrease in liver and pancreas fat content but is dependent upon capacity for beta cell recovery. Cell Metab 28(4):547-556e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.07.003
Bird SR, Hawley JA (2016) Update on the effects of physical activity on insulin sensitivity in humans. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 2(1):e000143. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2016-000143
Locatelli CAA, Mulvihill EE (2020) Islet health, hormone secretion, and insulin responsivity with low-carbohydrate feeding in diabetes. Metabolites 10(11):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10110455
Alejandro EU, Gregg B, Blandino-Rosano M, Cras-Meneur C, Bernal-Mizrachi E (2015) Natural history of beta-cell adaptation and failure in type 2 diabetes. Mol Aspects Med 42:19–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2014.12.002
Hudish LI, Reusch JE, Sussel L (2019) beta Cell dysfunction during progression of metabolic syndrome to type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 129(10):4001–4008. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI129188
Oh YS, Bae GD, Baek DJ, Park EY, Jun HS (2018) Fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity in pancreatic beta-cells during development of type 2 diabetes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:384. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00384
Katsoulis K, Paschou SA, Hatzi E, Tigas S, Georgiou I, Tsatsoulis A (2018) TCF7L2 gene variants predispose to the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus among individuals with metabolic syndrome. Hormones (Athens) 17(3):359–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-018-0047-z
Nolan CJ, Prentki M (2019) Insulin resistance and insulin hypersecretion in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: time for a conceptual framework shift. Diab Vasc Dis Res 16(2):118–127. https://doi.org/10.1177/1479164119827611
Chen M, Halter JB, Porte D (1987) The role of dietary carbohydrate in the decreased glucose tolerance of the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc 35(5):417–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1987.tb04663.x
Erion KA, Corkey BE (2017) Hyperinsulinemia: a cause of obesity? Curr Obes Rep 6(2):178–186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-017-0261-z
Halperin F, Lopez X, Manning R, Kahn CR, Kulkarni RN, Goldfine AB (2012) Insulin augmentation of glucose-stimulated insulin secretion is impaired in insulin-resistant humans. Diabetes 61(2):301–309. https://doi.org/10.2337/db11-1067
Weir GC, Gaglia J, Bonner-Weir S (2020) Inadequate β-cell mass is essential for the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 8(3):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2213-8587(20)30022-x
Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S (2013) Islet beta cell mass in diabetes and how it relates to function, birth, and death. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1281:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.12031
Erion K, Corkey BE (2018) beta-cell failure or beta-cell abuse? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:532. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00532
McKay AKA, Pyne DB, Peeling P, Sharma AP, Ross MLR, Burke LM (2019) The impact of chronic carbohydrate manipulation on mucosal immunity in elite endurance athletes. J Sports Sci 37(5):553–559. https://doi.org/10.1080/02640414.2018.1521712
Butler AE, Janson J, Bonner-Weir S, Ritzel R, Rizza RA (2003) Β-cell deficit and increased Β-cell apoptosis in humans with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 52:102–118. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.1.102
Fransson L, Franzen S, Rosengren V, Wolbert P, Sjoholm A, Ortsater H (2013) beta-cell adaptation in a mouse model of glucocorticoid-induced metabolic syndrome. J Endocrinol 219(3):231–241. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0189
Bock T, Pakkenberg B, Buschard K (2003) Increased islet volume but unchanged islet number in ob/ob mice. Diabetes 52(7):1716–1722. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.7.1716
Inaishi J, Saisho Y (2020) Beta-cell mass in obesity and type 2 diabetes, and its relation to pancreas fat: a mini-review. Nutrients 12(12):3846. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123846
Chen C, Cohrs CM, Stertmann J, Bozsak R, Speier S (2017) Human beta cell mass and function in diabetes: recent advances in knowledge and technologies to understand disease pathogenesis. Mol Metab 6(9):943–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2017.06.019
Yoon KH, Ko SH, Cho JH, Lee JM, Ahn YB, Song KH, Yoo SJ, Kang MI, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY, Kang SK, Kim HS, Lee IK, Bonner-Weir S (2003) Selective beta-cell loss and alpha-cell expansion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Korea. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(5):2300–2308. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2002-020735
Neutzsky-Wulff AV, Andreassen KV, Hjuler ST, Feigh M, Bay-Jensen AC, Zheng Q, Henriksen K, Karsdal MA (2012) Future detection and monitoring of diabetes may entail analysis of both β-cell function and volume: how markers of β-cell loss may assist. J Transl Med 10(1):214. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-10-214
Talchai C, Xuan S, Lin HV, Sussel L, Accili D (2012) Pancreatic beta cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic beta cell failure. Cell 150(6):1223–1234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.07.029
Inaishi J, Saisho Y, Hirakawa Y, Yoshida D, Hata J, Mukai N, Watanabe Y, Oda Y, Itoh H, Ninomiya T (2020) Association of glucose tolerance status with pancreatic beta- and alpha-cell mass in community-based autopsy samples of Japanese individuals: the Hisayama Study. J Diabetes Investig 11(5):1197–1206. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13232
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yuli Zhang had the idea for the article and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript by literature resource. Tuming Shen performed the literature search and data analysis. Songtao Wang revised and critically edited the manuscript. All authors agreed on the final version of the manuscript and Songtao Wang will act as the guarantor of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Ethical approval was not required for this review.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Shen, T. & Wang, S. Progression from prediabetes to type 2 diabetes mellitus induced by overnutrition. Hormones 21, 591–597 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-022-00399-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-022-00399-2