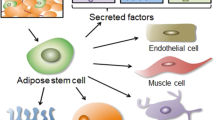
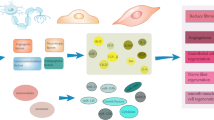
Abstract
Stem cell therapy has become a subject of great interest to researchers worldwide. One of the medical conditions being studied for possible treatment with the use of stem cells is erectile dysfunction, and particularly organic and post-radical prostatectomy erectile dysfunction. However, is stem cell therapy a viable treatment option for erectile dysfunction? The current body of literature provides a wide array of clinical trials performed on animal models simulating different types of human erectile dysfunction. Unfortunately, only a handful of studies have been performed on human patients and almost all of them were phase 1 studies limited by the small sample size. This review aims to summarize the available evidence on the use of stem cell therapy for the treatment of erectile dysfunction and also to provide an overview of upcoming and ongoing clinical trials in this field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
NIH Consensus Conference. Impotence. NIH Consensus Development Panel on Impotence. JAMA, 1993. 270(1): p. 83–90
Soebadi MA et al (2017) Stem cells in male sexual dysfunction: are we getting somewhere? Sex Med Rev 5(2):222–235
Feldman HA et al (1994) Impotence and its medical and psychosocial correlates: results of the Massachusetts Male Aging Study. J Urol 151(1):54–61
Gokce A et al (2016) Adipose tissue-derived stem cells for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Curr Urol Rep 17(2):14
Zhang H et al (2012) Stem cells: novel players in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. Asian J Androl 14(1):145–155
Albersen M et al (2010) Injections of adipose tissue-derived stem cells and stem cell lysate improve recovery of erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Sex Med 7(10):3331–3340
Rubina K et al (2009) Adipose stromal cells stimulate angiogenesis via promoting progenitor cell differentiation, secretion of angiogenic factors, and enhancing vessel maturation. Tissue Eng Part A 15(8):2039–2050
Shan H et al (2015) Stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction of cavernous nerve injury rats: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 10(4):e0121428
Chen X et al (2016) Neurotrophic effect of adipose tissue-derived stem cells on erectile function recovery by pigment epithelium-derived factor secretion in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Stem Cells Int 2016:5161248
Yang R et al (2015) Adipose-derived stem cells ameliorate erectile dysfunction after cavernous nerve cryoinjury. Andrology 3(4):694–701
Qiu X et al (2012) Effects of intravenous injection of adipose-derived stem cells in a rat model of radiation therapy-induced erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 9(7):1834–1841
Gokce A et al (2014) Adipose tissue-derived stem cell therapy for prevention and treatment of erectile dysfunction in a rat model of Peyronie’s disease. Andrology 2(2):244–251
Huang YC et al (2010) The effect of intracavernous injection of adipose tissue-derived stem cells on hyperlipidemia-associated erectile dysfunction in a rat model. J Sex Med 7(4 Pt 1):1391–1400
Ryu JK et al (2014) Intracavernous delivery of clonal mesenchymal stem cells restores erectile function in a mouse model of cavernous nerve injury. J Sex Med 11(2):411–423
Ryu JK et al (2016) Intracavernous delivery of clonal mesenchymal stem cells rescues erectile function in the streptozotocin-induced diabetic mouse. Andrology 4(1):172–184
Woo JC et al (2011) Transplantation of muscle-derived stem cells into the corpus cavernosum restores erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Korean J Urol 52(5):359–363
Cengiz T et al (2017) Intracavernous injection of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells improves erectile dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Sex Med 14(1):50–58
Baraniak PR, McDevitt TC (2010) Stem cell paracrine actions and tissue regeneration. Regen Med 5(1):121–143
You D et al (2015) Comparative study of autologous stromal vascular fraction and adipose-derived stem cells for erectile function recovery in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Stem Cells Transl Med 4(4):351–358
Song KM et al (2014) Intracavernous delivery of stromal vascular fraction restores erectile function through production of angiogenic factors in a mouse model of cavernous nerve injury. J Sex Med 11(8):1962–1973
Chen F et al (2017) Adipose-derived stem cell-derived exosomes ameliorate erectile dysfunction in a rat model of type 2 diabetes. J Sex Med 14(9):1084–1094
Xu Y et al (2014) Therapeutic potential of adipose-derived stem cells-based micro-tissues in a rat model of postprostatectomy erectile dysfunction. J Sex Med 11(10):2439–2448
Yang Q et al (2016) Transplantation of human urine-derived stem cells transfected with pigment epithelium-derived factor to protect erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. Cell Transplant 25(11):1987–2001
Sun X et al (2017) B cell lymphoma-2-modified bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation for the treatment of diabetes mellitus-induced erectile dysfunction in a rat model. Urol Int 98(3):358–366
Bivalacqua TJ et al (2007) Mesenchymal stem cells alone or ex vivo gene modified with endothelial nitric oxide synthase reverse age-associated erectile dysfunction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 292(3):H1278–H1290
Kendirci M et al (2010) Transplantation of nonhematopoietic adult bone marrow stem/progenitor cells isolated by p75 nerve growth factor receptor into the penis rescues erectile function in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Urol 184(4):1560–1566
Wu XJ et al (2017) Telomerase reverse transcriptase genetically modified adipose tissue derived stem cells improves erectile dysfunction by inhibiting oxidative stress and enhancing proliferation in rat model. Biomed Pharmacother 92:595–605
Lin H et al (2016) Nanoparticle improved stem cell therapy for erectile dysfunction in a rat model of cavernous nerve injury. J Urol 195(3):788–795
Shan HT et al (2017) Combination of low-energy shock-wave therapy and bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation to improve the erectile function of diabetic rats. Asian J Androl 19(1):26–33
Jeon SH et al (2016) Combination therapy using human adipose-derived stem cells on the cavernous nerve and low-energy shockwaves on the corpus cavernosum in a rat model of post-prostatectomy erectile dysfunction. Urology 88:226 e1–9
Martinez-Salamanca JI et al (2016) Dual strategy with oral phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition and intracavernosal implantation of mesenchymal stem cells is superior to individual approaches in the recovery of erectile and cavernosal functions after cavernous nerve injury in rats. J Sex Med 13(1):1–11
Bahk JY et al (2010) Treatment of diabetic impotence with umbilical cord blood stem cell intracavernosal transplant: preliminary report of 7 cases. Exp Clin Transplant 8(2):150–160
Levy JA et al (2016) Determining the feasibility of managing erectile dysfunction in humans with placental-derived stem cells. J Am Osteopath Assoc 116(1):e1–e5
Haahr MK et al (2016) Safety and potential effect of a single intracavernous injection of autologous adipose-derived regenerative cells in patients with erectile dysfunction following radical prostatectomy: an open-label phase I clinical trial. EBioMed 5:204–210
Yiou R et al (2016) Safety of intracavernous bone marrow-mononuclear cells for postradical prostatectomy erectile dysfunction: an open dose-escalation pilot study. Eur Urol 69(6):988–991
Yiou, R., et al.,(2017) Intracavernous injections of bone marrow mononucleated cells for postradical prostatectomy erectile dysfunction: final results of the INSTIN clinical trial. Eur Urol Focus,
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vakalopoulos, I., Memmos, D., Mykoniatis, I. et al. Stem cell therapy in erectile dysfunction: science fiction or realistic treatment option?. Hormones 17, 315–320 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-018-0050-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42000-018-0050-4