Key summary points
The purpose of this study is to analyze the changes in inflammatory markers and efficacy in the treatment of senior patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and community-acquired pneumonia with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion.
AbstractSection FindingsContinuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in the treatment of senior patients with T2DM and community-acquired pneumonia can effectively control fasting and postprandial blood glucose, significantly reduce the levels of inflammatory markers, and improve infection treatment efficacy.
AbstractSection MessageWe analyzed the changes in blood glucose and inflammatory markers, and improvement in clinical outcome in the treatment of senior patients with T2DM and community-acquired pneumonia, with CSII, to guide clinical practice.
Abstract
Objective
The purpose of this study is to analyze the changes in inflammatory markers and efficacy in the treatment of senior patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and community-acquired pneumonia with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII).
Methods
A total of 105 senior patients with T2DM and community-acquired pneumonia, were randomly divided into two groups, viz., treatment group and control group—52 patients in the treatment group were treated with CSII, and 53 patients in the control group with multiple daily insulin injections (MDI). The changes in fasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, total number of white blood cells, neutrophils, percentage of neutrophils, lymphocytes, percentage of lymphocytes, C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A, procalcitonin, interleukin-6 indexes, and the improvement in clinical outcome between the two groups were compared on the 5th and the 10th day of treatment.
Results
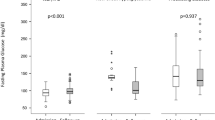
In the treatment group, there were 52 patients with an average age of (73.7 ± 8.5) years, which included 28 males and 24 females. In the control group, there were 53 patients, with 27 males and 26 females, with an average age of (74.8 ± 8.8) years. On the 5th and the 10th day of the treatment, the fasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, total number of white blood cells, neutrophils, percentage of neutrophils, lymphocytes, percentage of lymphocytes, C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A, procalcitonin and interleukin-6 of the treatment group were better than that of the control group (P < 0.05). The use of CSII was associated with a higher probability of a prompt recovery (P < 0.05).
Conclusion
The administration of CSII in the treatment of senior patients with T2DM and community-acquired pneumonia can effectively control fasting and postprandial blood glucose, significantly reduce the levels of inflammatory markers, and improve infection treatment efficacy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Lopez-de-Andres A, Albaladejo-Vicente R, de Miguel-Diez J, Hernandez-Barrera V, Ji Z, Zamorano-Leon JJ, Lopez-Herranz M, Jimenez-Garcia R (2020) Incidence and outcomes of hospitalization for community-acquired, ventilator-associated and non-ventilator hospital-acquired pneumonias in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Spain. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care 8(1):e001447
Huang D, He D, Gong L, Wang W, Yang L, Zhang Z, Shi Y, Liang Z (2021) Clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with mortality in patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Crit Care 25(1):419
Endocrinology Branch of Chinese Medical Association, diabetes Branch of Chinese Medical Association, Endocrinology Metabolism Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association Chinese Insulin pump treatment guidelines (2021 version) Chinese Journal of Endocrine Metabolism. 2021, 37(08):679–701.
Zhang J, Liu QQ, He WH et al (2021) Effects of different glucose-lowering strategies on the efficacy of elderly patients with diabetes mellitus combined with community-acquired pneumonia in non-critical conditions. China Primary Health Care 35(08):88–91
Diabetes Branch of Chinese Medical Association Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 diabetes (2020 Edition) Chinese Journal of diabetes, 2021; 13(4): 315–409.
Alberti KG, Zimmet PZ (1998) Definition, diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus and its complications. Part 1: diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus provisional report of a WHO consultation. Diabet Med 15(7):539–553
World Health Organization (2013) Use of glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) in the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus. Abbreviated report of a WHO consultation, 2011[EB/OL].
American Diabetes Association (2020) 2 Classification and diagnosis of diabetes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2020[J]. Diabetes Care 43(Suppl 1):S14–S31
Qu JM, Cao B. Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Chinese Adult Community Acquired Pneumonia (2016 Edition). Chinese J Tubercul Respirat Dis. 2016; 39(04): 253–279.
Compilation Group of Clinical Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 diabetes in the Elderly in China, Endocrine Metabolism Branch of the Chinese Geriatrics Society, Endocrine Metabolism Branch of the Chinese Geriatrics Health Care Research Society, etc Chinese Clinical Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Elderly Type 2 diabetes (2022). Chinese Journal of Internal Medicine. 2022; 61(1): 12–50.
Li X, Ren Y, Yan T (2022) A case-control study on risk factors of pulmonary infection in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its implications for clinical intervention. Comput Math Methods Med 12(2022):4492574
Baumann U, Routes JM, Soler-Palacín P, Jolles S (2018) The lung in primary immunodeficiencies: new concepts in infection and inflammation. Front Immunol 8(9):1837
Grunberger G, Bhargava A, Ly T, Zisser H, Ilag LL, Malone J, Fan L, Zhang S, Johnson J (2020) Human regular U-500 insulin via continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injections in adults with type 2 diabetes: The VIVID study. Diabetes Obes Metab 22(3):434–441
Dicembrini I, Mannucci E, Monami M, Pala L (2019) Impact of technology on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of randomized trials on continuous glucose monitoring and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion. Diabetes Obes Metab 21(12):2619–2625
Chatziravdeli V, Lambrou GI, Samartzi A, Kotsalas N, Vlachou E, Komninos J, Tsartsalis AN (2023) A systematic review and meta-analysis of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion vs. multiple daily injections in type-2 diabetes. Medicina 59(1):141
Ito A, Ishida T (2020) Diagnostic markers for community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Transl Med 8(9):609
Sinopalnikov AI, Rachina SA, Vasilyeva IS, Pigusova NA, Karpova OY (2023) Clarithromycin for community-acquired pneumonia in adults: focus on anti-inflammatory properties. Ter Arkh 94(12):1394–1400
Ma C, Li X, Gao X, He Q, Zhuan B, Ji W, Cai Z, Tian J, Liu L, Liu H, Wang P, Cao X (2022) Value of serum amyloid protein dynamic changes on evaluating condition and prognosis of patients with viral and mycoplasma community-acquired pneumonia. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 34(6):592–596. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210223-00273
Li LQ, Yao MY, Ma JX, Xue P, Li YK (2019) Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion combined with liraglutide reduced glycemic variability and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a study based on the flash glucose monitoring system. Endocr J 66(10):871–880
Acknowledgements
We are particularly grateful to all the people who have given us help on our article.
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from Qingdao Medical and Health Talents Training Project (QWKJZ [2019] No. 9).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
All authors have contributed significantly to the manuscript and declare that the work is original and has not been submitted or published elsewhere. None of the authors have any financial disclosure or conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was conducted in accordance with the declaration of Helsinki. This study was conducted with approval from the Ethics Committee of Qingdao The Eighth People’s Hospital (QBYLL-KY-2023–015). A written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from every individual whose data are included in this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, HF., Li, F., Xu, YX. et al. Changes in inflammatory markers and efficacy analysis of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion in senior patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus hospitalized with community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized controlled trial. Eur Geriatr Med 15, 519–525 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-023-00915-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-023-00915-6