Key summary points
To explore the factors affecting sarcopenia in older adults in the community.
AbstractSection FindingsPhysical activity, diabetes mellitus, age, marital status, nutrition and depression were important factors that have an impact on sarcopenia.
AbstractSection MessagePhysical activity, diabetes mellitus, age, marital status, nutrition and depression were important factors that have an impact on sarcopenia.
Abstract
Purpose
Research on sarcopenia has primarily focused on single fields such as physiology or psychology. However, there is a lack of clear evidence to determine the influence of social factors on sarcopenia. Therefore, our aim was to explore the multidimensional factors that contribute to sarcopenia in older adults within the community.
Methods
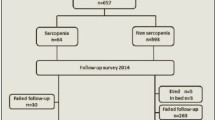
In this retrospective case–control study, we applied the diagnostic criteria from The Asian Working Group on Sarcopenia (AWGS) 2019 to categorize study subjects into control and case groups. Our aim was to examine the impact of physical, psychological, and social factors on community-dwelling older adults with sarcopenia across multiple dimensions. We utilized descriptive statistics, as well as simple and multivariate logistic regression analyses, to analyze the data. We compared the odds ratios (OR) of the factors between the two groups and ranked the importance of the influencing factors using the XGBoost algorithm in Python software.
Results
Combined with multivariate analysis and XGBoost algorithm results, it can be seen that physical activity is the strongest predictor of sarcopenia [OR] = 0.922(95% CI 0.906–0.948), followed diabetes mellitus [OR] = 3.454(95% CI 1.007–11.854), older age [OR] = 1.112(95% CI 1.023–1.210), divorced or widowed [OR] = 19.148 (95% CI 4.233–86.607), malnutrition [OR] = 18.332(95% CI 5.500–61.099), and depressed [OR] = 7.037(95% CI 2.391–20.710).
Conclusions
Factors associated with the development of sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults cover a multiplicity of physical, psychological, and social factors, physical activity, diabetes mellitus, age, marital status, nutrition, and depression were important factors that have an impact on sarcopenia.
Registration number
ChiCTR2200056297.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F et al (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis: report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in older people. Age Ageing 39(4):412–423. https://doi.org/10.1093/ageing/afq034
Chen LK, Woo J, Assantachai P, Auyeung TW, Chou MY, Iijima K et al (2020) Asian working group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on Sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc 21(3):300-307.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
Ren X, Zhang X, He Q, Du L, Chen K, Chen S, Pan Y (2022) Prevalence of sarcopenia in Chinese community-dwelling elderly: a systematic review. BMC Public Health 22(1):1702. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-022-13909-z
Antunes AC, Araújo DA, Veríssimo MT, Amaral TF (2017) Sarcopenia and hospitalisation costs in older adults: a cross-sectional study. Nutrition Dietetics:J Dietitians Association Australia 74(1):46–50. https://doi.org/10.1111/1747-0080.12287
Steffl M, Sima J, Shiells K, Holmerova I (2017) The increase in health care costs associated with muscle weakness in older people without long-term illnesses in the Czech Republic: results from the Survey of health, ageing and retirement in Europe (SHARE). Clin Interv Aging 12:2003–2007. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S150826
Tanaka, T., Takahashi, K., Hirano, H., Kikutani, T., Watanabe, Y., Ohara, Y., Furuya, H., Tetsuo, T., Akishita, M., Iijima, K. (2018). Oral Frailty as a Risk Factor for Physical Frailty and Mortality in Community-Dwelling Elderly. The journals of gerontology. Series A, Biological sciences and medical sciences, 73 (12) 1661–1667. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glx225
Verlaan S, Aspray TJ, Bauer JM, Cederholm T, Hemsworth J, Hill TR et al (2017) Nutritional status, body composition, and quality of life in community-dwelling sarcopenic and non-sarcopenic older adults: a case-control study. Clinical Nutrit (Edinburgh, Scotland) 36(1):267–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2015.11.013
Montazeri-Najafabady N, Dabbaghmanesh MH, Nasimi N, Sohrabi Z, Chatrabnous N (2021) The association between TP53 rs1625895 polymorphism and the risk of sarcopenic obesity in Iranian older adults: a case-control study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 22(1):438. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-021-04314-5
Wang LT, Huang WC, Hung YC, Park JH (2021) Association between depressive symptoms and risk of Sarcopenia in Taiwanese older adults. J Nutr Health Aging 25(6):790–794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-021-1631-5
Zasadzka E, Pieczyńska A, Trzmiel T, Kleka P, Pawlaczyk M (2021) Correlation between handgrip strength and depression in older adults-a systematic review and a meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 18(9):4823. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18094823
Petticrew M, Davey Smith G (2012) The monkey puzzle: a systematic review of studies of stress, social hierarchies, and heart disease in monkeys. PloS one 7(3):e27939. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0027939
Kappeler PM, Cremer S, Nunn CL (2015) Sociality and health: impacts of sociality on disease susceptibility and transmission in animal and human societies. Philosophical Trans Royal Soc London Series B, Biol sci. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2014.0116
Swan L, Warters A, O’Sullivan M (2021) Socioeconomic inequality and risk of Sarcopenia in community-dwelling older adults. Clin Interv Aging 16:1119–1129. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S310774
Geriatric Rehabilitation Group of the Chinese Medical Association Geriatrics Branch and Muscle Decay Syndrome Expert Consensus Writing Group (2017) Chinese expert consensus on muscle wasting syndrome (draft). Chinese J Geriatrics 07:711–718
Zhang HH (2017) Improvement and reliability and validity evaluation of the nutrition evaluation scale for the elderly in the community (Master's thesis, Shandong University).[in Chinese]https://kns.cnki.net/kcms2/article/abstract?v=6oglyc8kNW63i0-XvOFGCWJp8QW-_Inrc3N-V5sM7jVOL9ThgykDl4f-zI2CzlvAWuUz1cG9RlM80skxgCGEK6uTc3aMkoidkIczel5NdCD_bqzDo943SkhhBrnKzEUE_Ifvt_iyC7g=&uniplatform=NZKPT&language=CHS
Washburn RA, Smith KW, Jette AM, Janney CA (1993) The Physical activity scale for the elderly (PASE): development and evaluation. J Clin Epidemiol 46(2):153–162. https://doi.org/10.1016/0895-4356(93)90053-4
Kayser-Jones J, Bird WF, Paul SM, Long L, Schell ES (1995) An instrument to assess the oral health status of nursing home residents. Gerontologist 35(6):814–824. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/35.6.814
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB (2002) The PHQ-15: validity of a new measure for evaluating the severity of somatic symptoms. Psychosom Med 64(2):258–266. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006842-200203000-00008
Bonewald L (2019) Use it or lose it to age: a review of bone and muscle communication. Bone 120:212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2018.11.002
Angulo J, El Assar M, Álvarez-Bustos A, Rodríguez-Mañas L (2020) Physical activity and exercise: strategies to manage frailty. Redox Bio. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2020.101513
Wang M, Tan Y, Shi Y, Wang X, Liao Z, Wei P (2020) Diabetes and Sarcopenic obesity: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatments. Front Endocrinol 11:568. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00568
Pöllänen E, Kangas R, Horttanainen M, Niskala P, Kaprio J, Butler-Browne G, Kovanen V (2015) Intramuscular sex steroid hormones are associated with skeletal muscle strength and power in women with different hormonal status. Aging cell 14(2):236–248. https://doi.org/10.1111/acel.12309
Li CW, Yu K, Shyh-Chang N, Li GX, Jiang LJ, Yu SL, Li DJ (2019) Circulating factors associated with sarcopenia during ageing and after intensive lifestyle intervention. J Cachexia, Sarcopenia Muscle 10(3):586–600. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12417
Thoma A, Akter-Miah T, Reade RL, Lightfoot AP (2020) Targeting reactive oxygen species (ROS) to combat the age-related loss of muscle mass and function. Biogerontology 21(4):475–484. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-020-09883-x
Hamrick MW (2017) Role of the Cytokine-like Hormone Leptin in Muscle-bone crosstalk with aging. J Bone Metabolism 24(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1105/jbm.2017.24.1.1
Robinson S, Granic A, Sayer AA (2019) Nutrition and Muscle strength, as the key component of Sarcopenia: an overview of current evidence. Nutrients 11(12):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11122942
Huang YH, Chiu WC, Hsu YP, Lo YL, Wang YH (2020) Effects of Omega-3 fatty acids on muscle mass, muscle strength and muscle performance among the elderly: a meta-analysis. Nutrients 12(12):3739. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12123739
Li Z, Tong X, Ma Y, Bao T, Yue J (2022) Prevalence of depression in patients with sarcopenia and correlation between the two diseases: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 13(1):128–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcsm.12908
Funding
The research leading to these results received funding from National Social Science Found of China under Grant Agreement No 20BSH121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of North China University of Technology (No. 2021141); this trial was registered in the China Clinical Trials Center with registration number ChiCTR2200056297.
Informed consent
All participants gave written informed consent before participating in this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, P., Wang, F. et al. Influencing factors of sarcopenia in older adults based on the Newman system model: a case–control study. Eur Geriatr Med 14, 1049–1057 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-023-00822-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41999-023-00822-w