Abstract
The non-classical nucleation and growth mechanism for hydrothermal zeolite synthesis is a complex convolution of thermodynamic phase transformations, kinetic chemical condensations, three-phase mass transfer and spatial-temporal thermal gradients. The process is typically studied in batch autoclaves heated with laboratory ovens before being scaled in high temperature batch crystallizers. The experimental and theoretical work presented here proposes that transport limitations dominate batch process syntheses. Thus, kinetically-controlled, scalable crystallization must be achieved for accurate elucidation of the underlying crystallization mechanism. A segmented microdroplet crystallizer is used to remove internal and external heat transfer gradients during the synthesis of LTA zeolite crystals. The heat transfer regimes are carefully mapped, and specific criteria are established for overcoming thermal limitations.
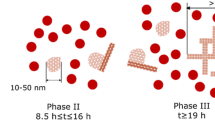
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Prasomsri T, Jiao W, Weng SZ, Garcia Martinez J (2015) Mesostructured zeolites: bridging the gap between zeolites and MCM-41. Chem Commun 51(43):8900–8911. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4CC10391B
Database of Zeolite Structures (2021) International Zeolite Association. http://www.iza-structure.org/databases/
Moreno A, Mendoza ME (2015) 31 - crystallization in gels. In: Rudolph P (ed) Handbook of crystal growthSecond edn. Elsevier, Boston, pp 1277–1315. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-444-63303-3.00031-6
Nikolakis V, Kokkoli E, Tirrell M, Tsapatsis M, Vlachos DG (2000) Zeolite growth by addition of subcolloidal particles: modeling and experimental validation. Chem Mater 12(3):845–853. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm990653i
Kumar M, Li R, Rimer JD (2016) Assembly and evolution of amorphous precursors in zeolite L crystallization. Chem Mater 28(6):1714–1727. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b04569
Alfaro S, Rodríguez C, Valenzuela MA, Bosch P (2007) Aging time effect on the synthesis of small crystal LTA zeolites in the absence of organic template. Mater Lett 61(23):4655–4658. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2007.03.009
Li R, Chawla A, Linares N, Sutjianto JG, Chapman KW, Martínez JG, Rimer JD (2018) Diverse physical states of amorphous precursors in zeolite synthesis. Ind Eng Chem Res 57(25):8460–8471. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b01695
Chernov AA, Givargizov EJ, Bagdasarov KS, Kuznetsov VA, Demianets LN, Lobachev AN (2012) Modern crystallography III: crystal growth. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Rossi D, Jamshidi R, Saffari N, Kuhn S, Gavriilidis A, Mazzei L (2015) Continuous-flow sonocrystallization in droplet-based microfluidics. Cryst Growth Des 15(11):5519–5529. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01153
Yazdanpanah N, Nagy ZK (2020) The handbook of continuous crystallization. Royal Society of Chemistry
Liu Z, Wakihara T, Nishioka D, Oshima K, Takewaki T, Okubo T (2014) One-minute synthesis of crystalline microporous aluminophosphate (AlPO4-5) by combining fast heating with a seed-assisted method. Chem Commun 50(19):2526–2528. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3CC49548E
Zhang J, Wang K, Teixeira AR, Jensen KF, Luo G (2017) Design and scaling up of microchemical systems: a review. Annual Review of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering 8(1):285–305. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060816-101443
Liu Z, Okabe K, Anand C, Yonezawa Y, Zhu J, Yamada H, Endo A, Yanaba Y, Yoshikawa T, Ohara K, Okubo T, Wakihara T (2016) Continuous flow synthesis of ZSM-5 zeolite on the order of seconds. Proc Natl Acad Sci 113(50):14267–14271. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1615872113
Degnan T, Chitnis G, Schipper PH (2000) History of ZSM-5 fluid catalytic cracking additive development at Mobil. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 35:245–252
Flanigen EM (1991) Chapter 2 zeolites and molecular sieves an historical perspective. In: van Bekkum H, Flanigen EM, Jansen JC (eds) Studies in surface science and catalysis, vol 58. Elsevier, pp 13–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-2991(08)63599-5
Zhang X, Liu D, Xu D, Asahina S, Cychosz KA, Agrawal KV, Al Wahedi Y, Bhan A, Al Hashimi S, Terasaki O, Thommes M, Tsapatsis M (2012) Synthesis of self-pillared zeolite nanosheets by repetitive branching. Science 336(6089):1684–1687. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1221111
Díaz I, Kokkoli E, Terasaki O, Tsapatsis M (2004) Surface structure of zeolite (MFI) crystals. Chem Mater 16(25):5226–5232. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm0488534
Boudreau LC, Kuck JA, Tsapatsis M (1999) Deposition of oriented zeolite a films: in situ and secondary growth. J Membr Sci 152(1):41–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(98)00166-5
Davis TM, Drews TO, Ramanan H, He C, Dong J, Schnablegger H, Katsoulakis MA, Kokkoli E, McCormick AV, Penn RL, Tsapatsis M (2006) Mechanistic principles of nanoparticle evolution to zeolite crystals. Nat Mater 5:400. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1636
Davis ME (1991) Zeolites and molecular-sieves - not JUST ordinary catalysts. Ind Eng Chem Res 30(8):1675–1683. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00056a001
Lobo RF, Zones SI, Davis ME (1995) Structure-direction in zeolite synthesis. In: Herron N, Corbin DR (eds) Inclusion chemistry with zeolites: nanoscale materials by design. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 47–78. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-011-0119-6_2
Davis ME (2002) Ordered porous materials for emerging applications. Nature 417(6891):813–821. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00785
Feng G, Cheng P, Yan W, Boronat M, Li X, Su J-H, Wang J, Li Y, Corma A, Xu R, Yu J (2016) Accelerated crystallization of zeolites via hydroxyl free radicals. Science 351(6278):1188–1191. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaf1559
Corma A (1997) From microporous to mesoporous molecular sieve materials and their use in catalysis. Chem Rev 97(6):2373–2420. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr960406n
Corma A (2003) State of the art and future challenges of zeolites as catalysts. J Catal 216(1–2):298–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0021-9517(02)00132-X
Moliner M, Román-Leshkov Y, Corma A (2019) Machine learning applied to zeolite synthesis: the missing link for realizing high-throughput discovery. Acc Chem Res 52(10):2971–2980. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00399
Rimer JD, Fedeyko JM, Vlachos DG, Lobo RF (2006) Silica self-assembly and synthesis of microporous and mesoporous silicates. Chem Eur J 12(11):2926–2934. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200500684
Thompson RW (1998) Recent advances in the understanding of zeolite synthesis. Synthesis, vol 1. Molecular Sieves. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, pp 1–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/3-540-69615-6_1
Thompson RW, Dyer A (1985) Mathematical analyses of zeolite crystallization. Zeolites 5(4):202–210. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-2449(85)90086-7
Kumar M, Luo H, Román-Leshkov Y, Rimer JD (2015) SSZ-13 crystallization by particle attachment and deterministic pathways to crystal size control. J Am Chem Soc 137(40):13007–13017. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b07477
Rimer JD (2018) Rational design of zeolite catalysts. Nature Catalysis 1(7):488–489. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41929-018-0114-5
Kumar S, Wang Z, Penn RL, Tsapatsis M (2008) A structural resolution Cryo-TEM study of the early stages of MFI growth. J Am Chem Soc 130(51):17284–17286. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja8063167
Ju J, Zeng C, Zhang L, Xu N (2006) Continuous synthesis of zeolite NaA in a microchannel reactor. Chem Eng J 116(2):115–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2005.11.006
Coker EN, Dixon AG, Thompson RW, Sacco A (1995) Zeolite synthesis in unstirred batch reactors II. Effect of non-uniform pre-mixing on the crystallization of zeolites A and X. Microporous Mater 3(6):637–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-6513(94)00070-C
Chen C-T, Iyoki K, Yamada H, Sukenaga S, Ando M, Shibata H, Ohara K, Wakihara T, Okubo T (2019) Zeolite crystallization triggered by intermediate stirring. J Phys Chem C 123(33):20304–20313. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.9b04778
Askari S, Miar Alipour S, Halladj R, Davood Abadi Farahani MH (2013) Effects of ultrasound on the synthesis of zeolites: a review. J Porous Mater 20(1):285–302. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10934-012-9598-6
Porcher F, Dusausoy Y, Souhassou M, Lecomte C (2000) Epitaxial growth of zeolite X on zeolite a and twinning in zeolite a: structural and topological analysis. Mineral Mag 64(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1180/002646100549012
Kumar M, Choudhary MK, Rimer JD (2018) Transient modes of zeolite surface growth from 3D gel-like islands to 2D single layers. Nat Commun 9(1):2129. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04296-4
Qin W, Jain R, Robles Hernández FC, Rimer JD (2019) Organic-free Interzeolite transformation in the absence of common building units. Chem Eur J 25(23):5893–5898. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.201901067
Bagi S, Wright AM, Oppenheim J, Dincă M, Román-Leshkov Y (2021) Accelerated synthesis of a Ni2Cl2(BTDD) metal–organic framework in a continuous flow reactor for atmospheric water capture. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 9(11):3996–4003. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c07055
Khater A, Mohammadi M, Mohamad A, Nezhad AS (2019) Dynamics of temperature-actuated droplets within microfluidics. Sci Rep 9(1):3832. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-40069-9
Yu L, Pan Y, Wang C, Zhang L (2013) A two-phase segmented microfluidic technique for one-step continuous versatile preparation of zeolites. Chem Eng J 219:78–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.009
Baroud CN, Gallaire F, Dangla R (2010) Dynamics of microfluidic droplets. Lab Chip 10(16):2032–2045. https://doi.org/10.1039/C001191F
Gualtieri A, Norby P, Artioli G, Hanson J (1997) Kinetics of formation of zeolite Na-A [LTA] from natural kaolinites. Phys Chem Miner 24(3):191–199. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002690050032
Thompson RW (1992) Analysis of zeolite crystallizations using Avrami transformation methods. Zeolites 12(6):680–684. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-2449(92)90115-6
Den Ouden CJJ, Thompson RW (1992) Analysis of zeolite crystallization using the "crystallization curve". Ind Eng Chem Res 31(1):369–373. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie00001a050
Mullin JW (2001) Crystallization. Elsevier Science
Karthika S, Radhakrishnan TK, Kalaichelvi P (2016) A review of classical and nonclassical nucleation theories. Cryst Growth Des 16(11):6663–6681. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.cgd.6b00794
Gaillac R, Chibani S, Coudert F-X (2020) Speeding up discovery of Auxetic zeolite frameworks by machine learning. Chem Mater 32(6):2653–2663. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.0c00434
Cubillas P, Anderson MW (2010) Synthesis mechanism: crystal growth and nucleation. Zeolites and catalysis. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co, KGaA, pp 1–55. https://doi.org/10.1002/9783527630295.ch1
Coronas J (2010) Present and future synthesis challenges for zeolites. Chem Eng J 156(2):236–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2009.11.006
Grand J, Awala H, Mintova S (2016) Mechanism of zeolites crystal growth: new findings and open questions. CrystEngComm 18(5):650–664. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CE02286J
Brar T, France P, Smirniotis PG (2001) Control of crystal size and distribution of zeolite a. Ind Eng Chem Res 40(4):1133–1139. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie000748q
Gora L, Thompson RW (1997) Controlled addition of aged mother liquor to zeolite NaA synthesis solutions. Zeolites 18(2):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-2449(96)00163-7
Bronić J, Subotić B (1995) Role of homogeneous nucleation in the formation of primary zeolite particles. Microporous Mater 4(2):239–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/0927-6513(94)00087-C
Warzywoda J, Edelman RD, Thompson RW (1991) Crystallization of high-silica ZSM-5 in the presence of seeds. Zeolites 11(4):318–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/0144-2449(91)80294-A
Davis TM, Drews TO, Ramanan H, He C, Dong J, Schnablegger H, Katsoulakis MA, Kokkoli E, McCormick AV, Penn RL, Tsapatsis M (2006) Mechanistic principles of nanoparticle evolution to zeolite crystals. Nat Mater 5 (5):400-408. http://www.nature.com/nmat/journal/v5/n5/suppinfo/nmat1636_S1.html
Fan W, Snyder MA, Kumar S, Lee P-S, Yoo WC, McCormick AV, Lee Penn R, Stein A, Tsapatsis M (2008) Hierarchical nanofabrication of microporous crystals with ordered mesoporosity. Nat Mater 7 (12):984-991. http://www.nature.com/nmat/journal/v7/n12/suppinfo/nmat2302_S1.html
Gharibeh M, Tompsett G, Lu F, Auerbach SM, Yngvesson KS, Conner WC (2009) Temperature distributions within zeolite precursor solutions in the presence of microwaves. J Phys Chem B 113(37):12506–12520. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp900394u
Burkett SL, Davis ME (1995) Mechanisms of structure direction in the synthesis of pure-silica zeolites. 1. Synthesis of TPA/Si-ZSM-5. Chem Mater 7(5):920–928. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm00053a017
Lupulescu AI, Rimer JD (2014) In situ imaging of silicalite-1 surface growth reveals the mechanism of crystallization. Science 344(6185):729–732. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1250984
Lee P-S, Zhang X, Stoeger JA, Malek A, Fan W, Kumar S, Yoo WC, Al Hashimi S, Penn RL, Stein A, Tsapatsis M (2010) Sub-40 nm zeolite suspensions via disassembly of three-dimensionally ordered mesoporous-imprinted Silicalite-1. J Am Chem Soc 133(3):493–502. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja107942n
Arafat A, Jansen JC, Ebaid AR, van Bekkum H (1993) Microwave preparation of zeolite Y and ZSM-5. Zeolites 13(3):162–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0144-2449(05)80272-6
Bonaccorsi L, Proverbio E (2008) Influence of process parameters in microwave continuous synthesis of zeolite LTA. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 112(1–3):481–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2007.10.028
Liu Z, Zhu J, Wakihara T, Okubo T (2019) Ultrafast synthesis of zeolites: breakthrough, progress and perspective. Inorganic Chemistry Frontiers 6(1):14–31. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8QI00939B
Yang S, Navrotsky A, Phillips BL (2001) An in situ calorimetric study of the synthesis of FAU zeolite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 46(2):137–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1387-1811(01)00268-2
Chen C-T, Iyoki K, Yonezawa Y, Okubo T, Wakihara T (2020) Understanding the nucleation and crystal growth of zeolites: a case study on the crystallization of ZSM-5 from a hydrogel system under Ultrasonication. J Phys Chem C 124(21):11516–11524. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpcc.0c02578
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund for financial support, ACS PRF 58609-DNI5.
Funding
The authors acknowledge the American Chemical Society Petroleum Research Fund for financial support, ACS PRF 58609-DNI5.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Not applicable.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/competing interests
Not applicable.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
• Five reactor designs that create distinct heat transfer regimes have been used to reveal heat transfer limitations during zeolite crystallization
• Segmented microdroplet microbatch crystallizers used to remove heat transfer limitations
• Nondimensional analysis performed to establish criteria and a regime map for isothermal, kinetically-limited environment
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 528 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crislip, J.C., Vicens, J., Pham, T. et al. Dominance of heat transfer limitations in conventional sol-gel synthesis of LTA revealed by microcrystallization. J Flow Chem 12, 397–408 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41981-022-00217-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41981-022-00217-1