Abstract
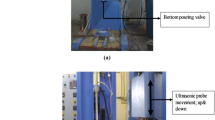
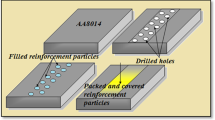
To produce the lightweight material for the high payload with excellent strength in particular for defense applications, reinforcements were introduced into the aluminum to form a hybrid composite. SiO2 was extracted through suitable techniques from rice husk ash particles. Through the ultrasonic probe sonication stir-casting process, the standard composition of 3% SiO2 was added along with varying weight percentages (3, 6, 9, and 12) of TiC particles as reinforcement in Al 6061 matrix. The machinability of the fabricated hybrid composite was evaluated through end face milling with varied machining parameters such as spindle speed, feed rate, and depth of cut. The output performance measurable characteristics were temperature and Ra. Thermal energy generated during the machining conditions was studied through the thermal image FLIR camera. From the machining conditions, machining level with SS of 1000, FR of 100, and DOC of 0.2 lead to having the highest temperature of 119 °C. The working temperature for the N2 sample was recorded to be 17% higher with an increase of 3% of TiC. The impact of wt% of reinforcements and governing parameters on tool wear was analyzed by SEM images. The addition of RHA and TiC reinforcements leads to raising cutting zone temperature, tool wear, and Ra. The thermal distortion effect on tool wear, chip morphology, and the surface profile of the samples were discussed and reported.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajith SAD, Pugazhenthi R, Kumar R, Vijayanath S (2019) Multi-objective prediction and optimization of control parameters in the milling of aluminium hybrid metal matrix composite using ANN and Taguchi-grey relational analysis. Def Technol 15:545–556
Alaneme KK, Michael OB, Adebimpe AA (2018) Microstructure, mechanical and fracture properties of groundnut shell ash and silicon carbide dispersion strengthened aluminium matrix composites. J King Saud Univ Eng Sci 30(1):96–103
An Q, Chen J, Ming W, Chen M (2020) Machining of SiC ceramic matrix composites: a review. Chin J Aeronaut 33(8):1–28
Arora G, Sharma SA (2018) Comparative study of AA6351 mono-composites reinforced with synthetic and agro waste reinforcement. Int J Precis Eng Manuf 19(4):631–638
Astakhov VP, Outeiro J (2019) Importance of temperature in metal cutting and its proper measurement/modeling. In: Davim J (ed) Measurement in machining and tribology. Materials forming, machining and tribology. Springer, Cham
Balamurugan K, Uthayakumar M, Thirumalai S, Samy GS, Pillai UTS (2019) Drilling study on lightweight structural Mg/SiC composite for defence applications. Def Technol 15(4):557–564
Benedicto F, Carou F, Rubio M (2017) Economic and environmental review of the lubrication/cooling systems used in machining processes. Proced Eng 184:99–116
Chen J, Yu W, Zuo Z, Li Y, Chen D, An Q, Wang H (2020) Effects of in-situ TiB2 particles on machinability and surface integrity in milling of TiB2/2024 and TiB2/7075 Al composites. Chin J Aeronaut 33(6):1–16
Chinnamahammad BA, Balamurugan K (2019) Fabrication and property evaluation of Al 6061 + x% (RHA + TiC) hybrid metal matrix composite. SN Appl Sci 1:977
Comak A, Altintas Y (2018) Dynamics and stability of turn-milling operations with varying time delay in discrete time domain. J Manuf Sci Eng 140(10):101013–101027
Davis B, Dabrow D, Ju L, Li A, Xu C, Huang Y (2017) Study of chip morphology and chip formation mechanism during machining of magnesium-based metal matrix composites. J Manuf Sci Eng 139(9):091008
Fenghong C, Chang C, Zhenyu W, Muthuramalingam T, Anbuchezhiyan G (2019) Effects of silicon carbide and tungsten carbide in aluminium metal matrix composites. Silicon 11:1–8
Harichandran R, Selvakumar N (2016) Effect of nano/micro B4C particles on the mechanical properties of aluminium metal matrix composites fabricated by ultrasonic cavitation-assisted solidification process. Arch Civ Mech Eng 16(1):147–158
Idrisi AH, Mourad AHI (2019) Conventional stir casting versus ultrasonic assisted stir casting process: mechanical and physical characteristics of AMCs. J Alloy Compd 805:502–508
Jebaraj M, Pradeep Kumar M, Yuvaraj N, Rahman MG (2019) Experimental study of the influence of the process parameters in the milling of Al6082-T6 alloy. Mater Manuf Process 34:1–17
Jiang F, Liu Z, Yang F, Zhong Z, Sun S (2018) Investigations on tool temperature with heat conduction and heat convection in high-speed slot milling of Ti6Al4V. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96(5–8):1847–1858
Karabulut S, Gökmen U, Çinici H (2017) Optimization of machining conditions for surface quality in milling AA7039-based metal matrix composites. Arab J Sci Eng 43:1071–1082
Liang X, Liu Z, Wang B (2019) State-of-the-art of surface integrity induced by tool wear effects in machining process of titanium and nickel alloys: a review. Measurement 132:150–181
Madhukar P, Selvaraj N, Gujjala R, Rao CSP (2019) Production of high performance AA7150-1% SiC nanocomposite by novel fabrication process of ultrasonication assisted stir casting. Ultrason Sonochem 58:104665
Owoeye SS, Folorunso DO, Oji B, Borisade SG (2019) Zinc-aluminum (ZA-27)-based metal matrix composites: a review article of synthesis, reinforcement, microstructural, mechanical, and corrosion characteristics. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100(4):373–380
Pham TH, Nguyen DT, Banh TL, Tong VC (2020) Experimental study on the chip morphology, tool–chip contact length, workpiece vibration, and surface roughness during high-speed face milling of A6061 aluminum alloy. Proc Inst Mech Eng Part B J Eng Manuf 234(3):610–620
Popov VA, Burghammer M, Rosenthal M, Kotov A (2018) In situ synthesis of TiC nano-reinforcements in aluminum matrix composites during mechanical alloying. Compos B Eng 145:57–61
Pramanik A, Zhang LC, Arsecularatne JA (2008) Machining of metal matrix composites: effect of ceramic particles on residual stress, surface roughness and chip formation. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 48:1613–1625
Rakesh M, Datta S (2019) Machining of Inconel 718 using coated WC tool: effects of cutting speed on chip morphology and mechanisms of tool wear. Arab J Sci Eng 44(9):797–816
Shayan M, Eghbali B, Niroumand B (2019) Synthesis of AA2024-(SiO2np+TiO2np) hybrid nanocomposite via stir casting process. Mater Sci Eng A 756:484–491
Singh J, Chauhan AA (2019) Review of microstructure, mechanical properties and wear behavior of hybrid aluminium matrix composites fabricated via stir casting route. Sadhana 44(1):1–18
Sravan KJ, Suresh KRN (2017) Machinability. Enhancement of stir cast Al-TiCp composites under cryogenic condition. Mater Manuf Process 32:1–49
Tamizharasan T, Senthilkumar N, Selvakumar V, Dinesh S (2019) Methodology of optimizing turning parameters over chip thickness ratio in machining P/M AMMC. SN Appl Sci 1:160
Unlu BS (2008) Investigation of tribological and mechanical properties Al2O3–SiC reinforced Al composites manufactured by casting or P/M method. Mater Des 29:2002–2008
Vinod B, Ramanathan S, Ananthi V, Slevakumar N (2019) Fabrication and characterization of organic and in-organic reinforced A356 aluminium matrix hybrid composite by improved double-stir casting. Silicon 11(2):817–829
Weiwei M, Jiaqiang D, Qinglong A, Ming C (2019) Chip formation and hole quality in dry drilling additive manufactured Ti6Al4V. Mater Manuf Process 35(1):43–51
Xuan Y, Nastac L (2018) The role of ultrasonic cavitation in refining the microstructure of aluminum based nanocomposites during the solidification process. Ultrasonics 83:94–102
Yıldırım CV, Kıvak T, Erzincanlı F (2019) Tool wear and surface roughness analysis in milling with ceramic tools of Waspaloy: a comparison of machining performance with different cooling methods. J Braz Soc Mech Sci Eng 41:83
Zeelanbasha N, Senthil V, Senthil Kumar BR (2018) An integrated approach of RSM and MOGA for the prediction of temperature rise and surface roughness in the end milling of Al 6061–T6. Trans FAMENA 42(3):115–128
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Centre of Excellence at VFSTR (Deemed to be University), Guntur, Andhra Pradesh, India for rendering their support and guidance to finish this work.
Funding
This work was supported by VFSTR (Deemed to be University) Guntur-522213, AP, India under Seed Grant F.No.:VFSTR/Reg/A4/30/2019-20/02 dated 17.07.2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhasha, A.C., Balamurugan, K. End mill studies on Al6061 hybrid composite prepared by ultrasonic-assisted stir casting. Multiscale and Multidiscip. Model. Exp. and Des. 4, 109–120 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-020-00083-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41939-020-00083-1