Abstract
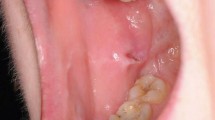
Orofacial pain is one of the most common patient complaint encountered in dental practices. After infectious diseases of the teeth and periodontium, oral ulcerative diseases represent one of the most common cause for dental patients presenting with orofacial pain. Oral inflammatory and ulcerative diseases may have similar clinical appearances with different etiopathogenesis that include traumatic, infectious, immunologic and neoplastic origin. Empirical therapy of oral ulcerative and inflammatory diseases without a specific diagnosis is not effective and has unintended consequences. Diagnostic evaluation of oral mucosal inflammatory and ulcerative diseases includes a detailed dental and medical history, review of systems, clinical examination and incisional biopsy in selected cases. Diagnosis of oral ulcerative diseases begins by determining three important features necessary to distinguish oral ulcers of different etiopathogenesis. The most important is whether the patient presents with a single, or solitary, ulcer, or whether there are multiple ulcers present. The second important distinguishing feature is whether the patient is experiencing a first ulcer episode or one of many recurrences. Finally, it is helpful to determine the duration of ulceration. Ulcers present for less than three weeks are considered acute, whereas those lasting over three weeks are considered chronic in nature. Table 7 provides the array of potential diagnoses for oral ulcerative diseases based on these diagnostic criteria. When a patient with oral ulceration does not benefit from initial therapy chosen on the basis of clinical presentation, an incisional biopsy is indicated for histopathologic evaluation and direct immunofluorescence testing if vesiculoerosive diseases are suspected. To optimize an accurate pathology diagnosis, clinicians should ensure that biopsy specimens are properly obtained from clinically affected but non-ulcerated mucosa and promptly submitted to the pathologic laboratory, preferably before the institution of any immunomodulating therapy.









Similar content being viewed by others
Further Reading
A. H. Jeske (ed) Contemporary Dental Pharmacology, Pharmacologic Management of Oral Mucosal Inflammatory and Ulcerative Diseases. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99852-7_9
Radulescu M (2016) The pharmacologic management of common lesions of the oral cavity. Dent Clin N Am 60(2):407–420
Stoopler ET, Sollecito TP (2014) Oral mucosal diseases: evaluation and management. Med Clin North Am 98(6):1323–1352
Yuan A, Woo SB (2015) Adverse drug events in the oral cavity. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 119(1):35–47
Chen HX et al (2017) Triggers of oral lichen planus flares and the potential role of trigger avoidance in disease management. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 124(3):248–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vigneswaran, N., Muller, S. Diagnosis of oral mucosal inflammatory and ulcerative diseases. Clin Dent Rev 4, 17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-020-00076-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-020-00076-w