Abstract
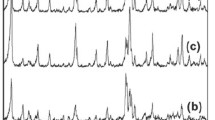
Novel CuO nanowire-zeolite composite was successfully fabricated through facile thermal decomposition of CuSO4 • 5H2O as the lone precursor. The natural zeolites have porous and plate-like structures, which suggest the presence of clinoptilolite-heulandite family of zeolites. After annealing of Cu-exchanged zeolite at 550 °C, CuO nanowires were synthesized with a mean diameter of 80 nm and length of 1.5 μm. XRD analysis revealed that the samples annealed at 550 °C showed clinoptilolite-heulandite peaks, as well as a broad CuO peak. Annealing at a higher temperature of 800 °C led to the amorphization of the zeolite peaks. The XPS spectra of the zeolite with Cu annealed at 400, 550, and 800 °C confirmed that annealing at 550 °C preferably forms CuO rather than Cu2O on zeolite surface. These analyses identified that annealing at 550 °C functionalized the Cu-exchanged zeolite surface, which is desirable for a wide variety of applications such as catalysis, sorbents for environmental applications, and gas sensors.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liu, A., Nie, S., Liu, G., Zhu, H., Zhu, C., Shin, B., Fortunato, E., Martins, R., Shan, F.: In situ one-step synthesis of p-type copper oxide for low-temperature, solution-processed thin-film transistors. J. Mater. Chem. C. 5, 2524–2530 (2017)
Tunesi, M., Soomro, R., Ozturk, R.: The in situ growth of CuO nanostructures on an ITO substrate and its application as a highly sensitive electrode for the electrochemical determination of N-acetyl-L-cysteine. J. Mater. Chem. C. 5, 2708–2716 (2017)
Rana, S., Jonnalagaddam, S.: CuO/graphene oxide nanocomposite as highly active and durable catalyst for selective oxidation of cyclohexane. ChemistrySelect. 2, 2277–2281 (2017)
Sierra-Pereira, C., Urquieta-González, E.: Reduction of NO with CO on CuO or Fe2O3 catalysts supported on TiO2 in the presence of O2, SO2 and water steam. Fuel. 118, 137–147 (2014)
Subalakshmi, P., Sivashanmugam, A.: CuO nano hexagons, an efficient energy storage material for Li-ion battery application. J. Alloys Compd. 690, 523–531 (2017)
Jeong, S., Jung, S., Yoo, K., Kim, S.: Selective catalytic reduction of NO by NH3 over a bulk sulfated CuO/γ-Al2O3 catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 38, 2210–2215 (1999)
Antony, A., Sun, M., Jin-Hyo, B., You, H.: Nano sheets, needles and grains-like CuO/γ-Al2O3 catalysts’ performance in carbon monoxide oxidation. J. Solid State Chem. 265, 431–439 (2018)
Subbulekshmi, N.L., Subramanian, E.: Nano CuO immobilized fly ash zeolite Fenton-like catalyst for oxidative degradation of p-nitrophenol and p-nitroaniline. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 5, 1360–1371 (2017)
Peng, G., Wu, S., Ellis, J., Xu, X., Xu, G., Yu, C., Star, A.: Single-walled carbon nanotubes templated CuO networks for gas sensing. J. Mater. Chem. C. 4, 6575–6580 (2016)
Sung, W.-Y., Kim, W.-J., Lee, S.-M., Lee, H.-Y., Kim, Y.-H., Park, K.-H., Lee, S.: Field emission characteristics of CuO nanowires by hydrogen plasma treatment. Vacuum. 81, 851–856 (2007)
Yu-Feng, T., Shu-Jun, H., Shi-Shen, Y., Liang-Mo, M.: Oxide magnetic semi-conductors: materials, properties, and devices. Chin. Phys. B. 22, 088505 (2013)
Langmar, O., Ganivet, C., Schol, P., Scharl, T., de la Torre, G., Torres, T., Costa, R., Guldi, D.: Improving charge injection and charge transport in CuO-based p-type DSSCs – a quick and simple precipitation method for small CuO nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C. 6, 5176–5180 (2018)
Siddiqui, H., Qureshi, M.S., Haque, F.: Hexamine (HMT) assisted wet chemically synthesized CuO nanostructures with controlled morphology and adjustable optical behavior. Opt. Quant. Electron. 48, 349 (2016)
Shaalan, N.M., Rashad, M., Abdel-Rahim, M.A.: CuO nanoparticles synthesized by microwave-assisted method for methane sensing. Opt. Quant. Electron. 48, 531 (2016)
Shehayeb, S., Deschanels, X., Karamé, I., Ghannam, L., Toquer, G.: Spectrally selective coatings obtained from electrophoretic deposition of CuO nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 322, 38–45 (2017)
Pelicano, C. M., Felizco, J. C., Balela, M. D.: Formation of copper oxide nanostructures by solution-phase method for antibacterial applications, Mosbeh Kaloop (Ed.), Advanced Materials, Structures and Mechanical Engineering, (2015) 203
Muiva, C., Maabong, K., Moditswe, C.: CuO nanostructured thin films synthesised by chemical bath deposition on seed layers deposited by successive ionic layer adsorption and reaction and chemical spray pyrolysis techniques. Thin Solid Films. 616, 48–54 (2016)
Pelicano, C.M., Yanagi, H.: Efficient solid-state perovskite solar cells based on nanostructured zinc oxide designed by strategic low temperature water oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. C. 5, 8059–8070 (2017)
Nezamzadeh-Ejhieh, A., Salimi, Z.: Heterogeneous photodegradation catalysis of o-phenylenediamine using CuO/X zeolite. Appl Catal, A. 390, 110 (2010)
Song, W., Li, G., Grassian, V.H., Larsen, S.C.: Development of improved materials for environmental applications: nanocrystalline NaY zeolites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 1214 (2005)
Seraj, S., Ferron, R., Juenger, M.: Calcining natural zeolites to improve their effect on cementitious mixture workability. Cem. Concr. Res. 85, 102–110 (2016)
Peric, J., Trgo, M., Vukojevic Medvidovic, N.: Removal of zinc, copper and lead by natural zeolite—a comparison of adsorption isotherms. Water Res. 38, 1893–1899 (2004)
Meshko, V., Markovska, L., Mincheva, M., Rodrigues, A.: Adsorption of basic dyes on granular activated carbon and natural zeolite. Water Res. 35, 3357–3366 (2001)
Poona, C., Lama, U., Koua, S., Lin, Z.: A study on the hydration rate of natural zeolite blended cement pastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 13, 427–432 (1999)
Lateef, A., Nazir, R., Jamil, N., Alam, S., Shan, R., Khan, M., Saleem, M.: Synthesis and characterization of zeolite based nano–composite: an environment friendly slow release fertilizer. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 232, 174–183 (2016)
Motsi, T., Rowson, N., Simmons, M.: Adsorption of heavy metals from acid mine drainage by natural zeolite. Int. J. Miner. Process. 92, 42–48 (2009)
Pavelic´, K., Hadžija, M., Bedrica, L., Pavelic´, J., Dikic, I., Katic, M., Kralj, M., Bosnar, M., Kapitanovic´, S., Poljak-Blaži, M., Križanac, S., Stojkovic´, R., Jurin, M., Subotic, B., Colic, M.: Natural zeolite clinoptilolite: new adjuvant in anticancer therapy. J. Mol. Med. 78, 708–720 (2001)
Herron, N., Tolman, C.: A highly selective zeolite catalyst for hydrocarbon oxidation. A completely inorganic mimic of the alkane ω-hydroxylases. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 109, 2837–2839 (1987)
Göltl, F., Bulo, R., Hafner, J., Sautet, P.: What makes copper-exchanged SSZ-13 zeolite efficient at cleaning car exhaust gases? J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 4, 2244–2249 (2013)
Hanna, S., Miller, R., Lenihan, H.: Accumulation and toxicity of copper oxide engineered nanoparticles in a marine mussel. Nanomaterials. 4, 535–547 (2014)
Ethiraj, A., Kang, D.: Synthesis and characterization of CuO nanowires by a simple wet chemical method. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 70–74 (2012)
Wu, H.-Q., Wei, X.-W., Shao, M.-W., Gu, J.-S., Qu, M.-Z.: Synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using carbon nanotubes as templates. Chem. Phys. Lett. 364, 152 (2002)
Xu, J., Ji, W., Shen, Z., Tang, S., Ye, X., Jia, D., Xin, X.: Preparation and characterization of CuO nanocrystals. J. Solid State Chem. 147, 516–519 (1999)
Bakhtiari, F., Zivdar, M., Atashi, H., Seyed Bagheri, S.A.: Bioleaching of copper from smelter dust in a series of airlift bioreactors. Hydrometallurgy. 90, 40–45 (2008)
Boruban, C., Nalbant Esenturk, E.: Synthesis of CuO nanostructures on zeolite-Y and investigation of their CO2 adsorption properties. J. Mater. Res. 32, 3669–3678 (2017)
Razavi, R., Loghman-Estarki, M.: Synthesis and characterizations of copper oxide nanoparticles within zeolite Y. J. Clust. Sci. 4, 1097–1106 (2012)
Cui, T., Liu, Z., Zheng, X., Liu, Z., Li, Y., Li, W., Wang, B., Guo, K., Han, J.: Zeolite-based CuO nanotubes catalysts: investigating the characterization, mechanism, and decolouration process of methylene blue. J. Nanopart. Res. 16, 2608 (2014)
Olegario-Sanchez, E.M., Pelicano, C.M.: Characterization of Philippine natural zeolite and its application for heavy metal removal from acid mine drainage (AMD), 407-411. Key Eng. Mater. 737, (2017). https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/KEM.737.407
Olegario, E., Pelicano, C. M., Felizco, J. C., Mendoza, H.: Thermal stability and heavy metal (As5+, Cu2+, Ni2+, Pb2+ and Zn2+) ions uptake of the natural zeolites from the Philippines. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 085204 (2019) https://doi.org/10.1088/2053-1591/ab1a73
Olegario-Sanchez, E., Felizco, J.C., Mulimbayan, F.: Investigation of the thermal behavior of Philippine natural zeolites. AIP Conference Proceedings. 1901, 070005 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5010514
Olegario-Sanchez, E., Pelicano, C.M.: Comparative study of As (III) and Zn (II) removal from aqueous solutions using Philippine natural zeolite and alumina. AIP Conference Proceedings. 1901, 070004 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5010513
Olegario, E., Pelicano, C.M., Dahonog, L., Nakajima, H.: Novel ZnO nanostructures on Philippine natural zeolite (PNZ) framework designed via thermal decomposition process of solution-based ZnCl2 precursor. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 015005 (2019)
Kaura, M., Muthea, K., Despandeb, S., Choudhuryc, S., Singhd, J., Vermae, N., Guptaa, S., Yakhmia, J.: Growth and branching of CuO nanowires by thermal oxidation of copper. J. Cryst. Growth. 289, 670–675 (2006)
Yanga, Q., Guo, Z., Zhou, X., Zou, J., Liang, S.: Ultrathin CuO nanowires grown by thermal oxidation of copper powders in air. Mater. Lett. 153, 128–131 (2015)
Duvarcı, O., Akdeniz, Y., Ozmıhc, F., Ulku, S., Balkose, D., Ciftcioglu, M.: Thermal behavior of a zeolitic tuff. Ceram. Int. 33, 795–801 (2007)
Hojabri, A., Hajakbari, F., Soltanpoor, N., Sadat Hedayati, M.: Annealing temperature effect on the properties of untreated and treated copper films with oxygen plasma. J. Theor. Appl. Phys. 8, 132 (2014)
Lin, C.-C., Li, Y.-Y.: Synthesis of ZnO nanowires by thermal decomposition of zinc acetate dehydrate. Mater. Chem. Phys. 113, 334–337 (2009)
Cruciani, G.: Zeolites upon heating: factors governing their thermal stability and structural changes. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 67, 1973–1994 (2006)
Bare, S., Knop-Gericke, A., Teschner, D., Hävacker, M., Blume, R., Rocha, T., Schlögl, R., Chan, A., Blackwell, N., Charochaka, M., Veen, R., Brongersma, H.: Surface analysis of zeolites: an XPS, variable kinetic energy XPS, and low energy ion scattering study. Surf. Sci. 648, 376–382 (2016)
Poulston, S., Parlett, P.M., Stone, P., Bowker, M.: Surface oxidation and reduction of CuO and Cu2O studied using XPS and XAES. Surf. Interface Anal. 24, 811–820 (1996)
Wang, Y., Lü, Y., Zhan, W., Xie, Z., Kuang, Q., Zheng, L.: Synthesis of porous Cu2O/CuO cages using Cu-based metal–organic frameworks as templates and their gas-sensing properties. J. Mater. Chem. A. 3, 12796–12803 (2015)
Gao, D., Zhang, J., Zhu, J., Qi, J., Zhang, Z., Sui, W., Shi, H., Xue, D.: Vacancy-mediated magnetism in pure copper oxide nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5, 769 (2010)
Funding
This study was funded by the Department of Science and Technology through the Engineering Research and Development for Technology (DOST-ERDT) and ADMATEL. The XPS experiment research was provided by the National Nanotechnology Center (NANOTEC) under the National Science and Technology Department Agency (NSTDA). The XPS measurements were supported by BL-5.3 SUT-NANOTEC-SLRI Beamline staff members. Support was also provided by SAILE Industries, Inc. for the minerals used in the study and its preliminary data analysis and Oceanagold Philippines for the research grant through its Mine Technology Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olegario, E., Felizco, J.C., Pelicano, C.M. et al. Philippine natural zeolite surface engineered with CuO nanowires via a one-step thermal decomposition route. J Aust Ceram Soc 56, 803–809 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00401-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-019-00401-y