Abstract
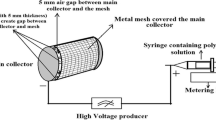
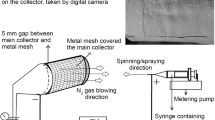
Nanofiber features in a scaffold provide favorable niche for cellular attachment, proliferation, and differentiation propelling their interest in tissue engineering. However, the inability of seeded cells to infiltrate inside 3D structures of electrospun nanofibers has remained a persistent bottleneck for their greater applicability. In the present work, an approach to address this problem is presented. Macro-pores are designed in common graphic software created by a laser-engraving machine on electrospun nanofiber sheets composed of a bioinspired material-N-methylene phosphonic chitosan for facilitating cellular infiltration into 3D scaffold. Effect of laser pulse energy and pulse per inch on pore morphology are investigated and FTIR spectrum is examined to preclude the degradation of material due to laser-engraving process. Furthermore, the micro-fabricated nanofiber sheets with multi-scalar porosity are rolled up to form a 3D scaffold as graft through biomimetic approach for bone-tissue engineering applications. Culture of MG-63 cells on rolled up nanofiber sheets containing laser-engraved macro-porous 3D scaffolds demonstrated no cytotoxicity induced by the scaffolds from MTT assay, while cellular migration into the sheets was evident from scanning electron microscopy. It is concluded that combined micro-fabrication-rolling approach may be simple, rapid way to design 3D bone grafts based on 2D electrospun nanofiber sheet of natural/semi-synthetic polymers for better osteoconductivity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rampichová M, Košt’áková Kuželová E, Filová E, Chvojka J, Šafka J, Pelcl M, Daňková J, Prosecká E, Buzgo M, Plencner M, Lukáš D, Amler E (2018) Composite 3D printed scaffold with structured electrospun nanofibers promotes chondrocyte adhesion and infiltration. Cell Adhes Migr 12:271–285. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336918.2017.1385713
Wu J, Hong Y (2016) Enhancing cell infiltration of electrospun fibrous scaffolds in tissue regeneration. Bioact Mater 1:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2016.07.001
Arslan A, Çakmak S, Gümüşderelioğlu M (2018) Enhanced osteogenic activity with boron-doped nanohydroxyapatite-loaded poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) fibrous 3D matrix. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2018.1470522
Whited BM, Whitney JR, Hofmann MC, Xu Y, Rylander MN (2011) Pre-osteoblast infiltration and differentiation in highly porous apatite-coated PLLA electrospun scaffolds. Biomaterials 32:2294–2304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.12.003
Gao J, Luo J, Xiong J (2017) A facile method for tailoring the three-dimensional porous nanofibrous scaffolds by the dual electrode electrospinning. Mater Lett 209:384–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2017.08.032
Zhong S, Zhang Y, Lim CT (2011) Fabrication of large pores in electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds for cellular infiltration: a review. Tissue Eng Part B Rev 18:77–87. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.teb.2011.0390
Wright LD, Andric T, Freeman JW (2011) Utilizing NaCl to increase the porosity of electrospun materials. Mater Sci Eng, C 31:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2010.02.001
Leong MF, Chan WY, Chian KS, Rasheed MZ, Anderson JM (2010) Fabrication and in vitro and in vivo cell infiltration study of a bilayered cryogenic electrospun poly(d, l-lactide) scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res, Part A 94:1141–1149. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.a.32795
Alsberg E, Bae MS, Lee JB, Kim CH, Heo DN, Yang DH, Kwon IK, Jeong SI (2011) Highly porous electrospun nanofibers enhanced by ultrasonication for improved cellular infiltration. Tissue Eng Part A 17:2695–2702. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.tea.2010.0709
Yang H, Wang L, Xiang C, Li L (2018) Electrospun porous PLLA and poly(LLA-: Co -CL) fibers by phase separation. New J Chem 42:5102–5108. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7nj04970f
Sooriyaarachchi D, Minière HJ, Maharubin S, Tan GZ (2019) Hybrid additive microfabrication scaffold incorporated with highly aligned nanofibers for musculoskeletal tissues. Tissue Eng Regen Med 16:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13770-018-0169-z
Lee SJ, Park YJ, Shim IK, Park WH, Seol YJ, Kim KH, Jung MR (2010) Novel three-dimensional scaffolds of poly(l-lactic acid) microfibers using electrospinning and mechanical expansion: Fabrication and bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res Part B Appl Biomater. 95:150–160. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.31695
Li H, Ding Q, Chen X, Huang C, Jin X, Ke Q (2019) A facile method for fabricating nano/microfibrous three-dimensional scaffold with hierarchically porous to enhance cell infiltration. J Appl Polym Sci 136:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.47046
Pal P, Srivas PK, Dadhich P, Das B, Maulik D, Dhara S (2017) Nano-/microfibrous cotton-wool-like 3D scaffold with core-shell architecture by emulsion electrospinning for skin tissue regeneration. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 3:3563–3575. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.7b00681
Johnson JK, Woon Choi H, Nam J, Farson DF, Lannutti J (2007) Structuring electrospun polycaprolactone nanofiber tissue scaffolds by femtosecond laser ablation. J Laser Appl 19:225–231. https://doi.org/10.2351/1.2795749
Chiussi S, Cordero D, Rebollar E, León B, Neves NM, Martins A, Reis RL (2010) Improvement of electrospun polymer fiber meshes pore size by femtosecond laser irradiation. Appl Surf Sci 257:4091–4095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.12.002
Jenness NJ, Wu Y, Clark RL (2012) Fabrication of three-dimensional electrospun microstructures using phase modulated femtosecond laser pulses. Mater Lett 66:360–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2011.09.015
Wu Y, Vorobyev AY, Clark RL, Guo C (2011) Femtosecond laser machining of electrospun membranes. Appl Surf Sci 257:2432–2435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.09.111
Lim YC, Wu Y, Choi HW, Lannutti JJ, Fei Z, Farson DF, Johnson J, Lee LJ (2010) Micropatterning and characterization of electrospun poly(ε-caprolactone)/gelatin nanofiber tissue scaffolds by femtosecond laser ablation for tissue engineering applications. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:116–126. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.22914
Datta P, Thakur G, Chatterjee J, Dhara S (2014) Biofunctional phosphorylated chitosan hydrogels prepared above pH 6 and effect of crosslinkers on gel properties towards biomedical applications. Soft Mater. 12:27–35. https://doi.org/10.1080/1539445X.2012.735315
Datta P, Ghosh P, Ghosh K, Maity P, Samanta SK, Ghosh SK, Das Mohapatra PK, Chatterjee J, Dhara S (2013) In vitro ALP and osteocalcin gene expression analysis and in vivo biocompatibility of n-methylene phosphonic chitosan nanofibers for bone regeneration. J Biomed Nanotechnol 9:870–879. https://doi.org/10.1166/jbn.2013.1592
Liu Y, Li X, Qu X, Zhu L, He J, Zhao Q, Wu W, Li D (2012) The fabrication and cell culture of three-dimensional rolled scaffolds with complex micro-architectures. Biofabrication. https://doi.org/10.1088/1758-5082/4/1/015004
Datta P, Dhara S, Chatterjee J (2012) Hydrogels and electrospun nanofibrous scaffolds of N-methylene phosphonic chitosan as bioinspired osteoconductive materials for bone grafting. Carbohydr Polym 87:1354–1362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.09.023
Kapat K, Rameshbabu AP, Maity PP, Mandal A, Bankoti K, Dutta J, Das DK, Dey G, Mandal M, Dhara S (2019) Osteochondral defects healing using extracellular matrix mimetic phosphate/sulfate decorated GAGs-agarose gel and quantitative micro-ct evaluation. ACS Biomater Sci Eng 5:149–164. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsbiomaterials.8b00253
Mao C, Pan H, Shao C, Chen C, Gu T, Tang R, Zheng B, Gu X, Sun J (2019) Phosphorylated chitosan to promote biomimetic mineralization of type I collagen as a strategy for dentin repair and bone tissue engineering. New J Chem 43:2002–2010. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj04889d
Zhang G, Lau CPY, He K, Wang XH, Kumta SM, Zheng LZ, Qin L, Tang T, Patrick Y, Xie XH, Wang XL (2011) Effect of water-soluble P-chitosan and S-chitosan on human primary osteoblasts and giant cell tumor of bone stromal cells. Biomed Mater 6:015004. https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-6041/6/1/015004
Aguilar CA, Lu Y, Mao S, Chen S (2005) Direct micro-patterning of biodegradable polymers using ultraviolet and femtosecond lasers. Biomaterials 26:7642–7649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.04.053
Lebouc F, Dez I, Madec PJ (2005) NMR study of the phosphonomethylation reaction on chitosan. Polymer (Guildf). 46:319–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.polymer.2004.11.017
Shulunov V (2019) A novel roll porous scaffold 3D bioprinting technology. Bioprinting. 13:e00042. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bprint.2019.e00042
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Datta, P., Dhara, S. Engineering Porosity in Electrospun Nanofiber Sheets by Laser Engraving: A Strategy to Fabricate 3D Scaffolds for Bone Graft Applications. J Indian Inst Sci 99, 329–337 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41745-019-00115-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41745-019-00115-x