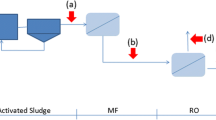
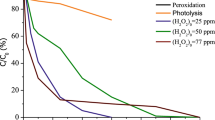
Abstract
17α-Ethinylestradiol (EE2) is a synthetic hormone, which has a high estrogenic potential, and it is usually discharged into the environment through sewage and industrial effluents. Low concentrations of EE2, and H2O2, which are not so common in the studies, were applied in removing process of micropollutants. Photodegradation and removal of EE2 from water were investigated using two treatment processes, UV/H2O2 and reverse osmosis (RO), respectively. Furthermore, changes in estrogenic activity using in vitro yeast estrogen screen assay, as well as the adsorption of EE2 by membrane (TW30-4040, polyamide) surface, were evaluated. All experiments showed that the concentration of H2O2 is a very important variable that influences the degradation of EE2 in all UV doses evaluated. Moreover, they showed estrogenic activity at the end of the treatment due to the amount of EE2 remaining after each experiment. The membrane rejection efficiency varied from 90 to 98% and the adsorption experiments with EE2 initial concentration of 1000 µg·L−1 resulted in11 mg·m−2 membrane surface adsorption. The RO membrane showed higher EE2 removal efficiency through size exclusion and adsorption than the UV/H2O2 process under the evaluated conditions.
Graphical abstract

Highlights
-
The membrane rejection efficiency varied from 90 to 98%.
-
Amount of EE2 remaining was responsible for all the observed estrogenic activity.
-
Higher concentration of EE2 adsorbed in 11 mg·m−2 on the membrane surface.
-
The RO membrane showed a greater EE2 removal efficiency than UV/H2O2.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, Moreira, C.G., upon reasonable request. Some datas analysed in the current study (two tables and two figures) are available as supplementary files.
References
Cartagena P, Kaddouri ME, Cases V, Trapote A, Prats D (2013) Reduction of emerging micropollutants, organic matter, nutrients and salinity from real wastewater by combined MBR-NF/RO treatment. Sep Purif Technol 110:132–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2013.03.024
Cédat B, De Brauer C, Métivier H, Dumont N, Tutundjan R (2016) Are UV photolysis and UV/H2O2 process efficient to treat estrogens in waters? Chemical and biological assessment at pilot scale. Water Res 100:357–366. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.040
Chen JL, Ravindran S, Swift S, Singhal N (2018) Changes in estrogenicity and micropollutant concentrations across unit processes in a biological wastewater treatment system. Water Sci Technol 77(6):1673–1682. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.047
Comerton AM, Andrews RC, Bagley DM, Yang P (2007) Membrane adsorption of endocrine disrupting compounds and pharmaceutically active compounds. J Membr Sci 303(1–2):267–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2007.07.025
De la Cruz N, Giménez J, Esplugas S, Grandjean D, Alencastro LF, Pulgarín C (2012) Degradation of 32 emerging contaminants by UV and neutral photo-fenton in domestic wastewater effluent previously treated by activated sludge. Water Res 46:1947–1957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.01.014
Harbert AC, Borges CP, Nobrega R (2006) Membrane separation processes. E-papers, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
He J, Guo J, Zhou Q, Yang J, Fang F, Huang Y (2019) Analysis of 17Α-ethinylestradiol and bisphenol A adsorption on anthracite surfaces by site energy distribution. Chemosphere 216:59–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.10.136
Inmetro (2018) Guidance on validation of analytical methods. General coordination of accreditation, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Judd S, Jefferson B (2003) Membranes for industrial wastewater recovery and reuse. Elsevier, London
Kimura K, Amy G, Drewes J, Watanabe Y (2003) Adsorption of hydrophobic compounds onto NF/RO membranes: an artifact leading to overestimation of rejection. J Membr Sci 221:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0376-7388(03)00248-5
Lee J, Lee BC, Ra JS, Cho J, Kim IS, Chang NI, Kim HK, Kim SD (2008) Comparison of the removal efficiency of endocrine disrupting compounds in pilot scale sewage treatment processes. Chemosphere 71(8):1582–1592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.11.021
Linares RV, Yangali-Quintanilla V, Li Z, Amy G (2011) Rejection of micropollutants by clean and fouled forward osmosis membrane. Water Res 45:6737–6744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.037
Luna TO, Plautz SC, Salice CJ (2015) Chronic effects of 17α-ethinylestradiol, fluoxetine, and the mixture on individual and population-level end points in daphnia magna. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 68(4):603–611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-014-0119-2
Luo Y, Guo W, Ngo HH, Nghiem LD, Hai FI, Zhang J, Liang S, Wang XC (2014) A review on the occurrence of micropollutants in the aquatic environment and their fate and removal during wastewater treatment. Sci Total Environ 473–474:619–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2013.12.065
Ma X, Zhang C, Deng J, Song Y, Li Q, Guo Y, Li C (2015) Simultaneous degradation of estrone, 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinyl estradiol in an aqueous UV/H2O2 system. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(10):12016–12029. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121012016
Moreira CG, Moreira MH, Silva VMOC, Santos HG, Bila DM, Fonseca FV (2020) Treatment of bisphenol A (BPA) in water using UV/H2O2 and reverse osmosis (RO) membranes: assessment of estrogenic activity and membrane adsorption. Water Sci Technol 80:2169–2178. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.024
Moreira CG, Santos HG, Bila DM, Fonseca FV (2021) Assessment of fouling mechanisms on reverse osmosis (RO) membrane during permeation of 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) solutions. Enviro Technol 43:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.1916087
Moreira CG, Souza LC, Castor Neto TC, Gomes G, Bila DM, Fonseca FV (2022) Combined reverse osmosis and UV/H2O2 treatment of aqueous solutions of bisphenol A and 17α-ethinylestradiol: assessment of estrogenic activity. Environ Technol. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2022.2051608
Park J, Jeong K, Baek S, Park S, Ligaray M, Chong TH, Cho KH (2019) Modeling of NF/RO membrane fouling and flux decline using real-time observations. J Memb Sci 576:66–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2019.01.031
Ren D, Huang B, Xiong D, He H, Meng X, Pan X (2017) Photodegradation of 17α-ethynylestradiol in dissolved humic substances solution: kinetics, mechanism and estrogenicity variation. J Environ Sci (china) 54:196–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.03.002
Rodrigues KLT (2012) Development of analytical methodology for the simultaneous determination of emerging micro-contaminants in surface waters by gem chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Universidade Federal de Ouro Preto, Ouro Preto
Rodriguez-Mozaz S, Ricart M, Köck-Schulmeyer M, Guasch H, Bonnineau C, Proia L, Alda ML, Sabater S, Barceló D (2015) Pharmaceuticals and pesticides in reclaimed water: efficient assessment of a microfiltration-reverse osmosis (MF-RO) pilot plant. J Hazard Mater 282:165–173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.015
Rosenfeldt EJ, Linden KG (2004) Degradation of endocrine disrupting chemicals bisphenol A, ethinylestradiol, and estradiol during UV photolysis and advanced oxidation processes. Environ Sci Technol 38:5476–5483. https://doi.org/10.1021/es035413p
Rosenfeldt EJ, Chen PJ, Kullman S, Linden KG (2007) Destruction of estrogenic activity in water using UV advanced oxidation. Sci Total Environ 377:105–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2007.01.096
Routledge EJ, Sumpter JP (1996) Estrogenic activity of surfactants and some of their degradation products assessed using a recombinant yeast screen. Environ Toxicol Chem 15(3):241–248. https://doi.org/10.1002/etc.5620150303
Sahar E, David I, Gelman Y, Chikurel H, Aharoni A, Messalem R, Brenner A (2011) The use of RO to remove emerging micropollutants following CAS/UF or MBR treatment of municipal wastewater. Desalination 273(1):142–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2010.11.004
Schäfer AI, Nghiem LD, Oschmann N (2006) Bisphenol A retention in the direct ultrafiltration of greywater. J Membr Sci 283(1–2):233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2006.06.035
Semião AJC, Schäfer AI (2011) Estrogenic micropollutant adsorption dynamics onto nanofiltration membranes. J Memb Sci 381:132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.memsci.2011.07.031
Sharma J, Mishra IM, Kumar V (2015) Degradation and mineralization of bisphenol A (BPA) in aqueous solution using advanced oxidation processes: UV/H2O2 and UV/S2O82- oxidation systems. J Environ Manage 156:266–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.03.048
Silva LLS, Moreira CG, Curzio BA, Fonseca FV (2017) Micropollutant removal from water by membrane and advanced oxidation processes—a review. J Water Resour Prot 9:411–431. https://doi.org/10.4236/jwarp.2017.95027
Snyder AS, Adham S, Redding AM, Cannon FS, Decarolis J, Oppenheimer J, Wert EC, Yoon Y (2007) Role of membranes and activated carbon in the removal of endocrine disruptors and pharmaceuticals. Desalination 202:156–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2005.12.052
Teske SS, Arnold RG (2008) Removal of natural and xeno-estrogens during conventional wastewater treatment. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 7:107–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11157-008-9129-8
USEPA (2003) Ultraviolet disinfection guidance manual. EPA Office of Water, Washington
Yangali-Quintanilla V, Sadmani A, Mcconville M, Kennedy M, Amy G (2009) Rejection of pharmaceutically active compounds and endocrine disrupting compounds by clean and fouled nanofiltration membranes. Water Res 43:2349–2362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.02.027
Zanette JC, Veit MT, Gonçalves GC, Palácio SM, Scremin FR, Torquato AS, Vieira MRSA (2018) A study on the removal of prednisone from aqueous solutions by adsorption onto a vegetal activated carbon. Water Sci Technol 78:2328–2337. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2018.515
Zhang Z, Feng Y, Liu Y, Sun Q, Gao P, Ren N (2010) Kinetic degradation model and estrogenicity changes of EE2 (17α-ethinylestradiol) in aqueous solution by UV and UV/H2O2 technology. J Hazard MAter 181:1127–1133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.05.132
Funding
This research was funded by Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior—Brasil (CAPES)—Grant number 31001017037037P9—Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—Brasil (CNPq) Grant number 313457/2017-4—and by Fundação Carlos Chagas Filho de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro—Brasil (FAPERJ)—Grant number E-26/110.102/2014.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CGM: investigation, formal analysis, methodology, software, validation, visualization, data curation and writing. TCCN: writing and editing. DMB: investigation, reviewing and funding acquisition. FVF: investigation, reviewing and funding acquisition.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent for participation
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, C.G., Neto, T.C., Bila, D.M. et al. Treatment of 17α-Ethinylestradiol (EE2) in Water Using UV/H2O2 and Reverse Osmosis (RO) Membranes: Assessment of Estrogenic Activity and Membrane Adsorption. Int J Environ Res 17, 1 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00489-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00489-4