Abstract
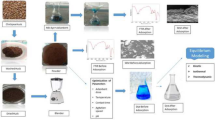
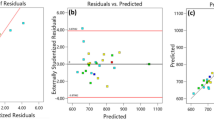
In the study, Fe3O4/TiO2 nanocomposite (FTNC) is synthesized and employed for Direct Green 26 (DG26) adsorption from aqueous solutions. The instruments of X-ray diffraction (XRD), energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy, field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) were utilized for nanocomposite characterization. The experiments were conducted based on a Box-Behnken design including the FTNC dosage (A: 0.16 − 0.40 g L−1), pH (B: 3 − 9), contact time (C: 16 − 30 min), and ionic strength (D: 0.01 − 0.05 mol L−1), as the independent variables. The obtained data were fitted to a second-order response surface model with a high correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.9699) which predicted the optimum conditions (A = 0.40 g L−1, B = 3, C = 29 min, and D = 0.03 mol L−1) with an adsorption percentage of 97.50 ± 0.60. The kinetic data agreed well (R2 > 0.99) with the pseudo-second-order model. Moreover, investigating the adsorption isotherms of Langmuir, Temkin, Dubinin-Radushkevich, and Freundlich showed that DG26-FTNC adsorption system followed Langmuir model and an adsorption capacity of 200 mg g−1 was achieved for the magnetic nanocomposite.
Article Highlights
-
Fe3O4/TiO2 magnetic nanocomposite was synthesized and employed for Direct Green 26 adsorption from aqueous solutions.
-
The effects of the nanocomposite dosage, pH, contact time and ionic strength on the dye removal efficiency were investigated by conducting a Box-Behnken experimental design.
-
Response surface modeling accurately predicted the optimum conditions of operation.
-
The magnetic nanocomposite showed a monolayer adsorption capacity of 200 mg g-1.
-
The dye-nanocomposite adsorption system followed the pseudo-second order kinetic model.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
All data generated and analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Change history
08 December 2022
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00497-4
References
Abbas M, Parvatheeswara Rao B, Reddy V, Kim C (2014) Fe3O4/TiO2 core/shell nanocubes: Single-batch surfactantless synthesis, characterization and efficient catalysts for methylene blue degradation. Ceram Int B 40(7):11177–11186
Abou-Gamra ZM, Ahmed MA (2015) TiO2 Nanoparticles for removal of malachite green dye from waste water. Adv Chem Eng Sci 5:373–388
Alabbad EA, Bashir S, Liu JL (2022) Efficient removal of direct yellow dye using chitosan crosslinked isovanillin derivative biopolymer utilizing triboelectric energy produced from homogeneous catalysis. Catal Today 400–401:132–145
Alberghina G, Bianchini R, Fichera M, Fisichella S (2000) Dimerization of cibacron blue F3GA and other dye: influence of salts and temperature. Dyes Pigm 46(3):129–137
Allen SJ, Mckay G, Khader KYH (1989) Intraparticle diffusion of a basic dye during adsorption onto sphagnum peat. Environ Pollut 56:39–50
Borth KW, Galdino CW, Teixeira VC, Anaissi FJ (2021) Iron oxide nanoparticles obtained from steel waste recycling as a green alternative for Congo red dye fast adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 546:149126
Box GEP, Hunter JS, Hunter WG (2005) Statistics for experiments, 2nd edn. Wiley Interscience, New York
Carlotti ME, Ugazio E, Gastaldi L, Sapino S, Vione D, Fenoglio I, Fubini B (2009) Specific effects of single antioxidants in the lipid peroxidation caused by nano-titania used in sunscreen lotions. J Photochem Photobiol B 96(2):130–135
Çelebi Ö (2019) The applicability of evaluable wastes for the adsorption of Reactive Black 5. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:135–146
Çelebi Ö, Şimşek İ, Çelebi H (2021) Escherichia coli inhibition and arsenic removal from aqueous solutions using raw eggshell matrix. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18(10):1–16
Dinçer AR, Günes Y, Karakaya N, Günes E (2007) Comparison of activated carbon and bottom ash for removal of reactive dye from aqueous solution. Biores Technol 98(4):834–839
Dubinin MM, Radushkevich LV (1947) Equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal. Proc Acad Sci USSR Phys Chem Sect 55:331–333
Ferreira SLC, Bruns RE, Ferreira HS, Matos GD, David JM, Brandão GC, da Silva EGP, Portugal LA, dos Reis PS, Souza AS, dos Santos WNL (2007) Box-Behnken design: An alternative for the optimization of analytical methods. Anal Chim 597(2):179–186
Foo KY, Hameed BH (2010) Insights into the modeling of adsorption isotherm systems. Chem Eng J 156(1):2–10
Freundlich HZ (1906) Over the adsorption in solution. J Phys Chem 57:385–471
Gao Q, Chen F, Zhang J, Hong G, Ni J, Wei X, Wang D (2009) The study of novel Fe3O4@γ–Fe2O3 core/shell nanomaterials with improved properties. J Magn Magn Mater 321(8):1052–1057
GAPS water treatment (2020) Chemviron envirocarb 207C activated carbon. https://www.gapswater.co.uk/cgi-bin/ca000001.pl
Germa’n-Heins J, Flury M (2000) Sorption of brilliant blue FCF in soils as affected by pH and ionic strength. Geoderma 97(1):87–101
Gopal N, Asaithambi M, Sivakumar P, Sivakumar V (2014) Adsorption studies of a direct dye using polyaniline coated activated carbon prepared from Prosopis juliflora. J Water Process Eng 2:87–95
Gupta V, Moradi O, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Sadegh H, Shahryari-Ghoshekandi R, Makhlouf A, Goodarzi M, Goodarzi A (2016) Study on the removal of heavy metal ions from industry waste by carbon nanotubes: effect of the surface modification: a review. J Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 46(2):93–118
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivos A, Vermeulen T (1966) Pore and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 5(2):212–223
Hashem A, Ahmad F, Badawy SM (2015) Adsorption of direct green 26 onto fix 3500 treated sawdust: equilibrium, kinetic and isotherms. Desalin Water Treat 57(28):13334–13346
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465
Hu H, Wang Z, Pan L, Zhao S, Zhu S (2010) Ag-coated Fe3O4@SiO2 three-ply composite microspheres: Synthesis, characterization, and application in detecting melamine with their surface-enhanced raman scattering. J Phys Chem C 114:7738–7742
Jing J, Li J, Feng J, Li W, Yu WW (2013) Photodegradation of quinoline in water over magnetically separable Fe3O4/TiO2 composite photocatalysts. Chem Eng J 219:355–360
Kadirvelu K, Kavipriya M, Karthika C, Radhika M, Vennilamani N, Pattabhi S (2003) Utilization of various agricultural wastes for activated carbon preparation and application for the removal of dyes and metal ions from aqueous solutions. Biores Technol 87(1):129–132
Kavcı E (2021) Adsorption of direct red 243 dye onto clay: kinetic study and isotherm analysis. Desalin Water Treat 212:452–461
Kiwaan HA, Atwee TM, Azab EA, El-Bindary AA (2020) Photocatalytic degradation of organic dyes in the presence of nanostructured titanium dioxide. J Molecular Struct 1200:127115
Lagergren S (1898) About the theory of so called adsorption of soluble substances. Ksver Veterskapsakad Handl 24:1–6
Langmuir I (1918) The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J Am Chem Soc 40:1361–1403
Liao Y, Que W (2010) Preparation and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanotube powders derived by a rapid anodization process. J Alloys Compd 505(1):243–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.04.010
Liu N, Wang H, Weng C-H, Hwang C-C (2018) Adsorption characteristics of direct red 23 azo dye onto powdered tourmaline. Arab J Chem 11(8):1281–1291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2016.04.010
Lu J, Wang M, Deng C, Zhang X (2013) Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@ mesoporous TiO2 microspheres for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides for phosphoproteomics analysis. Talanta 105:20–27
Luo X, Zhang L (2009) High effective adsorption of organic dyes on magnetic cellulose beads entrapping activated carbon. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):340–347
Mahmoud HR, Ibrahim SM, El-Molla SA (2016) Textile dye removal from aqueous solutions using cheap MgO nanomaterials: adsorption kinetics, isotherm studies and thermodynamics. Adv Powder Technol 27(1):223–231
Mahvi AH, Dalvand A (2020) Kinetic and equilibrium studies on the adsorption of direct red 23 dye from aqueous solution using montmorillonite nanoclay. Water Qual Res J 55(2):132–144
MiarAlipour Sh, Friedmann D, Scott J, Amal R (2018) TiO2/porous adsorbents: recent advances and novel applications. J Hazard Mater 341:404–423
Myers RH, Montgomery DC (1995) Response surface methodology: process and product optimization using designed experiments. John Wiley & Sons, New York
Noreen S, Khalid U, Ibrahim SM, Javed T, Ghani A, Naz Iqbal M (2020) ZnO, MgO and FeO adsorption efficiencies for direct sky Blue dye: equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics studies. J Mater Res Technol 9(3):5881–5893
Panda SK, Aggarwal I, Kumar H, Prasad L, Kumar A, Sharma A, Vo D-VN, Thuan DV, Mishra V (2021) Magnetite nanoparticles as sorbents for dye removal: a review. Environ Chem Lett 19(3):1–39
Pichat P (2015) A short overview of the state of the art and perspectives on the main basic factors hindering the development of photocatalytic treatment of water. Water Sci Technol Water Supply 15:1–10
Polanyi M (1932) Section III. Theories of the adsorption of gases. A general survey and some additional remarks. Trans Faraday Soc 28:316–333
Poots VJP, McKay G, Healy JJ (1978) Removal of basic dye from effluent using wood as an adsorbent. J Water Pollut Control Fed 50:926–939
Qin Q, Sun T, Yin W, Xu Y (2017) Rapid and efficient removal of methylene blue by freshly prepared manganese dioxide. Cogent Eng 4(1):1345289
Qu S, Yang H, Ren D, Kan S, Zou G, Li D, Li M (1999) Magnetite nanoparticles prepared by precipitation from partially reduced ferric chloride aqueous solutions. J Colloid Interface Sci 215(1):190–192
Rafatullah M, Sulaiman O, Hashim R, Ahmad A (2010) Adsorption of methyleneblue on low-cost sorbents: a review. J Hazard Mater 177(1–3):70–80
Reghioua A, Barkat D, Jawad AH, Abdulhameed AS, Al-Kahtani AA, Al-Othman ZA (2021) Parametric optimization by Box-Behnken design for synthesis of magnetic chitosan-benzil/ZnO/Fe3O4 nanocomposite and textile dye removal. J Environ Chem Eng 9(3):105166
Sadegh H, Zare K, Maazinejad B, Shahryari-Ghoshekandi R, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2016) Synthesis of MWCNT-COOH-Cysteamine composite and its application for dye removal. J Mol Liq 215(4):221–228
Sadegh H, Ali GAM, Gupta VK, Makhlouf ASH, Shahryari-Ghoshekandi R, Nadagouda MN, Sillanpää M, Megiel E (2017) The role of nanomaterials as effective adsorbents and their applications in wastewater treatment. J Nanostruct Chem 7:1–14
Safa F, Alinezhad Y (2020) Ternary nanocomposite of SiO2/Fe3O4/multi-walled carbon nanotubes for efficient adsorption of malachite green: response surface modeling, equilibrium isotherms and kinetics. Silicon 12(4):1619–1637
Sakarkar S, Muthukumran S, Jegatheesan V (2020) Factors affecting the degradation of remazol turquoise blue (RTB) dye by titanium dioxide (TiO2) entrapped photocatalytic membrane. J Environ Manag 272:111090
Shen D, Fan J, Zhou W, Gao B, Yue Q, Kang Q (2009) Adsorption kinetics and isotherm of anionic dyes onto organo-bentonite from single and multisolute systems. J Hazard Mater 172(1):99–107
Singha B, Kumar Das SK (2013) Adsorptive removal of Cu (II) from aqueous solution and industrial effluent using natural/agricultural wastes. Colloids Surf b: Biointerfaces 107:97–106
Sivashankar R, Sathya AB, Vasantharaj K, Sivasubramanian V (2014) Magnetic composite an environmental super adsorbent for dye sequestration—a review. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 1–2:36–49
Syafiuddin A, Salmiati S, Jonbi J, Fulazzaky MA (2018) Application of the kinetic and isotherm models for better understanding of the behaviors of silver nanoparticles adsorption onto different adsorbents. J Environ Manag 218:59–70
Tan L, Zhang X, Liu Q, Jing X, Liu J, Song D, Hu S, Liu L, Wang J (2015) Synthesis of Fe3O4@TiO2 core–shell magnetic composites for highly efficient sorption of uranium (VI). Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Aspects 469:279–286
Teh CM, Mohamed AR (2011) Roles of titanium dioxide and ion-doped titanium dioxide on photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants (phenolic compounds and dyes) in aqueous solutions: a review. J Alloys Compd 509(5):1648–1660
Temkin MI, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalysts. Acta Physiochim USSR 12:327–356
Treybal RE (1980) Mass transfer operations, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Uzun K, Çevik E, Şenel M, Sözeri H, Baykal A, Abasıyanık MF, Toprak MS (2010) Covalent immobilization of invertase on PAMAM dendrimer modified superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. J Nanopart Res 12:3057–3067
Vadivelan V, Kumar KV (2005) Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk. J Colloids Interface Sci 286(1):90–100
Venkataraghavan R, Thiruchelvi R, Sharmila D (2020) Statistical optimization of textile dye effluent adsorption by Gracilaria edulis using Plackett-Burman design and response surface methodology. Heliyon 6(10):E05219
Weber WJ, Morris JC (1963) Kinetics of adsorption on carbon from solution. J Sanit Eng Div 89:31–60
Wei W, Yang L, Zhong WH, Li SY, Cui J, Wei ZG (2015) Fast removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution by adsorption onto poorly crystalline hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Dig J Nanomater Biostruct 10:1343–1363
Wei W, Han X, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zheng C (2020) Macromolecular humic acid modified nano-hydroxyapatite for simultaneous removal of Cu (II) and methylene blue from aqueous solution: experimental design and adsorption study. Int J Biol Macromol 150:849–860
Xing S, Zhou Z, Ma Z, Wu Y (2011) Characterization and reactivity of Fe3O4/FeMnOx core/shell nanoparticles for methylene blue discoloration with H2O2. Appl Catal B: Environ 107(3–4):386–392
Yadla SV, Sridevi V, Chandana Lakshmi MVV (2012) A review on adsorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution. J Chem Biol Phys Sci 2:1585–1593
Yetilmezsoy K, Demirel S, Vanderbei RJ (2009) Response surface modeling of Pb (II) removal from aqueous solution by Pistacia vera L.: Box-Behnken experimental design. J Hazard Mater 171(1–3):551–562
Yogesh Kumar K, Muralidhara HB, Arthoba Nayaka Y, Balasubramanyam J, Hanumanthappa H (2013) Low-cost synthesis of metal oxide nanoparticles and their application in adsorption of commercial dye and heavy metal ion in aqueous solution. Powder Technol 246:125–136
Zafar MN, Dar Q, Nawaz F, Zafar MN, Iqbal M, Faizan Nazar MF (2019) Effective adsorptive removal of azo dyes over spherical ZnO nanoparticles. J Mater Res Technol 8(1):713–725
Acknowledgements
The authors thankfully acknowledge the support from Rasht Branch, Islamic Azad University, Iran.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MA: experimentation, data analysis, writing the original draft of the manuscript. FS: supervision, project administration, interpretation, writing—review & editing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Consent for publication
The authors give full consent for publication of this research work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
41742_2022_467_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 Fig. S1 Plots of a) pseudo-second order and b) intraparticle diffusion kinetic models for DG26-FTNC adsorption system (FTNC dosage of 0.40 g L-1, pH=3 and ionic strength of 0.03 mol L-1). (TIF 326 KB)
41742_2022_467_MOESM4_ESM.tif
Supplementary file4 Fig. S1 Plots of a) pseudo-second order and b) intraparticle diffusion kinetic models for DG26-FTNC adsorption system (FTNC dosage of 0.40 g L-1, pH=3 and ionic strength of 0.03 mol L-1). (TIF 250 KB)
41742_2022_467_MOESM5_ESM.tif
Supplementary file5 Fig. S2 Plots of qt versus time for assessing DG26 adsorption onto FTNC by isotherm models of a) Langmuir, b) D-R, c) Temkin and d) Freundlich (FTNC dosage of 0.40 g L-1, pH=3 and ionic strength of 0.03 mol L-1). (TIF 330 KB)
41742_2022_467_MOESM6_ESM.tif
Supplementary file6 Fig. S2 Plots of qt versus time for assessing DG26 adsorption onto FTNC by isotherm models of a) Langmuir, b) D-R, c) Temkin and d) Freundlich (FTNC dosage of 0.40 g L-1, pH=3 and ionic strength of 0.03 mol L-1). (TIF 323 KB)
41742_2022_467_MOESM7_ESM.tif
Supplementary file7 Fig. S2 Plots of qt versus time for assessing DG26 adsorption onto FTNC by isotherm models of a) Langmuir, b) D-R, c) Temkin and d) Freundlich (FTNC dosage of 0.40 g L-1, pH=3 and ionic strength of 0.03 mol L-1). (TIF 319 KB)
41742_2022_467_MOESM8_ESM.tif
Supplementary file8 Fig. S2 Plots of qt versus time for assessing DG26 adsorption onto FTNC by isotherm models of a) Langmuir, b) D-R, c) Temkin and d) Freundlich (FTNC dosage of 0.40 g L-1, pH=3 and ionic strength of 0.03 mol L-1). (TIF 341 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Alizadeh, M., Safa, F. Magnetic Nanocomposite of TiO2 as Efficient Adsorbent for Direct Green 26 Dye: Multivariate Optimization, Kinetic and Equilibrium Isotherms. Int J Environ Res 16, 107 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00467-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41742-022-00467-w